Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(AWS A5.1 E7016) : Product Highlight
(AWS A5.1 E7016) : Product Highlight
Uploaded by
rendraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(AWS A5.1 E7016) : Product Highlight
(AWS A5.1 E7016) : Product Highlight
Uploaded by
rendraCopyright:
Available Formats
Product Highlight
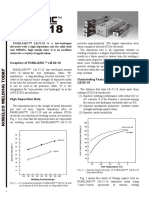
LB-52U
(AWS A5.1 E7016)
FAMILIARC™ LB-52U is the world's No. 1 LB-52U, you will choose it again and again for
covered electrode for uranami welding, or the root unsurpassed performance.
pass melt-through welding with penetration beads.
With FAMILIARC™ LB-52U your welding will be Table 1: Chemical and mechanical properties of FAMILIARC™
LB-52U
easier and faster, and you will have confidence in the
quality of your welds in any kind of pipe welding of Chemical composition of weld metal (%)
mild steel and 490MPa high tensile steel. C Si Mn P S
0.08 0.64 0.86 0.012 0.008
Inception of FAMILIARC™ LB-52U
KOBELCO WELDING TODAY
Mechanical properties of weld metal
[H]d1
FAMILIARC™ LB-52U was developed around 0.2%YS (MPa) TS (MPa) EL (%) vE–29°C (J) (ml/100g)
1954. The letter "L" stands for low hydrogen, while "B"
480 560 31 80 3.5
symbolizes a slag shielding covered electrode. The
digits "52" refer to the level of approximate tensile 1. Diffusible hydrogen in the weld metal made in the welding atmosphere
of 21°C × 10%RH (Gas-chromatographic method)
strength of the deposited metal when it was developed.
The letter "U" was coined from "uranami" welding.
(2) Superior crack resistance and mechanical
properties
What Makes FAMILIARC™ LB-52U
the Best for "Uranami" Welding? FAMILIARC™ LB-52U provides superior crack
resistibility due to a lower level of diffusible hydrogen
(1) Unsurpassed usability in all-position welding in the weld metal. In addition, its impact strength is high
over a range of testing temperatures — Fig. 2. Therefore,
FAMILIARC™ LB-52U features a very stable arc
it can be used for low-temperature applications as well
and low spatter over a wide range of welding currents.
as moderate high-temperature applications.
In particular,FAMILIARC™ LB-52U really shines in
the "uranami" welding of horizontally fixed pipes.
160
FAMILIARC™ LB-52U features very smooth,
glossy "uranami" beads, or the penetration beads
Absorbed energy (J)
protruded on the reverse side of the groove — Fig. 1. 120
FAMILIARC™ LB-52U can accommodate wider
tolerance of the root opening, which is an advantage in
site welding. Once you have used FAMILIARC™ 80
40
0
–50 –40 –30 –20 –10 0 10 20 30
Test Temp. (ºC)
Fig. 2 — Charpy impact test results of the FAMILIARC™
LB-52U weld metal by using DC-EP welding current
in the vertical-up position
Fig. 1 — The surface and macrosectional profiles of a (3) A field-proven electrode in the worldwide markets
penetration bead protruding on the reverse side of a
single-V-groove weld. The unsurpassed usability of FAMILIARC™
1
Product Highlight
Semi-
Weaving
Keyhole Crater
Groove Face
Semi-Weaving
Along the Edge
of the Crator
Fig. 4 — The keyhole technique
A: Deeper B: Deep C: Shallow
(a)
KOBELCO WELDING TODAY
A
A
(b) B (c)
C B
A B C
Fig. 3 — A pipeline-welding site in Russia where FAMILIARC™ (d)
LB-52U is used for joining the girth joints in freezing
weather
Fig. 5 — The relationship between the weld penetration (a),
LB-52U in the "uranami" welding of pipe joints has the arc exposure spot (b), the electrode holding
satisfied users around the world. FAMILIARC™ angle (c) and the electrode oscillation width (d) in the
"uranami" welding of horizontally fixed pipes
LB-52U has been popular for a variety of piping jobs
across Russia, Asia and the Pacific region. Particularly
in Russia, FAMILIARC™ LB-52U has made a great (3) Terminate the crater on the groove face in order to
contribution to the construction of very long, oil and gas prevent the crater cracking ― Fig. 6.
pipelines under freezing weather with a long history of
reliability — Fig. 3. Since 1982, about 80,000 metric
tons of FAMILIARC™ LB-52U has been consumed in Turn onto Expose the Arc into the Keyhole
the Groove Face
the construction of the Russian pipelines. to Make Better Fusion before
Turn to the Groove Face.
Key Points in the "Uranami" Welding of Crater
Treatment
Pipes with FAMILIARC™ LB-52U Welding Direction
(1) Use the keyhole technique. Right after you get the
arc by striking the groove face, control the molten Fig. 6 — How to terminate the weld crater in order to prevent
pool to form the keyhole crater: then manipulate the crater from cracking
the electrode along the edge of the keyhole by
using the semi-weaving technique — Fig. 4. (4) Grind both the starting and ending terminals of the
preceding weld beads to assure a smooth joint of
(2) Control the weld penetration in the root of the weld beads with the succeeding welds.
groove by controlling the arc exposure spot, the
electrode holding angle and the electrode (5) When joining the weld beads, start the arc on the
oscillation width — Fig. 5 (a, b, c, d). Fig. 5 (a) preceding bead, and expose the arc into the
relates to the other figures of (b), (c), and (d) keyhole to assure better fusion: then follow the
respectively. same procedure as in Fig. 4.
2
You might also like
- Code - Interim Guidelines On Testing of UCS of Cement Stabilised Soil Cores in Hong KongDocument43 pagesCode - Interim Guidelines On Testing of UCS of Cement Stabilised Soil Cores in Hong Kongjames_frank100% (2)
- Lesson Plan in Science IV-ways To Protect Ourselves From SunDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Science IV-ways To Protect Ourselves From SunJhenalyn Perlada88% (24)
- Handbook of Structural Welding: Processes, Materials and Methods Used in the Welding of Major Structures, Pipelines and Process PlantFrom EverandHandbook of Structural Welding: Processes, Materials and Methods Used in the Welding of Major Structures, Pipelines and Process PlantRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Lesson Plan - Building SwitchDocument3 pagesLesson Plan - Building Switchapi-372321353No ratings yet
- Spotlight 01Document2 pagesSpotlight 01RohimNo ratings yet
- Kobe WeldingDocument1 pageKobe WeldingLauw Tjun NjiNo ratings yet
- Lincolnweld 761Document2 pagesLincolnweld 761Huascar Rafael Robles CaceresNo ratings yet
- 25kv Class Fused Loadbreak Elbow Connector Catalog Ca650070enDocument8 pages25kv Class Fused Loadbreak Elbow Connector Catalog Ca650070enHugo OsunaNo ratings yet
- 147-168 62gb SeriesDocument22 pages147-168 62gb SeriesJdhdkdidbdjdubdnjfbebeirhrbNo ratings yet
- Cooper Deadbreak Elbow 55010Document4 pagesCooper Deadbreak Elbow 55010denzil_1000No ratings yet
- Cooper Loadbreak Elbow 500287Document8 pagesCooper Loadbreak Elbow 500287denzil_1000No ratings yet
- 2019 OCEANLED SPECS Sport S3124dDocument2 pages2019 OCEANLED SPECS Sport S3124dRichard LeongNo ratings yet
- Lincolnweld 960Document2 pagesLincolnweld 960pratik charkhawalaNo ratings yet
- LSI Sunburst Series Spec Sheet 1985Document4 pagesLSI Sunburst Series Spec Sheet 1985Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Metal Oxide Varistor Elbow M o V e Surge Arrester Catalog Ca235025enDocument8 pagesMetal Oxide Varistor Elbow M o V e Surge Arrester Catalog Ca235025enale_1905No ratings yet
- Nsulating Material Accessories For Boxes, Trunking and CablesDocument2 pagesNsulating Material Accessories For Boxes, Trunking and CablesOvidiu GavrilasNo ratings yet
- ITT American Electric Bay Beam Luminaire Series 56-57-156-157 Spec Sheet 9-81Document12 pagesITT American Electric Bay Beam Luminaire Series 56-57-156-157 Spec Sheet 9-81Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- 15kv Class Fused Loadbreak Elbow Connector Catalog Ca650069enDocument8 pages15kv Class Fused Loadbreak Elbow Connector Catalog Ca650069enHugo OsunaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12-ABE 43-Welding and Joining ProcessDocument5 pagesLecture 12-ABE 43-Welding and Joining ProcessAria MoonNo ratings yet
- LB 52uDocument2 pagesLB 52uSuryanarayanan VenkataramananNo ratings yet
- 200 A 35 KV Class Three-Phase (Purple Cuff) Loadbreak Elbow ConnectorDocument4 pages200 A 35 KV Class Three-Phase (Purple Cuff) Loadbreak Elbow ConnectorAlvaro DiazNo ratings yet
- Fluxofil 51Document1 pageFluxofil 51ThermalsprayNo ratings yet
- Ca650068en PDFDocument4 pagesCa650068en PDFCel NimapNo ratings yet
- Prysmian Separable Connectors v1.03Document12 pagesPrysmian Separable Connectors v1.03Muhammad SyaifulhaqNo ratings yet
- Cuznpb2 LeadedDocument3 pagesCuznpb2 Leadedwjjt6chgtmNo ratings yet
- HubbellDocument46 pagesHubbellanon-50886100% (2)
- Copperweld Grounding Wire & StrandDocument4 pagesCopperweld Grounding Wire & StrandNelson RuizNo ratings yet
- Oerlikon Fluxofil 42Document1 pageOerlikon Fluxofil 42karthiksaadhanaNo ratings yet
- ITT American Electric Package B Dusk-To-Dawn Series 11 Spec Sheet 8-80Document4 pagesITT American Electric Package B Dusk-To-Dawn Series 11 Spec Sheet 8-80Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- First Philec DTDocument8 pagesFirst Philec DTJM Si MirNo ratings yet
- Helukabel M32520 en GBDocument2 pagesHelukabel M32520 en GBivanramljakNo ratings yet
- 200a 25kv Class Posi Break Loadbreak Elbow Connector With Optional Integral Jacket Seal Catalog Ca650100enDocument8 pages200a 25kv Class Posi Break Loadbreak Elbow Connector With Optional Integral Jacket Seal Catalog Ca650100enLeonardo RobertoNo ratings yet
- 3c 600-1000v MC-HL (Xhhw-2) Copper Section4-Sheet1Document4 pages3c 600-1000v MC-HL (Xhhw-2) Copper Section4-Sheet1Kiran KarthikNo ratings yet
- 3238018C10MDocument8 pages3238018C10MAlbita PintoNo ratings yet
- LDS 0300 1-1592307Document6 pagesLDS 0300 1-1592307eduardo rodriguesNo ratings yet
- Product Selection Guide: Cable AccessoriesDocument44 pagesProduct Selection Guide: Cable Accessoriesricardo139No ratings yet
- Amphenol 62GB Series: Mil-Dtl-26482 Performance Without Mis-MatingDocument3 pagesAmphenol 62GB Series: Mil-Dtl-26482 Performance Without Mis-MatingOsamaAliBangashNo ratings yet
- Scotch® 25 Electrical Grounding Braid: Data SheetDocument3 pagesScotch® 25 Electrical Grounding Braid: Data Sheetprincesa762No ratings yet
- 200a 25kv Class Insulated Protective Cap Catalog Ca650085enDocument4 pages200a 25kv Class Insulated Protective Cap Catalog Ca650085enLeonardo RobertoNo ratings yet
- 147-168 62gb Series 62GB-57A14-15SNDocument22 pages147-168 62gb Series 62GB-57A14-15SNwiradesNo ratings yet
- Jameco Part Number 797881: Distributed byDocument5 pagesJameco Part Number 797881: Distributed byIqbal MakhdoomNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Elastimold (Cable Accesories) PG-CA-0307Document44 pagesCatalogo Elastimold (Cable Accesories) PG-CA-0307Mike RockeNo ratings yet
- TMC - P101 - Rfou, Rfcu, RfbuDocument9 pagesTMC - P101 - Rfou, Rfcu, RfbucweilietNo ratings yet
- HRC Fuse Link & BasesDocument8 pagesHRC Fuse Link & Baseshemant kumarNo ratings yet
- 600 A 25 KV Class Bushing Adapter For T-OP™ II Connector SystemDocument4 pages600 A 25 KV Class Bushing Adapter For T-OP™ II Connector SystemCarlos PlaceresNo ratings yet
- Lapp LeRoy Catalog C-1 12-01-2017 PDFDocument14 pagesLapp LeRoy Catalog C-1 12-01-2017 PDFdeltaNo ratings yet
- Ul Ti Mate Range - Model Number - S02860 - : Underwater Lights LimitedDocument1 pageUl Ti Mate Range - Model Number - S02860 - : Underwater Lights LimitedEdi IrimescuNo ratings yet
- (H) RADOXDATABUS120OHMnx0.5XMDocument3 pages(H) RADOXDATABUS120OHMnx0.5XM다원시스No ratings yet
- 15LIC200 MinDocument3 pages15LIC200 MinJoãoNo ratings yet
- SB Ibl P CBL Submersible Power CableDocument23 pagesSB Ibl P CBL Submersible Power CableMuhammad ShahrukhNo ratings yet
- Giunzione e ManutenzioneDocument29 pagesGiunzione e Manutenzionerenhat parulian sitorusNo ratings yet
- Catalogo FusiblesDocument8 pagesCatalogo FusiblesChristianM.LeandroYauriNo ratings yet
- KAP 12-24 KV 300 ENACC MVACC DS ENDocument1 pageKAP 12-24 KV 300 ENACC MVACC DS ENMd Imran pashaNo ratings yet
- Mca-I-Gf: Self-Regulating Heating Cables For Anti-Freeze Corrosives and AcidsDocument1 pageMca-I-Gf: Self-Regulating Heating Cables For Anti-Freeze Corrosives and AcidsJosé VeraNo ratings yet
- 600a 15 and 25 KV Class Cleer Grounding Elbow Catalog Ca650013enDocument8 pages600a 15 and 25 KV Class Cleer Grounding Elbow Catalog Ca650013enPeter BuchananNo ratings yet
- Long-Lasting Distinguished Design: Simon, S.A. Vietnam Office of Simon ElectricDocument12 pagesLong-Lasting Distinguished Design: Simon, S.A. Vietnam Office of Simon Electricnghia luuNo ratings yet
- 2594 TigDocument1 page2594 TigAnonymous skBAwexNo ratings yet
- Fluxofil 41 (T 55 6 1nimo B M, C 3 h5)Document1 pageFluxofil 41 (T 55 6 1nimo B M, C 3 h5)brunizzaNo ratings yet
- Toggle Switch Carling MTS 2M Series-3050577Document15 pagesToggle Switch Carling MTS 2M Series-3050577kawykazyNo ratings yet
- ITT American Electric Package B Dusk-To-Dawn Series 11 Spec Sheet 3-82Document4 pagesITT American Electric Package B Dusk-To-Dawn Series 11 Spec Sheet 3-82Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Sylvania Vanguard Dual 400w HID Industrial Series Spec Sheet 1968Document8 pagesSylvania Vanguard Dual 400w HID Industrial Series Spec Sheet 1968Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Advances in High Voltage Insulation and Arc Interruption in SF6 and VacuumFrom EverandAdvances in High Voltage Insulation and Arc Interruption in SF6 and VacuumNo ratings yet
- Semiconducting III–V Compounds: International Series of Monographs on SemiconductorsFrom EverandSemiconducting III–V Compounds: International Series of Monographs on SemiconductorsNo ratings yet
- Business ProcessesDocument122 pagesBusiness ProcessesMAKENGO ELIASNo ratings yet
- Amit Kumar: Education: SummaryDocument2 pagesAmit Kumar: Education: SummarysugandhtNo ratings yet
- Different Modeling For Amharic PDFDocument14 pagesDifferent Modeling For Amharic PDFInderjeetSinghNo ratings yet
- Flat Slab - Types of Flat Slab Design and Its AdvantagesDocument7 pagesFlat Slab - Types of Flat Slab Design and Its AdvantagesnandanaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence in Banking - Where To Start PDFDocument27 pagesArtificial Intelligence in Banking - Where To Start PDFNIKHIL T N100% (1)
- SOR Civil Engineering Works 2016Document31 pagesSOR Civil Engineering Works 2016guees897067100% (1)
- Perkembangan Embrio Dan Penentuan Jenis Kelamin DOC (Day-Old Chicken) Ayam Jawa SuperDocument17 pagesPerkembangan Embrio Dan Penentuan Jenis Kelamin DOC (Day-Old Chicken) Ayam Jawa SuperMuhammad Fahreza Rizky WNo ratings yet
- LAPS OperationsGuideDocument24 pagesLAPS OperationsGuidesarrpaNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint HaTab6krDocument30 pagesPowerpoint HaTab6krNaveen PandeNo ratings yet
- Equivalent Units of Production - Molding Department:: MaterialsDocument3 pagesEquivalent Units of Production - Molding Department:: MaterialsElaine Fiona VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- 1 Concept Paper On The 6-Year CurriculumDocument9 pages1 Concept Paper On The 6-Year CurriculumJoseph Tabadero Jr.100% (3)
- ChatMail (Basic)Document5 pagesChatMail (Basic)akongapopalasiian13No ratings yet
- Unit 1: Atmosphere, Environment and Climate ChangeDocument24 pagesUnit 1: Atmosphere, Environment and Climate Changenidhi140286No ratings yet
- Maygi's HoH 1-100 Handbook (Solo - Party)Document40 pagesMaygi's HoH 1-100 Handbook (Solo - Party)Adrià GomisNo ratings yet
- Unit Grammar Vocabulary Pronunciation: Welcome SectionDocument1 pageUnit Grammar Vocabulary Pronunciation: Welcome SectionJosué Iván Gómez CalderaNo ratings yet
- Karunya UniversityDocument7 pagesKarunya UniversitypreethiNo ratings yet
- Frame Saw Manual 1902Document111 pagesFrame Saw Manual 1902wolf143No ratings yet
- Single Point Cutting ToolDocument22 pagesSingle Point Cutting ToolMeer UmarNo ratings yet
- Cambridge University Press Unlock ListenDocument2 pagesCambridge University Press Unlock ListenPiono pionNo ratings yet
- Performance Anxiety While Performing Music Huanhuan Xie Sophie RW5Document11 pagesPerformance Anxiety While Performing Music Huanhuan Xie Sophie RW5api-289670333No ratings yet
- KYAXXDocument1 pageKYAXXSAMUEL WAGEMANo ratings yet
- Microlivestock - PDF NNNDocument1 pageMicrolivestock - PDF NNNsampath kushanNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Precision Thickness Gages: 35, 35DL, 35HP & 35DL-HPDocument8 pagesUltrasonic Precision Thickness Gages: 35, 35DL, 35HP & 35DL-HPLaurence BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Ra 7719Document7 pagesRa 7719misterdodiNo ratings yet
- Air DryerDocument44 pagesAir DryerJayashankerPeriyaswamyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyHennah Reblando100% (3)
- Datasheet+Fech3+Fixed+03gf0348 2Document2 pagesDatasheet+Fech3+Fixed+03gf0348 2andalibazarNo ratings yet