Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2-Cardiac Arrest Algrthm
Uploaded by
terminallll0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views1 pageqwq
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentqwq
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views1 page2-Cardiac Arrest Algrthm
Uploaded by
terminallllqwq
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
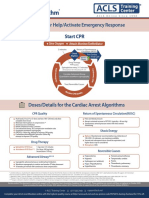
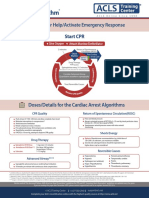
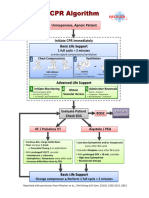
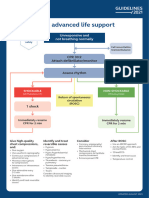
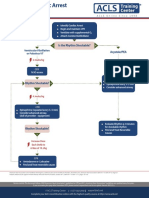
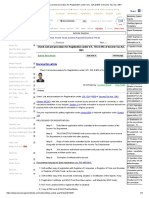
Cardiac Arrest Algorithm
Shout for Help / Active Emergency Response
Doses/ Details
1
Start CPR CPR Quality
• Push hard (≥ 2 inches *5 cm+) and fast (≥
• Give oxygen 100/min) and allow complete chest recoil
• Attach monitor / defibrillator • Minimize interruption in compressions
• Avoid excessive ventilation
• Rotate compressor every 2 minutes
• If no advance airway, 30:2 compression-
Yes No ventilation ratio
Rhythm schockable?
2 • Quantitative waveform capnography
- If PETCO2 <10 mm Hg, attempt to
9 improve CPR quality
VF/VT Asystole/PEA • Intra-arterial pressure
- If relaxation phase (diastolic) pressure
3 Shock <20 mm Hg, attempt to improve CPR
4 quality
CPR 2 min Return of Spontaneous CirculatIon (ROSC)
• IV/IO access • Pulse and blood pressure
• Abrupt sustained increase in PETCO2
(typically ≥40 mm Hg)
No • Spontaneous arterial pressure waves
Rhythm schockable? with intra-arterial monitoring
Shock Energy
Yes Shock • Biphasic: Manufacturer recommendation
5 10 (120-200 J); if unknown, use maximum
6 available.
CPR 2 min Second and subsequent doses should be
CPR 2 min
• IV/IO access equivalent, and higher doses may be
• Epinephrine every 3-5 min considered.
• Epinephrine every 3-5 min
• Consider advance airway, • Monophasic : 360 J
• Consider advance airway,
capnography
capnography
Drug Therapy
• Epinephrine IV/IO Dose:
1 mg every 3-5 minutes
No Yes • Vasopressin IV/IO Dose:
Rhythm schockable? Rhythm schockable? 40 units can replace first or second dose
of epinephrine
• Amiodarone IV/IO Dose:
Yes First dose: 300 mg bolus.
Shock Second dose: 150 mg.
7 No
Advance Airway
• Supraglottic advanced airway or
8 11 endotracheal intubation
CPR 2 min • Waveform capnography to confirm and
CPR 2 min monitor ET tube placement
• Amiodarone • Treat reversible causes • 8-10 breaths per minute with continuous
•Treat reversible causes chest compression
No Yes Reversible Causes:
₋ Hypovolemia
Rhythm schockable? ₋ Hypoxia
₋ Hydrogen ion (acidosis)
12 ₋ Hypo-/Hyperkalemia
₋ Hypothermia
• If no sign of return of spontaneous circulation Go to ₋ Tension pneumothorax
₋ Tamponade, cardiac
(ROSC), go to 10 or 11 5 or 7 ₋ Toxins
• If ROSC, go to Post – Cardiac Arrest Care ₋ Thrombosis, pulmonary
₋ Thrombosis, coronary
Reference by: 2010 Handbook of Emergency Cardiovascular Care for Healthcare providers
You might also like
- Adult Cardiac Arrest Algorithm: VF/PVT Asystole/PEADocument8 pagesAdult Cardiac Arrest Algorithm: VF/PVT Asystole/PEAVitor Hugo100% (2)
- Wa0000.Document7 pagesWa0000.benitez1228No ratings yet
- Figure 4 AlgorithmACLS CACOVID 220101Document1 pageFigure 4 AlgorithmACLS CACOVID 220101AndhikaNo ratings yet
- Adult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityDocument1 pageAdult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityChris LeeNo ratings yet
- Adult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityDocument1 pageAdult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityAlexis HospitalNo ratings yet
- Acls 2023Document5 pagesAcls 2023Mohamed Helal100% (5)
- Algorithms of AHA 2020Document23 pagesAlgorithms of AHA 2020Emirhan llkhanNo ratings yet
- Algorithm-ACLS CA 200731Document1 pageAlgorithm-ACLS CA 200731Hyunsoo EllisNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrest VF/Pulseless VT Learning Station ChecklistDocument5 pagesCardiac Arrest VF/Pulseless VT Learning Station ChecklistMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Start CPR 2 M IN UT ESDocument1 pageCardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Start CPR 2 M IN UT ESjohndoe1995No ratings yet
- Checklist & Algoritma ACLSDocument16 pagesChecklist & Algoritma ACLSNadhif JovaldyNo ratings yet
- Checklist & Algoritma ACLSDocument16 pagesChecklist & Algoritma ACLSNadhif JovaldyNo ratings yet
- Poster 10 PALS 01 01 ENG V20100927 PDFDocument1 pagePoster 10 PALS 01 01 ENG V20100927 PDFAndy XiaoNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Advanced Life Support: Call For Help 2222 Commence/continue CPR (5 Initial Breaths Then CV Ratio 15:2)Document1 pagePaediatric Advanced Life Support: Call For Help 2222 Commence/continue CPR (5 Initial Breaths Then CV Ratio 15:2)Vijay RNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac ArrestDocument1 pageAdvanced Cardiac ArrestDebbie MeyerNo ratings yet
- ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm For Suspected or Confirmed COVID-19 PatientsDocument2 pagesACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm For Suspected or Confirmed COVID-19 PatientsDeny PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Adult Immediate Post Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm 2015 UpdateDocument1 pageAdult Immediate Post Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm 2015 UpdateRyggie Comelon0% (1)
- Algo ArrestDocument2 pagesAlgo ArrestLocomotorica FK UkiNo ratings yet
- ACLS 2015 Algorithm and Anesthesia ACLS PDFDocument14 pagesACLS 2015 Algorithm and Anesthesia ACLS PDFTaufiqurrahman RizkiNo ratings yet
- CPR PosterDocument1 pageCPR PosterHemantNo ratings yet
- Advance Life Support MaterialDocument2 pagesAdvance Life Support MaterialmayNo ratings yet
- Start CPR Shout For Help/Activate Emergency Response: Give Oxygen Attach Monitor/DefibrillatorDocument2 pagesStart CPR Shout For Help/Activate Emergency Response: Give Oxygen Attach Monitor/DefibrillatorFelicia ErikaNo ratings yet
- Acls Study Guide 2016Document2 pagesAcls Study Guide 2016nova939100% (2)
- ACLS Pocket Card PDFDocument6 pagesACLS Pocket Card PDFdang vu hoang ducNo ratings yet
- Recover CPR AlgorithmDocument1 pageRecover CPR Algorithmkt496No ratings yet
- Adult Advanced Life Support Algorithm 2021 Aug 2023Document1 pageAdult Advanced Life Support Algorithm 2021 Aug 2023cknihilnewNo ratings yet
- ACLS - Guidelines From 2005USADocument62 pagesACLS - Guidelines From 2005USAsbontchevNo ratings yet
- ACLS HandoutsDocument4 pagesACLS HandoutshasanNo ratings yet
- 8-Adult Advanced Life Support Algorithm 2021Document1 page8-Adult Advanced Life Support Algorithm 2021khaledNo ratings yet
- AclsDocument1 pageAclsJoice DasNo ratings yet
- Acls Study Guide 2016Document2 pagesAcls Study Guide 2016Caridad RodasNo ratings yet
- Acls Patient Algorithms: Greg Cook's Version of A Phoenix Fire DPT ClasicDocument4 pagesAcls Patient Algorithms: Greg Cook's Version of A Phoenix Fire DPT ClasicDouglas Greg CookNo ratings yet
- Troponin PathwayDocument1 pageTroponin PathwayAllana AngelesNo ratings yet
- Henti Jantung Acls Inkavin PinDocument9 pagesHenti Jantung Acls Inkavin PinIndriani SulistyaningsihNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrest Algorithm: Give OxygenDocument2 pagesCardiac Arrest Algorithm: Give OxygenJunius SimarmataNo ratings yet
- ACLS Cardiac Arrest AlgorithmDocument1 pageACLS Cardiac Arrest AlgorithmLuisa RojasNo ratings yet
- Adult Asystole or PeaDocument1 pageAdult Asystole or PeamayNo ratings yet
- AlgorithmsDocument16 pagesAlgorithmsirish laglevaNo ratings yet
- Algoritmos AHA ACLS AdultoDocument4 pagesAlgoritmos AHA ACLS AdultoChristianFelipePorrasCastroNo ratings yet
- Henti Jantung: Dr. Wisudawan M.Kes SP - JP FIHADocument9 pagesHenti Jantung: Dr. Wisudawan M.Kes SP - JP FIHAFajriah SaraswatiNo ratings yet
- Adult Bradycardia Algorithm: Identify and Treat Underlying CauseDocument1 pageAdult Bradycardia Algorithm: Identify and Treat Underlying CausenebrasNo ratings yet
- Adult Bradycardia Algorithm: Identify and Treat Underlying CauseDocument1 pageAdult Bradycardia Algorithm: Identify and Treat Underlying CauseAlexis HospitalNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrest Circular AlgorhythmDocument4 pagesCardiac Arrest Circular AlgorhythmAisyah Nur KarimahNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac Life SupportDocument37 pagesAdvanced Cardiac Life SupportRoy Acosta GumbanNo ratings yet
- PalsDocument1 pagePalslordroentgenNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Bradycardia With A Pulse AlgorithmDocument1 pagePediatric Bradycardia With A Pulse AlgorithmRatna TambaNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument7 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromePuskesmas Pinang JayaNo ratings yet
- Peri-Arrest ArrythmiaDocument14 pagesPeri-Arrest Arrythmiamohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithms 3Document1 pageACLS Algorithms 3frankie-jay paicotNo ratings yet
- 2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Tachycardia AlgorithmDocument1 page2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Tachycardia AlgorithmRyggie ComelonNo ratings yet
- Henti JantungDocument9 pagesHenti JantungfauzannizwarNo ratings yet
- Perkembangan Baru Resusitasi Jantung ParuDocument27 pagesPerkembangan Baru Resusitasi Jantung ParuMarcelina Aprisia PrimadiNo ratings yet
- Emergency Treatment CardsDocument2 pagesEmergency Treatment CardsChristina XavierNo ratings yet
- Algo Pals Pediatric Cardiac ArrestDocument1 pageAlgo Pals Pediatric Cardiac Arrestpedjoang fkupr2017No ratings yet
- Acls PDFDocument2 pagesAcls PDFKyrie Diosabeth TumbagaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Article 662Document8 pages2016 Article 662terminallllNo ratings yet
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocument10 pagesWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientiststerminallllNo ratings yet
- 6-Tachycardia With A Pulse AlgorithmDocument1 page6-Tachycardia With A Pulse AlgorithmterminallllNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Copsyc 2020 04 005Document6 pages10 1016@j Copsyc 2020 04 005terminallllNo ratings yet
- 8-Suspected Stroke AlgrthmDocument1 page8-Suspected Stroke AlgrthmterminallllNo ratings yet
- 5-Bradycardia With A Pulse AlgorthmDocument1 page5-Bradycardia With A Pulse AlgorthmterminallllNo ratings yet
- Science Year 3/grade 8: Middle Years ProgrammeDocument4 pagesScience Year 3/grade 8: Middle Years Programmeakshyta gantanNo ratings yet
- Session 5 E4 - Ms. CabanillasDocument8 pagesSession 5 E4 - Ms. CabanillasLUIS MIGUEL LIMO PRIETONo ratings yet
- Blood TransfusionDocument102 pagesBlood TransfusionhatirebNo ratings yet
- Make Her Make MoveDocument32 pagesMake Her Make MoveAlfredo GomezNo ratings yet
- Art History Research ProjectDocument3 pagesArt History Research Projectapi-245037226No ratings yet
- Perssuasive EssayDocument5 pagesPerssuasive Essayapi-512789628No ratings yet
- Com 200 ResearchpaperfinalDocument7 pagesCom 200 Researchpaperfinalapi-674132286No ratings yet
- 5.0 Problem Solving in MathDocument51 pages5.0 Problem Solving in MathRose Suba100% (3)
- Unit 1 Tpde & Pde Lecture Notes PDFDocument36 pagesUnit 1 Tpde & Pde Lecture Notes PDFpoojaabanindranNo ratings yet
- 12A & 80G ProcedureDocument4 pages12A & 80G ProcedurekshripalNo ratings yet
- Brihadisvara Temple, ThanjavurDocument22 pagesBrihadisvara Temple, ThanjavurAllen Antony Kurisingal100% (1)
- Theme: Is Cell Phone Dangerous? Speaker 1 Positive TeamDocument4 pagesTheme: Is Cell Phone Dangerous? Speaker 1 Positive TeamLILIS ROHAYATINo ratings yet
- Road To WWII RevisionDocument2 pagesRoad To WWII RevisionAngelWithAShotgun07No ratings yet
- Combinatorial Chemistry Amp High Throughput Screening PDFDocument2 pagesCombinatorial Chemistry Amp High Throughput Screening PDFLamarcusNo ratings yet
- Write Up Newsletter p1Document5 pagesWrite Up Newsletter p1api-378872280No ratings yet
- British LiteratureDocument13 pagesBritish LiteratureAlexa BaloghNo ratings yet
- Ifa Tourneeausstellungen 2021 ENDocument112 pagesIfa Tourneeausstellungen 2021 ENsextoNo ratings yet
- Metformin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMetformin Drug StudyArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- Whats The Weather LikeDocument3 pagesWhats The Weather Likechristian sosaNo ratings yet
- Writing A Case Study: Quick Guide For StudentsDocument3 pagesWriting A Case Study: Quick Guide For StudentsManish AhujaNo ratings yet
- Montage As Perceptual Experience: Mario SluganDocument256 pagesMontage As Perceptual Experience: Mario SluganAnja VujovicNo ratings yet
- Diass (Module 6)Document41 pagesDiass (Module 6)Jocelyn Baculi AutenticoNo ratings yet
- RISD D+M Lecture Series Poster Fall 2008Document1 pageRISD D+M Lecture Series Poster Fall 2008Digital MediaNo ratings yet
- Collocation SDocument20 pagesCollocation SGurjinder SinghNo ratings yet
- MSC Mental Health: School of Health SciencesDocument9 pagesMSC Mental Health: School of Health SciencesRawoo KowshikNo ratings yet
- David Miano - Why Ancient History Matters v02Document16 pagesDavid Miano - Why Ancient History Matters v02Esteban LVNo ratings yet
- 01 VIOLATION WARNING COLl MAGISTRATE COURT OF CHATHAM COUNTY ANDREA ROBERTSON Inola Enapay Bey Ex Relatione ANNETTA JAMES BROWNDocument3 pages01 VIOLATION WARNING COLl MAGISTRATE COURT OF CHATHAM COUNTY ANDREA ROBERTSON Inola Enapay Bey Ex Relatione ANNETTA JAMES BROWNstonsome100% (1)
- Durga Anand Sanipilli: Obile Mail Nandsanipilli Gmail COMDocument3 pagesDurga Anand Sanipilli: Obile Mail Nandsanipilli Gmail COMDurgaAnandNo ratings yet
- Refutation of Catherine Emerick and Padre PioDocument12 pagesRefutation of Catherine Emerick and Padre PioMarie Julianna BoweNo ratings yet
- 24941-100-30R-G01-00073 Tunra 6299 Report FinalDocument96 pages24941-100-30R-G01-00073 Tunra 6299 Report FinalcmahendrNo ratings yet