Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Clinical Manifestations: Diagnostic Findings
Uploaded by
Melodia Turqueza Gandeza0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views8 pagesOriginal Title
SCHEM D3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views8 pagesClinical Manifestations: Diagnostic Findings
Uploaded by
Melodia Turqueza GandezaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
Diagnostic findings
Cardiac catheterization: A long, thin flexible tube is threaded
through a blood vessel in the arm or groin and to the heart.
Clinical manifestations
Contrast material is injected through the tube and a type of X-ray
video is taken to show how the heart functions and to look for heart
blockages.
Chest X-ray: A common imaging test of the lungs, heart and aorta.
Echocardiogram: This ultrasound exam uses soundwaves to take
moving pictures of the heart’s chambers and valves.
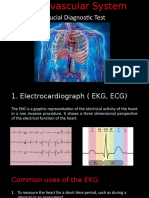
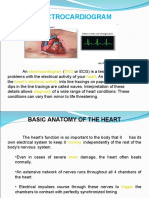
Electrocardiogram (EKG): This test measures the electrical
activity of the heart and can help determine if parts of the heart are
enlarged, overworked or damaged. The heart’s electrical currents
are detected by 12 to 15 electrodes that are attached to the arms,
legs and chest via sticky tape.
Electrophysiology study: This test records the heart’s electrical
activities and pathways. It can help find what’s causing heart
rhythm problems and identify the best treatment.
Radionuclide imaging (thallium stress test): This non-invasive
procedure can identify if there is severe heart damage. A
radioactive isotope is injected into a vein and a special camera or
scanner records how it travels through the heart. Any heart damage
can be plotted, locating the damaged area of the heart. This
procedure can be done with an electrocardiogram, during both rest
an exercise.
Treadmill Exercise Test with Peak V02: This test measures a
patient’s capacity to exercise and the amount of oxygen the heart
provides muscles during the test. Results reveal the severity of the
left-sided heart failure and helps provide a prognosis.
You might also like
- Heart Procedures GlossaryDocument2 pagesHeart Procedures Glossary姜華No ratings yet
- Instrumental Diagnostic Methods of Heart DiseasesDocument15 pagesInstrumental Diagnostic Methods of Heart DiseasesA A D H INo ratings yet
- Diagnosis: Additional TestsDocument2 pagesDiagnosis: Additional TestsChristopher John Balagot100% (1)
- Diagnostic Test For Heart DiseasesDocument16 pagesDiagnostic Test For Heart DiseasesJaimee Jonah ChristieNo ratings yet
- Different DiagnosticDocument26 pagesDifferent DiagnosticDanica Alyssa EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiograph Y (ECG / Ekg) : Rose Dyane F - Nunag, RMT, MPHDocument52 pagesElectrocardiograph Y (ECG / Ekg) : Rose Dyane F - Nunag, RMT, MPHClaire GonoNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between An ECG and Echo Tests Done For Heart Ailments? An Is Used To MeasureDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between An ECG and Echo Tests Done For Heart Ailments? An Is Used To MeasureSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Electro Cardiogram: NCM 112:skills LaboratoryDocument7 pagesElectro Cardiogram: NCM 112:skills LaboratoryFaye Domini FederisNo ratings yet
- What Is An ECG?: Heart DiseaseDocument4 pagesWhat Is An ECG?: Heart DiseaseAjay Pal NattNo ratings yet
- Cardiac TestsDocument6 pagesCardiac TestsRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disorders Diagnostic Tests and ProceduresDocument16 pagesCardiovascular Disorders Diagnostic Tests and ProceduresMonette Abalos MendovaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrocardiogram (Ecg) : Mr. Hamza Ratrout Revised By: Dr. Irene RocoDocument28 pagesBasic Electrocardiogram (Ecg) : Mr. Hamza Ratrout Revised By: Dr. Irene Rocoأبوأحمد الحكيمNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing Heart DiseaseDocument3 pagesDiagnosing Heart DiseaseJaz SantosNo ratings yet
- Major Project Phase 1 Report CloudDocument35 pagesMajor Project Phase 1 Report CloudPraj CNo ratings yet
- ECGfinalDocument10 pagesECGfinalSarah FerguzonNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Diagnostic Tests and ProceduresDocument27 pagesCardiovascular Diagnostic Tests and ProceduresSajjal JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Metodos DiagnosticosDocument2 pagesMetodos Diagnosticosapi-541766630No ratings yet
- Diagnostic Procedure PresentationDocument18 pagesDiagnostic Procedure PresentationKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Indications: PurposeDocument13 pagesIndications: PurposeIRA ODETTE GATUSNo ratings yet
- Echocardiograph Y: Rose Dyane F - Nunag, RMT, MPHDocument17 pagesEchocardiograph Y: Rose Dyane F - Nunag, RMT, MPHClaire GonoNo ratings yet
- Non Invasive Diagnostic Instruments: By. Kailash - Pandey Aditya - MayekarDocument32 pagesNon Invasive Diagnostic Instruments: By. Kailash - Pandey Aditya - MayekarkrupalithakkerNo ratings yet
- Ecg Basic ConceptsDocument18 pagesEcg Basic ConceptsDaniel SolonyaNo ratings yet
- Ecg / EkgDocument10 pagesEcg / EkgSilver Villota Magday Jr.No ratings yet
- Haemodynamic mo-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesHaemodynamic mo-WPS Officermconvidhya sri2015No ratings yet
- Tress Test: The Gale Encyclopedia of MedicineDocument7 pagesTress Test: The Gale Encyclopedia of MedicineSalsabilla KimikoNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document53 pagesElectrocardiogram (ECG)eric100% (1)
- Cardiology Laboratory TestsDocument2 pagesCardiology Laboratory TestsBeatrice SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Tests To Diagnose A Congenital Heart Defect Include: Heart Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)Document2 pagesTests To Diagnose A Congenital Heart Defect Include: Heart Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)Charmane MorelosNo ratings yet
- Electro CardiogramDocument2 pagesElectro CardiogrambinukirubaNo ratings yet
- CardiovascularDocument16 pagesCardiovascularMilena VargasNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Tests in CardiologyDocument38 pagesDiagnostic Tests in CardiologyDea Amelia YolandaNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography (ECG)Document11 pagesElectrocardiography (ECG)Hassan AnwarNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Tests in CardiologyDocument38 pagesDiagnostic Tests in CardiologyDea Amelia YolandaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System TestDocument28 pagesCardiovascular System TestEla Angela RumapeaNo ratings yet
- What Is EcgDocument5 pagesWhat Is EcgLeeyan MeeNo ratings yet
- EKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!From EverandEKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!No ratings yet
- ElectrocardiogramDocument1 pageElectrocardiogramDONNA BETH CABILLANo ratings yet
- 2D Echocardiogram (Bulletin)Document2 pages2D Echocardiogram (Bulletin)karen bondaNo ratings yet
- Test CardiomegalyDocument2 pagesTest CardiomegalyArdi Armedi AzniNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram: Electrocardiogram EKG Heart Heart's Electrical Activity DiagnosisDocument38 pagesElectrocardiogram: Electrocardiogram EKG Heart Heart's Electrical Activity DiagnosislorhenzsoNo ratings yet
- Echocardiography: Not To Be Confused WithDocument3 pagesEchocardiography: Not To Be Confused Withgreathari1998No ratings yet
- Grp. 5 Coronary Artery Disease WrittenDocument9 pagesGrp. 5 Coronary Artery Disease WrittenCha AlegriaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Monitor: Other Names For An ElectrocardiogramDocument7 pagesCardiac Monitor: Other Names For An ElectrocardiogramRizzia BalabisNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Report: Malabar Institute of Medical Sciences LTD KottakkalDocument27 pagesBiomedical Report: Malabar Institute of Medical Sciences LTD KottakkalSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- Modern Electronic InstrumentsDocument7 pagesModern Electronic InstrumentsuatilakarathnaNo ratings yet
- Instrumental MethodDocument24 pagesInstrumental Methodzerish0208No ratings yet
- Cardiac Monitor, ECG and CauterizationDocument28 pagesCardiac Monitor, ECG and CauterizationGlaiza Mae Olivar-ArguillesNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Tests: Aleth Therese L. Dacanay, MSCDocument59 pagesDiagnostic Tests: Aleth Therese L. Dacanay, MSCMikee MeladNo ratings yet
- ECGDocument2 pagesECGScaramoucheNo ratings yet
- Echocardiogram: Echocardiogram, Also Known As Echocardiography, or Heart Ultrasound Is ADocument23 pagesEchocardiogram: Echocardiogram, Also Known As Echocardiography, or Heart Ultrasound Is AKarl RobleNo ratings yet
- Presentation On EchocardiogramDocument17 pagesPresentation On EchocardiogramSoniya NakkaNo ratings yet
- ECG/EKG Interpretation: An Easy Approach to Read a 12-Lead ECG and How to Diagnose and Treat ArrhythmiasFrom EverandECG/EKG Interpretation: An Easy Approach to Read a 12-Lead ECG and How to Diagnose and Treat ArrhythmiasRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Two Phase Heart Disease Diagnosis System Using Deep LearningDocument16 pagesTwo Phase Heart Disease Diagnosis System Using Deep LearninganuragNo ratings yet
- Medical LaboratoryDocument17 pagesMedical LaboratoryAshokvannan100% (1)
- Medical Laboratory 4 PDF FreeDocument17 pagesMedical Laboratory 4 PDF FreeUdo ifeoma mirabelNo ratings yet
- CardiovascularDocument36 pagesCardiovascularShield Mae BalanlayNo ratings yet
- G Lossary of Terms Using Image Manual Training For Icon Medical ImagingDocument6 pagesG Lossary of Terms Using Image Manual Training For Icon Medical ImagingMario LeonNo ratings yet
- ElectrocardiogramDocument4 pagesElectrocardiogramazeeroNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.: 06: Title: Study and Simulation of ECG RecorderDocument7 pagesExperiment No.: 06: Title: Study and Simulation of ECG RecorderVISHWESH KULKARNINo ratings yet
- Preg and CovidDocument2 pagesPreg and CovidMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- D N C 8Document26 pagesD N C 8Melodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Changing Because They're Always FindingDocument27 pagesChanging Because They're Always FindingMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Sections: My Account Contact UsDocument7 pagesSections: My Account Contact UsMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- English: Although We Don't Have That Much Data On COVID-19 and Pregnancy, What We Do Have Suggests ThatDocument3 pagesEnglish: Although We Don't Have That Much Data On COVID-19 and Pregnancy, What We Do Have Suggests ThatMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- English: Although We Don't Have That Much Data On COVID-19 and Pregnancy, What We Do Have Suggests ThatDocument3 pagesEnglish: Although We Don't Have That Much Data On COVID-19 and Pregnancy, What We Do Have Suggests ThatMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- 1Document44 pages1Melodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- DrugDocument10 pagesDrugMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Pregnant? Here's What To Know About Coronavirus Risk: Primary MenuDocument9 pagesPregnant? Here's What To Know About Coronavirus Risk: Primary MenuMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Drug-Drug: DecreasedDocument10 pagesDrug-Drug: DecreasedMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- 203Document39 pages203Melodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Mine-Analysis OfdataDocument1 pageMine-Analysis OfdataMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- 0000678998Document1 page0000678998Melodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Drug-Drug: DecreasedDocument10 pagesDrug-Drug: DecreasedMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 6Document7 pagesQuiz 6Melodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- What Are The Symptoms of Bulimia?: Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia SymptomsDocument13 pagesWhat Are The Symptoms of Bulimia?: Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia SymptomsMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Symptoms Prevention BulemiaDocument19 pagesSymptoms Prevention BulemiaMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- SchoologyanaphylecDocument7 pagesSchoologyanaphylecMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Complication of BulimiaDocument5 pagesComplication of BulimiaMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- NSG Man BulimiaDocument21 pagesNSG Man BulimiaMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- What Is A PICOT Question?Document1 pageWhat Is A PICOT Question?melodia gandezaNo ratings yet
- PicotDocument1 pagePicotMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- PICOT QuestionDocument1 pagePICOT Questionmelodia gandezaNo ratings yet
- Treatmemt Med ManagementDocument9 pagesTreatmemt Med ManagementMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 7Document11 pagesQuiz 7Melodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Xcopri Complete Drug StudyDocument2 pagesXcopri Complete Drug StudyMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Assess Patient's Vital Signs and Characteristics of Respirations at Least Every 4 HoursDocument1 pageAssess Patient's Vital Signs and Characteristics of Respirations at Least Every 4 HoursMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation Case Questions&AnswersDocument20 pagesMechanical Ventilation Case Questions&AnswersRaghavendra PrasadNo ratings yet
- To ReadDocument10 pagesTo ReadMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Medical Care Protocol: General ConsiderationsDocument150 pagesMedical Care Protocol: General ConsiderationsMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet