Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WkstKey 9 PDF
WkstKey 9 PDF
Uploaded by
night ting0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views5 pagesOriginal Title
WkstKey-9.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views5 pagesWkstKey 9 PDF
WkstKey 9 PDF
Uploaded by
night tingCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
NAME
B Chapter 9
REINFORCEMENT
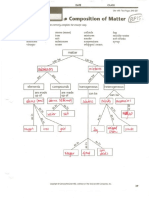
@ Composition of Matter Gels
Use the words listed below to correctly complete the concept map.
Class
Use with Text Pages 246-251
atoms (different) atoms (same) colloids fog
gold iron mixtures muddy water
Sygen salt smoke soft drinks
solutions substances suspensions syrup
vinegar ‘water whipped cream
matter
oe Qebe
Subsian ees mixtures
& e
Sy
[elements | ‘compounds homogeneous] [heterogeneous
are made are made
=e [asa a 26
[Laloms (em] [aloms Uiferet)] — [ schatuns ] [coils | [suseensins
INS, z
Q Ss
salt will 40
@
smoke
S&S
Vunlegay
Copyright © Genoe/McGrav 2 don of The McGraw Companies In.
39
(One key term has been scrambied in each ofthe following statements. Unscramble the term. On the lines provided,
rewrite the entre statement with the unscrambled term. Then find eace unscramibied key term in the hidden word puzzle,
1. A(n) ethgnesuoereo mixture has different materials that are spread out unevenly.
2. Ain) cildclo is a heterogeneous mixture whose particles never settle and are large enough to
scatter light. 0}
3. A homogeneous mixture in which particles are so small that they cannot be seen without a
microscope is a(n) tuolsion. solution
4. A(n) ssinnopue is a liquid heterogeneous mixture in which visible particles settle.
Suspension
5. A(a) coudnmpc is a material made from atoms of two or more combined elements.
Compound
6. Tfall the atoms in a sample of matter are alike, that kind of matter is a(n) neemetl.
7. A(p) oogostenelem mixture has substances that are uniformly spread out.
Homogeneous
Conyight © Glreae/McCratil dion of The MeCrasistil Compe, ne. 39
DATE CLASS
Coa
© Classification of Matter
Part A. Vocabulary Review
Match the definitions in Col It the terran Coun I. Wie the letter ofthe correct term i he blak atthe
Left of Column
Column | Column tt
1. atype of mixture in which all substances ae uni- a, element
formly spread out
ny b. homogeneous mixture
2. a change in size, shape, or state of matter
\ ¢. heterogeneous mixture
3. mixture of air and water droplets
4. physical property
spread out unevenly €. chemical change
a:
Cs & wipge dita ticWtncn ni ee
hm £. colloid
5. matter in which all atoms are alike
D\_. 6. explains that matier is neither created nor destroyed | & compound
during a chemical change he. fog
7. heterogeneous mixture containing a liquid in which
visible particles settle
i. solution
a material made from atoms of two or more ele- J: Tyndall effect
‘ments that are combined k. chemical property
clumps of small particles 1. coagulation
|. a characteristic of a material that can be easily am, law of conservation of
observed without changing the substances that eemenene
make up the material in. physical change
. a heterogeneous mixture that does not separate 9. suspension
a characteristic that helps to identify a substance by
describing how the substance will undergo a chemi-
cal change
a homogeneous mixture that remains uniformly and
constantly mixed
|. a change of one substance in a material to a differ-
ent substance
5. scattering of light by particles in a mixture
Copyaght © GlecoerMeGra tl 3 dnion of The McGrail Companies, 2
: @ Describing Matter
Complete tne folowing by fling in each blank with the correct term.
‘Scientists try to explain how changes in substances take place. By applying energy, you can tear
a sheet of paper into pieces and cause a(n)
in the paper. If you place a balloon filled with air into the reftig-
erator, the balloon will get smaller. The balloon undergoes a(n) phy sicah
- Ona hot summer day, water vapor will condense into water
droplets on the outside of g glass of iced tea. The glass of iced tea is a(n)
mixture (Solution) _ of sugar tea, lemon, and water Ice is water in the solid state. The
density of ice is less than that of liquid water. Therefore, ice floats on the tea. The melting point of
ice is 0°C. This temperature is also the freezing point of liquid water. Water is a clear, colorless
igui at room temperature. The words clear and colorless describe two
—fysial properties or water. ‘The melting ofthe ie in
iced tea is a(n) —Pnysial chm i
Incomparsona(a) Chemical __chpnge _ produces
new substances. When a candle burns, physical and changes take
place. The. i! of the wax is a physical change. The melted wax is
now in the liquid state. However, when burning occurs, a(n) i
change takes place. The melted wax, as it bums, combines with gaseous
oxygen in air. Afier the chemical change, water vapor and carbon dioxide gas are formed. The
mass of all substances before a chemical change ‘the mass of all
substances after a chernical change.
Copy © Glencoe Maw, dsm of The MeGravtil Compan, Inc. a1
NAME
‘Use wth Text Pages 254-261
ee @ Describing Matter
Analogies
Beloto are two sets of words. Complete the second set ky choosing a word from those listed below the blank. The foo
‘words must be related in the same way as the frst set of words.
fara
EXAMPLE
Ietter-envelope:pillow:{ease]
case, sheet, soft, bed
1, steam:water:swater: __IC@
heat, molecules, ice, matter
2. solid:melting:liquid: Maporidinf) —_
condensing, heating, mixiAg, vaporizing
3. physical:chemical:size: ‘bur Ain
burning, taste solubility, acid 4 ~
4, liquid-vaporizing:solid:
melting, freezing. decomposing, evaporating
5. ironrustisitver: __-HAimnish
reaction, oxygen, tamish, water
6. chemical-rust=physical: I
compound, condensation, solid, or
7. element:compound:oxygen:
water, hydrogen, matter, mixture
8. compound:mixture:chemical: i
physical, separation, property,
9, hydrogen-water::carbon:
carbon dioxide, graphite, coal, gas,
10. solid:steel=gaseous: __ Qu
coal, air, water, gasoline
11. burning:candle:;corresion: CODQOC
vaporization, physical property, copper, mixture.
Copright © Glencoe NeGaw Hl, a dvsion of The MeCianll Compan, Ie
ar
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- NuevoDocumento 2020-03-13 16.59.23Document2 pagesNuevoDocumento 2020-03-13 16.59.23night tingNo ratings yet
- Spend Your Summer at The Worlds Most Amazing Summer Camp!Document12 pagesSpend Your Summer at The Worlds Most Amazing Summer Camp!night tingNo ratings yet
- Los Angeles: BostonDocument20 pagesLos Angeles: Bostonnight tingNo ratings yet
- WkstKey 9Document5 pagesWkstKey 9night tingNo ratings yet
- Starters & To Share: (Corn Soft Tortillas)Document4 pagesStarters & To Share: (Corn Soft Tortillas)night tingNo ratings yet
- WkstKey 6Document12 pagesWkstKey 6night tingNo ratings yet