Professional Documents
Culture Documents
300-101 (Tagwa 41 QS) PDF
300-101 (Tagwa 41 QS) PDF
Uploaded by
Mao BourichaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
300-101 (Tagwa 41 QS) PDF
300-101 (Tagwa 41 QS) PDF
Uploaded by
Mao BourichaCopyright:
Available Formats
CCNP 300-101-NEW QUESTIONS
LAST-UPDATES 31-OCT-2016
Question 1
What is the function of the snmp-server manager command?
A. To enable the device to send and receive SNMP requests and responses
B. To enable the device to send SNMP traps to the SNMP server
C. To disable SNMP messages from getting to the SNMP engine
D. To configure the SNMP server to store log data
Answer:A
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
The SNMP manager process sends SNMP requests to agents and receives SNMP responses and notifications from agents.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios/12_2/configfun/command/reference/ffun_r/frf014.html#wp1022914
Question 2
Refer to the following configuration command.
router(config)# ip nat inside source static tcp 172.16.10.8 8080 172.16.10.8 80
Which statement about the command is true?
A. Any packet that is received in the inside interface with a source IP port address of
172.16.10.8:80 is translated to 172.16.10.8:8080.
B. Any packet that is received in the inside interface with a source IP port address of
172.16.10.8:8080 is translated to 172.16.10.8:80.
C. The router accepts only a TCP connection from port 8080 and port 80 on IP address
172.16.10.8.
D. Any packet that is received in the inside interface with a source IP address of 172.16.10.8
is redirected to port 8080 or port 80.
Answer:A
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
Having a web server on the internal network is another example of when it may be necessary for devices on the internet to initiate communication
with internal devices. In some cases the internal web server may be configured to listen for web traffic on a TCP port other than port 80. For
example, the internal web server may be configured to listen to TCP port 8080. In this case, you can use NAT to redirect traffic destined to TCP port
80 to TCP port 8080.
After you define the interfaces as shown in the previous network diagram, you may decide that you want NAT to redirect packets from the outside
destined for 172.16.10.8:80 to 172.16.10.8:8080. You can use a static nat command in order to translate the TCP port number to achieve this.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/network-address-translation-nat/13772-12.ht
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 1
Question 3
When the tunnel interface is configured in default mode, which statement about routers and
the tunnel destination address is true?
A-The router must have a route installed towards the tunnel destination
B-the router must have wccp redirects enabled inbound from the tunnel destination
C-the router must have cisco discovery protocol enabled on the tunnel to form a CDP
neighborship with the tunnel destination
D-the router must have redirects enabled outbound towards the tunnel destination
Answer:A
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
. If routing is not carefully configured, the tunnel may have a recursive routing problem. When the best path to the "tunnel destination" is via the tunnel
itself, recursive routing causes the tunnel interface to flap. To avoid recursive routing problems, keep the control-plane routing separate from the tunnel
routing using the following methods:
–Use a different autonomous system number or tag.
–Use a different routing protocol.
–Use static routes to override the first hop (but watch for routing loops).
When you have recursive routing to the tunnel destination, the following error appears:
%TUN-RECURDOWN Interface Tunnel 0
temporarily disabled due to recursive routing
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios/12_4/interface/configuration/guide/inb_tun.html
Question 4
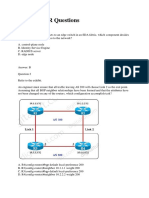
Refer to the exhibit.
A network engineer has configured GRE between two IOS routers. The state of the tunnel
interface is continuously oscillating between up and down. What is the solution to this
problem?
A. Create a more specific static route to define how to reach the remote router.
B. Create a more specific ARP entry to define how to reach the remote router.
C. Save the configuration and reload the router.
D. Check whether the internet service provider link is stable
Answer:A
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/enhanced-interior-gateway-routing-protocol-eigrp/22327-gre-flap.html
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 2
Question 5
Other than a working EIGRP configuration, which option must be the same on all routers for
EIGRP authentication key rolleover to work correctly?
A. SMTP
B. SNMP
C. Passwords
D. Time
Answer:D
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
Router3(config)#key chain ROLLOVER
Router3(config-keychain)#key 1
Router3(config-keychain-key)#accept-lifetime 00:00:00 Jan 1 2013 01:00:00 Jan 1 2014
Router3(config-keychain-key)#send-lifetime 00:00:00 Jan 1 2013 01:00:00 Jan 1 2014
Router3(config-keychain)#key 2
Router3(config-keychain-key)#accept-lifetime 23:00:00 Dec 31 2013 01:00:00 Jan 1 2015
Router3(config-keychain-key)#send-lifetime 23:00:00 Dec 31 2013 01:00:00 Jan 1 2015
https://www.sash.jp/cciers/eigrp-automatic-key-rollover
Question 6
Which two statements about NTP operation are true? (Choose two.)
A. If multiple NTP servers are configured, the one with the lowest stratum is preferred
B. By default, NTP communications use UDP port 123.
C. If multiple NTP servers are configured, the one with the highest stratum is preferred.
D. Locally configured time overrides time received from an NTP server.
E. “Stratum” refers to the number of hops between the NTP client and the NTP server.
Answer:A,B
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
NTP is designed to synchronize the time on a network of machines. NTP runs over the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), using port 123 as both the
source and destination, which in turn runs over IP. NTP Version 3 RFC 1305 leavingcisco.com is used to synchronize timekeeping among a set of
distributed time servers and clients. A set of nodes on a network are identified and configured with NTP and the nodes form a synchronization subnet,
sometimes referred to as an overlay network. While multiple masters (primary servers) may exist, there is no requirement for an election protocol.
An NTP network usually gets its time from an authoritative time source, such as a radio clock or an atomic clock attached to a time server. NTP then
distributes this time across the network. An NTP client makes a transaction with its server over its polling interval (from 64 to 1024 seconds) which
dynamically changes over time depending on the network conditions between the NTP server and the client. The other situation occurs when the
router communicates to a bad NTP server (for example, NTP server with large dispersion); the router also increases the poll interval. No more than
one NTP transaction per minute is needed to synchronize two machines. It is not possible to adjust the NTP poll interval on a router.
NTP uses the concept of a stratum to describe how many NTP hops away a machine is from an authoritative time source. For example, a stratum 1
time server has a radio or atomic clock directly attached to it. It then sends its time to a stratum 2 time server through NTP, and so on. A machine
running NTP automatically chooses the machine with the lowest stratum number that it is configured to communicate with using NTP as its time
source. This strategy effectively builds a self-organizing tree of NTP speakers. NTP performs well over the non-deterministic path lengths of packet-
switched networks, because it makes robust estimates of the following three key variables in the relationship between a client and a time server
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/availability/high-availability/19643-ntpm.html
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 3
Question 7
What type of IPv6 packet will indicate traffic from single host and single node?
A. multicast
B. unicast
C. broadcast
D. anycast
Answer:B
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
IPv6 has three types of addresses, which can be categorized by type and scope:
Unicast addresses. A packet is delivered to one interface.
Multicast addresses. A packet is delivered to multiple interfaces.
Anycast addresses. A packet is delivered to the nearest of multiple interfaces (in terms of routing distance).
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc757359(v=ws.10).aspx
Question 8
In which two ways can split horizon issues be overcome in a Frame Relay network environment?
(choose two.)
A. Configuring one physical serial interface with Frame Relay to various remote sites.
B. Configure a loopback interface with Frame Relay to various remote sites.
C. Configuring multiple subinterfaces on a single physical interface to various remote sites.
D. Enabling split horizon.
E. Disabling split horizon.
Answer:C,E
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
1/ IP split horizon checking is disabled by default for Frame Relay encapsulation to allow routing updates to go in and out of the same interface. An
exception is the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) for which split horizon must be explicitly disabled.
2/Configuring Frame Relay subinterfaces ensures that a single physical interface is treated as multiple virtual interfaces. This capability allows you to
overcome split horizon rules so packets received on one virtual interface can be forwarded to another virtual interface, even if they are configured on the
same physical interface.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/wan/frame-relay/14168-fr-faq.html
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 4
Question 9
Refer to Exhibit:
Which three NTP features can be deduced on the router? (choose three)
A. only accepts time requests from 192.168.1.1
B. only handle four requests at a time
C. only is in stratum 4
D. only updates its time from 192.168.1.1
E. only accepts time requests from 192.168.1.4
F. only updates its time from 192.168.1.4
Answer:A,C,F
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
IOS router defines the following four types of access for NTP:
1) Peer – permits router to respond to NTP requests and accept NTP updates. NTP control queries are also accepted. This is the only class
which allows a router to be synchronized by other devices.
2) Serve – permits router to reply to NTP requests, but rejects NTP updates (e.g. replies from a server or update packets from a peer). Control
queries are also permitted.
3) Serve-only – permits router to respond to NTP requests only. Rejects attempt to synchronize local system time, and does not access control queries.
4) Query-only – only accepts NTP control queries. No response to NTP requests are sent, and no local system time synchronization with remote system
is permitted.
http://blog.ine.com/2008/07/28/ntp-access-control
Question 10
What command can you enter to configure an enable password that uses an encrypted password
from another configuration?
A. enable secret $abc%!e.Cd34$!ao0
B. enable secret 7 Sabc%!e.Cd34$!ao0
C. enable secret 0 Sabc%U*.Cd34$!ao0
D. enable secret 5 $abc%!e.Cd34$!ao0
E. enable secret 15 $abc%ie.Cd34$!ao0
F. enable secret 6 $abc%!e.Cd34$!ao0
Answer:D
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
EXAMPLE
Router(config)#enable secret aaa
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 5
Question 11
A network engineer receives reports about poor voice quality issues at a remote site. The network
engineer does a packet capture and sees out-of-order packets being delivered. Which option can
cause the VOIP quality to suffer?
A. traffic over backup redundant links
B. misconfigured voice vlan
C. speed duplex link issues
D. load balancing over redundant links
Answer:D
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
In traditional packet forwarding systems, using different paths have varying latencies that cause out of order packets,
eventually resulting in far lower performance for the network application. Also
, if some packets are process switched quickly by the routing engine of the router while others are interrupt switched (which takes more time)
then it could result in out of order packets. The other options would cause packet drops or latency, but not out of order packets.
Question 12
Refer to the exhibit.
A network engineer is troubleshooting a DMVPN setup between the hub and the spoke. The
engineer executes the command show crypto isakmp sa and observes the output that is
displayed. What is the problem?
A. That ISAKMP is not enabled
B. That ISAKMP is using default settings
C. An incompatible IP sec transform set
D. An incompatible ISAKMP policy
Answer:B
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
EXAMPLE
note that these SAs are in "QM_IDLE" state, meaning that the ISAKMP SA is authenticated and can be used for subsequent Quick Mode (Phase 2)
exchanges. The ISAKMP SA can exist in a number of other states.
tahts state default .
*That ISAKMP is not enabled -------> no output
*default settings -------> QM_Idle
* incompatible IP sec transform set -------> Has nothing to do with Phase 1
*incompatible ISAKMP policy -----> Possibly MM_KEY_EXCH
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/security-vpn/ipsec-negotiation-ike-protocols/5409-ipsec-debug-00.html
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 6
Question 13
Which two attributes describe UDP within a TCP/IP network? (Choose two.)
A. Acknowledgments
B. Unreliable delivery
C. Connectionless communication
D. Connection-oriented communication
E. Increased headers
Answer:B,C
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
UDP Characteristics
presents the structure of a UDP segment header. Because UDP is considered to be a
connectionless, unreliable protocol, it lacks the sequence numbering, window size, and
acknowledgment numbering present in the header of a TCP segment.
Rather the UDP segment’s
Because a UDP segment header is so much smaller than a TCP segment header, UDP becomes a good
candidate for the transport layer protocol serving applications that need to maximize bandwidth and
do not require acknowledgments.
https://www.safaribooksonline.com/library/view/ccnp-routing-and/9780133149883/ch01lev3sec7.html
Question 14
Which three IP SLA performance metrics can you use to monitor enterprise-class networks? (Choose
three.)
A. Packet loss
B. Delay
C. bandwidth
D. Connectivity
E. Reliability
F. traps
Answer:A,B,D
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
Performance metrics collected by IP SLAs operations include the following:
* Delay (both round-trip and one-way)
* Jitter (directional)
*Packet loss (directional)
*Packet sequencing (packet ordering)
* Path (per hop)
*Connectivity (directional)
*Server or website download time
* Voice quality scores
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/ipsla/configuration/15-mt/sla-15-mt-book/sla_overview.html
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 7
Question 15
A network administrator notices that the BGP state drops and logs are generated for missing BGP
hello keepalives. What is the potential problem?
A. Incorrect neighbor options
B. Hello timer mismatch
C. BGP path MTU enabled
D. MTU mismatch
Answer:D
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
Problem
BGP neighbors form; however, at the time of prefix exchange, the BGP state drops and the logs generate missing BGP hello keepalives
or the other peer terminates the session.
Here are some possible causes:
*The interface MTU on both routers do not match.
*The interface MTU on both routers match, but the Layer 2 domain over which the BGP session is formed does not match.
*Path MTU discovery determined the incorrect max datasize for the TCP BGP session.
*The BGP Path Maximum Transmission Unit Discovery (PMTUD) could be failing due to PMTUD ICMP packets blocked (firewal or ACL)
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/border-gateway-protocol-bgp/116377-troubleshoot-bgp-mtu.html
Question 16
A network engineer wants to notify a manager in the events that the IP SLA connection loss
threshold reached. Which two feature are need to implements this functionality? (choose two)
A. MOS
B. Threshold action
C. Cisco IOS EEM
D. SNMP traps
E. logging local
Answer:B,D
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
IP SLAs supports threshold monitoring for performance parameters such as average jitter, unidirectional latency and bidirectional round trip time and
connectivity. This proactive monitoring capability provides options for configuring reaction thresholds for important VoIP related parameters including
unidirectional jitter, unidirectional packet loss, and unidirectional VoIP voice quality scoring (MOS scores).
IP SLAs can generate system logging (syslog) messages when the reaction threshold increases or decreases beyond the configured values for packet
loss, average jitter, or MOS. These system logging messages can then be sent as SNMP notifications (traps) using the CISCO-SYSLOG-MIB.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios/12_4/ip_sla/configuration/guide/hsla_c/hsthresh.html
Question 17
Which easy virtual networking configuration component significantly decreases network configuration?
A. Easy Trunk
B. dot1e
C. virtual network trunk
D. VNET tags
E. MBGP
Answer:C
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
EVN reduces network virtualization configuration significantly across the entire network infrastructure with the Virtual Network Trunk.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/ios-nx-os-software/easy-virtual-network-evn/index.html
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 8
Question 18
A network engineer wants to display the statistics of an active tunnel on a DMVPN network. Which
command should the administrator execute to accomplish this task?
A. Router#show crypto ipsec sa
B. Router#show crypto isakmp peers
C. Router#show crypto isakmp sa
D. Router#show crypto ipsec transform-set
E. Router#show crypto engine connections active
Answer:A
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
show crypto engine connection active—Displays the total encrypts and decrypts per SA.
show crypto ipsec sa—Displays the stats on the active tunnels.
show crypto isakmp sa—Displays the state for the the ISAKMP SA.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/security-vpn/ipsec-negotiation-ike-protocols/29240-dcmvpn.html#veri
Question 19
Which IP SLA operation can be used to measure round-trip delay for the full path and hop-by-hop
round-trip delay on the network?
A. HTTP
B. ICMP path echo
C. TCP connect
D. ICMP echo
Answer:B
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
The ICMP Path Echo operation computes hop-by-hop response time between a Cisco router and any IP device on the network.
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/technologies/tk648/tk362/tk920/technologies_white_paper09186a00802d5efe.html
Question 20
In which form does PAP authentication send the username and password across the link?
A. Encrypted
B. Password protected
C. Clear text
D. Hashed
Answer:C
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
PAP (Password Authentication Protocol)
In this protocol, password is sent in clear text format that makes it less secure in comparison with CHAP.
http://www.computernetworkingnotes.com/ccna-study-guide/ppp-protocol-and-encapsulation-method-explained.html
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 9
Question 21
What is the administrative distance for EBGP?
A. 200
B. 30
C. 70
D. 20
Answer:D
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/border-gateway-protocol-bgp/15986-admin-distance.html
Question 22
Considering the IPv6 address independence requirements, which process do you avoid when you use
NPTv6 for translation?
A. rewriting of higher layer information
B. checksum verification
C. ipv6 duplication and conservation
D. IPSEC AH header modification
Answer:A
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
The IPv6-to-IPv6 Network Prefix Translation (NPTv6) serves as a useful mechanism for implementing address independence in an IPv6 environment. A
major benefit associated with NPTv6 is the fact that it avoids the requirement for an NPTv6 Translator to rewrite the transport layer headers
which reduces the load on network devices.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/ipaddr_nat/configuration/xe-16/nat-xe-16-book/iadnat-asr1k-nptv6.html
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 10
Question 23
What is the optimal location from which to execute a debug command that produces an excessive
amount of information?
A. Vty lines
B. SNMP commands
C. A console port
D. An AUX port
Answer:A
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/dial-access/integrated-services-digital-networks-isdn-channel-associated-signaling-cas/10374-
debug.html
Question 24
A network engineer is configuring the router for NetFlow data exporting. What is required in order
for NDE to begin exporting data?
A. Source
B. Flow mask
C. Destination
D. Interface type
E. Traffic type
F. NetFlow version
Answer:C
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
NetFlow Multiple Export Destinations—To configure redundant NDE data streams, which improves the
probability of receiving complete NetFlow data, you can enter the ip flow-export destination command
twice and configure a different destination IP address in each command. Configuring two destinations
increases the RP CPU utilization, as you are exporting the data records twice.
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/Test/dwerblo/broken_guide/nde.html#wp1139278
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 11
Question 25
Refer to the exhibit.
Router 1 cannot ping router 2 via the Frame Relay between them. Which two statements describe
the problems? (Chooses two.)
A. Encapsulation is mismatched.
B. Frame Relay map is configured.
C. DLCI is active.
D. DLCI is inactive or deleted.
E. An access list is needed to allow ping.
Answer:A,D
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
Frame Relay: Cannot ping Remote Router :
1-Encapsulation mismatch has occurred.
2-DLCI is inactive or has been deleted.
3-DLCI is assigned to the wrong subinterface.
4-An access list was misconfigured.
5-The frame-relay map command is missing.
6-No broadcast keyword is found in frame-relay map statements.
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/internetworking/troubleshooting/guide/tr1918.html
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 12
Question 26
An engineer is using a network sniffer to troubleshoot DHCPv6 between a router and hosts on the
LAN with the following configuration:
Interface Ethernet0
Ipv6 dhcp server DHCPSERVERPOOL rapid-commit
!
Which two DHCPv6 messages will appear in the snifer logs?
A. reply
B. request
C. advertise
D. acknowledge
E. solicit
F. accept
Answer:A,E
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
he Rapid Commit option is used to indicate the use of the two-
message exchange for address assignment. The code for the Rapid
Commit option is 80. The format of the option is:
Code Len
+-----+-----+
| 80 | 0 |
+-----+-----+
A client MUST include this option in a DHCPDISCOVER message if the
client is prepared to perform the DHCPDISCOVER-DHCPACK message
exchange described earlier.
A server MUST include this option in a DHCPACK message sent in a
response to a DHCPDISCOVER message when completing the DHCPDISCOVER-
DHCPACK message exchange.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/ios-nx-os-software/enterprise-ipv6-solution/whitepaper_c11-689821.html
Question 27
At which layer does Cisco Express Forwarding use adjacency tables to populate addressing
information?
A. Layer4
B. Layer 2
C. Layer 1
D. Layer 3
Answer:B
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
Adjacency table - Nodes in the network are said to be adjacent if they can reach each other with a single hop across a link layer. In addition to the FIB,
CEF uses adjacency tables to prepend Layer 2 addressing information. The adjacency table maintains Layer 2 next-hop addresses for all FIB entries
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/routers/12000-series-routers/47321-ciscoef.html
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 13
Question 28
A network engineer wants to ensure an optimal end-to-end delay bandwidth product. The delay is
less than 64 KB. Which TCP feature ensures steady state throughput?
A. Window scaling
B. Network buffers
C. Round-trip timers
D. TCP acknowledgments
Answer:A
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
options can be carried in a TCP header. Those relevant to TCP performance include
Window-scale option : This option is intended to address the issue of the maximum window size in the face of paths that exhibit a high-delay bandwidth
product. This option allows the window size advertisement to be right-shifted by the amount specified (in binary arithmetic, a right-shift corresponds to a
multiplication by 2). Without this option, the maximum window size that can be advertised is 65,535 bytes (the maximum value obtainable in a 16-bit field).
The limit of TCP transfer speed is effectively one window size in transit between the sender and the receiver. For high-speed, long-delay networks, this
performance limitation is a significant factor, because it limits the transfer rate to at most 65,535 bytes per round-trip interval, regardless of available
network capacity. Use of the window-scale option allows the TCP sender to effectively adapt to high-band-width, high-delay network paths, by allowing
more data to be held in flight. The maximum window size with this option
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/about/press/internet-protocol-journal/back-issues/table-contents-5/ipj-archive/article09186a00800c8417.html
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 14
Question 29
Drag and drop the challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol steps from the left into the
correct order in which they occur on the right.
The peer responds with a value calculated through a
one-way hash function (MD5) target 1
The authenticator checks the response against its own
calculation of the expected hash value if the values
match the authentication is successful . otherwise ,
the connection is terminated
target 2
when the LCP phase is complete and CHAP is
negotiated between both devices,the authenticator target 3
sends a challenge message to the peer
Answer:
when the LCP phase is complete and CHAP is
negotiated between both devices,the authenticator
sends a challenge message to the peer
The peer responds with a value calculated through
a one-way hash function (MD5)
The authenticator checks the response against its
own calculation of the expected hash value if the
values match the authentication is successful .
otherwise , the connection is terminated
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
The Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) (defined in RFC 1994 leavingcisco.com) verifies the identity of the peer by means of a three-
way handshake. These are the general steps performed in CHAP:
1-After the LCP (Link Control Protocol) phase is complete, and CHAP is negotiated between both devices, the authenticator sends a challenge
message to the peer.
2-The peer responds with a value calculated through a one-way hash function (Message Digest 5 (MD5)).
3-The authenticator checks the response against its own calculation of the expected hash value. If the values match, the authentication is
successful. Otherwise, the connection is terminated.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/wan/point-to-point-protocol-ppp/25647-understanding-ppp-chap.html
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 15
Question 30
A network administrator creates a static route that points directly to a multi-access interface, instead
of the next-hop IP address. The administrator notices that Cisco Express Forwarding ARP requests are
being sent to all destinations. Which issue might this configuration create?
A. Low bandwidth usage
B. High memory usage
C. Cisco Express Forwarding routing loop
D. High bandwidth usage
E. IP route interference
Answer:C
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
If the serial connection fails between R2 and R4,
all traffic is routed with the use of a floating static route out Ethernet 0/0 because R2 has a floating static route that points to the multi-access interface
Ethernet 0/0,
and not to the Ethernet IP address 192.168.12.1 of R1. Therefore, for all unknown destinations, Router R2 sends out an ARP request through the
Ethernet0/0 interface.
In this case, R2 has lost the more specific route to the 10.10.34.0 network. Therefore, when the data packet arrives for the hosts on this network,
it generates an ARP request via the Ethernet interface. Since Proxy ARP is enabled by default on R1's Ethernet interface and it has a default route that
points to R3,
it responds back with an Proxy ARP reply with its own MAC address. Hence, R2 sends all traffic to R1, and R1 forwards all traffic with the use of its
default route (0.0.0.0/0) out to AS 12,
and consequently to 10.10.34.4 via the Internet.
When R2 receives the proxy ARP reply from R1, it creates a /32 valid Cisco Express Forwarding adjacency that points out interface Ethernet 0/0.
This Cisco Express Forwarding entry does not age out until the proxy ARP router R1 is present on the Ethernet segment.
Thus, the /32 Cisco Express Forwarding entry continues to be used to Cisco Express Forwarding-switch the packets,
even after the serial connection between R2 and R4 is back up and the routing table default route points out Serial 8/0 towards AS 10. The result is a
routing loop.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/express-forwarding-cef/26083-trouble-cef.html
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 16
Question 31
Refer to Exhibit
Refer to the exhibit showing complete command output. What type of OSPF router is Router A?
A. internal router
B. ASBR
C. ABR
D. edge router
Answer:C
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
An area is interface specific. A router that has all of its interfaces within the same area is called an internal router (IR). A router that has interfaces in
multiple areas is called an area border router (ABR).
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/open-shortest-path-first-ospf/7039-1.html#t8
Question 32
How should a router that is being used in a Frame Relay network be configured to keep split horizon
issues from preventing routing updates?
A. Configure a separate subinterface for each PVC with a unique DLCI and subnet assigned to the
subinterface.
B. Configure each Frame Relay circuit as a point-to-point line to support multicast and broadcast traffic.
C. Configure many subinterfaces in the same subnet.
D. Configure a single subinterface to establish multiple PVC connections to multiple remote router interfaces.
Answer:A
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
If you have a serial port configured with multiple DLCIs connected to multiple remote sites, split horizon rules, stop route updates received on an interface
from being sent out the same interface. By creating subinterfaces for each PVC, you can avoid the split horizon issues when using Frame Relay.
http://www.indiabix.com/networking/wide-area-networks/015004
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 17
Question 33
Which mode of uRPF causes a router interface to accept a packet, if the network to which
the packet’s source IP address belongs is found in the router’s FIB?
A. Strict mode
B. Loose mode
C. Auto mode
D. Desirable mode
Answer:B
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
A number of common types of DoS attacks take advantage of forged or rapidly changing source IP addresses, allowing attackers to thwart efforts by ISPs
to locate or filter these attacks. Unicast RPF was originally created to help mitigate such attacks by providing an automated, scalable mechanism to
implement the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Best Common Practices 38/Request for Comments 2827 (BCP 38/RFC 2827) anti-spoofing
filtering on the customer-to-ISP network edge. By taking advantage of the information stored in the Forwarding Information Base (FIB) that is
created by the CEF switching process, Unicast RPF can determine whether IP packets are spoofed or malformed by matching the IP source address
and ingress interface against the FIB entry that reaches ―back‖ to this source (a so-called ―reverse lookup‖). Packets that are received from one of the
best reverse path routes back out of the same interface are forwarded as normal. If there is no reverse path route on the same interface from which the
packet was received, it might mean that the source address was modified, and the packet is dropped (by default).
.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/sec_data_urpf/configuration/xe-3s/sec-data-urpf-xe-3s-book/sec-unicast-rpf-loose-
mode.html?referring_site=RE&pos=1&page=http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios/12_0s/feature/guide/srpf_gsr.html#GUID-FFFA94D5-
EEFB-4215-9EE1-DB37CD01C2CA
Question 34
Which of the following are characteristics of TACACS+? (Choose two.)
A. Uses UDP
B. Encrypts an entire packet
C. Offers robust accounting
D. Cisco-proprietary
Answer:B,D
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
CHARACTERISTICS O TACACS+
1-TACACS+ encrypts the entire body of the packet
2- TACACS+ uses TCP
3-TACACS+ uses the AAA architecture, which separates AAA
4-TACACS+ offers multiprotocol support.
5-TACACS+ is Cisco proprietary protocol
6-TACACS+ is a heavy-weight protocol consuming more resources
7-TACACS+ uses TCP port 49
8-Mainly used for Device Administration
9-TACACS+ supports 15 privilege levels
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/security-vpn/remote-authentication-dial-user-service-radius/13838-10.html7
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 18
Question 35
Which two options are causes of out-of-order packets? (Choose two.)
A. a routing loop
B. a router in the packet flow path that is intermittently dropping packets
C. high latency
D. packets in a flow traversing multiple paths through the network.
E. some packets in a flow being process-switched and others being interrupt-switched on a
transit Router.
Answer:D,E
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
In traditional packet forwarding systems, using different paths have varying latencies that cause out of
order packets, eventually resulting in far lower performance for the network application. Also, if some
packets are process switched quickly by the routing engine of the router while others are interrupt
switched (which takes more time) then it could result in out of order packets. The other options would
cause packet drops or latency, but not out of order packets.
Question 36
Your company uses Voice over IP (VoIP). The system sends UDP datagrams containing the
voice data between communicating hosts. When areas of the network become busy, some
of the datagrams arrive at their destination out of order. What happens when this occurs?
A. UDP will send an ICMP Information request message to the source host.
B. UDP will pass the information in the datagrams up to the next OSI layer in the order in
which they arrive.
C. UDP will drop the datagrams that arrive out of order.
D. UDP will use the sequence numbers in the datagram headers to reassemble the data into
the
Answer:B
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 19
Question 37
Which alerts will be seen on the console when running the command: logging console warnings.?
A. warnings only
B. warnings, notifications, error, debugging, informational
C. warnings, errors, critical, alerts, emergencies
D. notifications, warnings, errors
E. warnings, errors, critical, alerts
Answer:C
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
The Message Logging is divided into 8 levels as listed below
The highest level is level 0 (emergencies). The lowest level is level 7. If you specify a level with the ―logging console level‖ command, that level and all the
higher levels will be displayed. For example, by using the ―logging console warnings‖ command, all the logging of emergencies, alerts, critical, errors,
warnings will be displayed
http://www.networktut.com/?s=commands+used
Question 38
Which IP SLA operation requires Cisco endpoints?
A. UDP Jitter for VoIP
B. ICMP Path Echo
C. ICMP Echo
D. UDP Jitter
Answer:A
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
UDP Jitter Operation
With the addition of real-time traffic (ie: VoIP), the focus shifts not just in the reliability of the network, but also on the delays involved in transmitting the
data. Real-time traffic is delay sensitive. For Voice data, packet loss is manageable to some extent, but frequent losses impair communication between
endpoints. The UDP jitter operation is the most popular operation because the user can obtain packet loss, jitter and latency from one operation. This also
includes unidirectional measurements as well.
The Jitter operation is designed to measure the delay, delay variance and packet loss in IP networks by generating active UDP traffic. It sends N packets,
each of size S, from source router to a target router (which requires Cisco IOS IP SLAs responder enabled) each T milliseconds apart. All these
parameters are user configurable.
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/technologies/tk648/tk362/tk920/technologies_white_paper09186a00802d5efe.html
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 20
Question 39
Which two functionalities are specific to stateless NAT64? (Choose two.)
A. No requirement exists for the characteristics of Ipv6 address assignment
B. It does not conserve Ipv4 addresses
C. It provides 1-to-1 translation.
D. It uses address overloading.
E. State or bindings are created on the translation.
Answer: B,C
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/ios-nx-os-software/enterprise-ipv6-solution/white_paper_c11-676277.html
Question 40
Meaning of priority 0 configured in ospf router?
Answer:
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
If needed, you can set the priority value to 0 in order to configure a router to never become a DR/BDR.
This is necessary in hub and spoke networks where the hub should be configured to become the DR,
where as the spokes should neither be DR nor BDR.
Question 41
What following parameters for the EIGRP authentication need to match in order for EIGRP neighbors to
establish a neighbor
relationship?
A. Autonomous System number.
B. K-Values
C. If authentication is used both: the key number, the password, and the date/time.
D. The neighbors must be on common subnet (all IGPs follow this rule).
Answer:C
EXPLANATION/REFRENCE
DEVELOPED BY : TAGWA - TAGELSIR Page 21
You might also like
- Data Center Facility StandardDocument8 pagesData Center Facility Standardtevfikuret100% (1)
- Plumbing Learning ModuleDocument131 pagesPlumbing Learning ModuleCharlotte's Web86% (14)
- CCNP Ccie 300 410 Enarsi DigitalTUT New-Q PDFDocument14 pagesCCNP Ccie 300 410 Enarsi DigitalTUT New-Q PDFCristihan RenteriaNo ratings yet
- DigitalTut - New ENCOR QuestionsDocument30 pagesDigitalTut - New ENCOR QuestionsNilNirjoneNo ratings yet
- CCNA Revision PDFDocument34 pagesCCNA Revision PDFSaint ChinozNo ratings yet
- CCNP Ccie 350 401 New 29 Jun 2020Document101 pagesCCNP Ccie 350 401 New 29 Jun 2020Aly Abdelhamed88% (8)
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Housing Typology 2Document16 pagesLecture 8 Housing Typology 2Kranthi Kumar Chowdary Manam0% (1)
- CCNA Questions July 2019Document294 pagesCCNA Questions July 2019Emmanuel Teixeira de SousaNo ratings yet
- Suspension Bridge - Lecture and Problems HSDocument7 pagesSuspension Bridge - Lecture and Problems HSMervin BocatcatNo ratings yet
- CCNP Route 300-101 Dump by Alozie CharlesDocument101 pagesCCNP Route 300-101 Dump by Alozie CharlesKAy Cee100% (4)
- CCNP Ccie 350 401 Encor Digitaltut 30 10 2020Document131 pagesCCNP Ccie 350 401 Encor Digitaltut 30 10 2020Pak ChannNo ratings yet
- Objects in Context: Theorizing Material CultureDocument174 pagesObjects in Context: Theorizing Material CultureReActivatingObjects100% (3)
- HCIA Datacom Exam 50 Q & Answers + ExplainationDocument42 pagesHCIA Datacom Exam 50 Q & Answers + ExplainationMohamed ElsadanyNo ratings yet
- Cisco 300-410 v2022-04-01 q84Document64 pagesCisco 300-410 v2022-04-01 q84beloow beloowNo ratings yet
- Cisco ActualTests 300-101 v2016-06-22 by Mangary 127qDocument149 pagesCisco ActualTests 300-101 v2016-06-22 by Mangary 127qGabriela PopescuNo ratings yet
- 300 101Document119 pages300 101chetan666123No ratings yet
- Cisco Route Exam TrialDocument88 pagesCisco Route Exam TrialkofiNo ratings yet
- 300-410 15 Q&AsDocument15 pages300-410 15 Q&AsmshafiNo ratings yet
- ENCOR July 2020 v2Document95 pagesENCOR July 2020 v2Himawan Widjonarko100% (1)
- ENCOR July 2020Document82 pagesENCOR July 2020SyedNo ratings yet
- Cisco Real-Exams 300-101 v2019-03-23 by Barbra 469qDocument243 pagesCisco Real-Exams 300-101 v2019-03-23 by Barbra 469qJorge ArmasNo ratings yet
- CCNP Routing TutorialDocument46 pagesCCNP Routing TutorialGossan AnicetNo ratings yet
- PArt 5+6 - QDocument36 pagesPArt 5+6 - Qalecs.jonNo ratings yet
- 300 101.examcollection - Premium.exam.149qDocument128 pages300 101.examcollection - Premium.exam.149qjustanotherrandomdudeNo ratings yet
- CCNP RouteDocument326 pagesCCNP RouteJoão MunizNo ratings yet
- Exam: 642-801 Titl E: Building Scalable Cisco Internetworks (BSCI) Ver: 03-22-05Document59 pagesExam: 642-801 Titl E: Building Scalable Cisco Internetworks (BSCI) Ver: 03-22-05Ariel H. CochiaNo ratings yet
- B. Identity Service Engine: AnswerDocument35 pagesB. Identity Service Engine: AnswernoerxNo ratings yet
- Cisco 300-101Document181 pagesCisco 300-101sanjinZNo ratings yet
- Route - 300-101 TQDocument320 pagesRoute - 300-101 TQNguyen Anh0% (1)
- 350 401.v2022 02 14.q176Document101 pages350 401.v2022 02 14.q176Abebe BelachewNo ratings yet
- 300-101.examcollection - Premium.exam.149q: 300-101 Implementing Cisco IP RoutingDocument41 pages300-101.examcollection - Premium.exam.149q: 300-101 Implementing Cisco IP RoutingGabriela PopescuNo ratings yet
- 300 101 CCNP Route PADocument483 pages300 101 CCNP Route PASisir KarmakerNo ratings yet
- New Multiple Choice Questions CCNP TSHOOTDocument15 pagesNew Multiple Choice Questions CCNP TSHOOTJulio Edison EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Vendor: Exam Code: Exam Name:: Cisco 300-101 Implementing Cisco IP Routing DemoDocument18 pagesVendor: Exam Code: Exam Name:: Cisco 300-101 Implementing Cisco IP Routing Demofredf1No ratings yet
- CCNP (300 101) 2019.02.26 320Qs PDFDocument122 pagesCCNP (300 101) 2019.02.26 320Qs PDFjackNo ratings yet
- Cisco Examcollection Premium 300-101 v2015-11-18 Kaltzone 116q PDFDocument192 pagesCisco Examcollection Premium 300-101 v2015-11-18 Kaltzone 116q PDFleotrimNo ratings yet
- 350 001 V4Document231 pages350 001 V4ryanshin10No ratings yet
- CCNAquestions July 2019 PDFDocument294 pagesCCNAquestions July 2019 PDFAlbertoNo ratings yet
- Answer: Which of The Following Are True Regarding Passwords On A Cisco Router?Document37 pagesAnswer: Which of The Following Are True Regarding Passwords On A Cisco Router?dijeshkelothNo ratings yet
- CCNAquestions Oct 2019 PDFDocument337 pagesCCNAquestions Oct 2019 PDFMuzafarNo ratings yet
- Latest Version - CCNP Route - 300-101 - Version 2018 - 91q - Prince-V1 PDFDocument33 pagesLatest Version - CCNP Route - 300-101 - Version 2018 - 91q - Prince-V1 PDFtho anhNo ratings yet
- Ccna TestDocument24 pagesCcna TestArt CamposNo ratings yet
- 300 101 Project X Digital Tut CERTbus PassLeader Updated by Dexter v1.8 15.12.2017Document248 pages300 101 Project X Digital Tut CERTbus PassLeader Updated by Dexter v1.8 15.12.2017AyoubBelNo ratings yet
- 01 Encore 350-401-Newq - HasDocument10 pages01 Encore 350-401-Newq - HasTak Man PONo ratings yet
- 640 802parte1Document133 pages640 802parte1adrianaNo ratings yet
- HCIA-Routing 0 Switching V2.5 Mock ExamDocument5 pagesHCIA-Routing 0 Switching V2.5 Mock Exammark jayNo ratings yet
- Đề Thi Trắc Nghiệm CCNA FullDocument90 pagesĐề Thi Trắc Nghiệm CCNA FullTieu Ngoc LyNo ratings yet
- Route Sep 2015Document45 pagesRoute Sep 2015Pobu PopoNo ratings yet
- CCNA Practice Certification Exam 2Document11 pagesCCNA Practice Certification Exam 2Gabriel GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Route Oct 2019Document445 pagesRoute Oct 2019Alex AndruNo ratings yet
- Examen 1 - 110pDocument56 pagesExamen 1 - 110ptelecomnasaNo ratings yet
- New Questions (Added On 30th-Jan-2021)Document25 pagesNew Questions (Added On 30th-Jan-2021)Hoai Duc HoangNo ratings yet
- MtcnaDocument5 pagesMtcnaj7tNo ratings yet
- Hillstone All Series Device Troubleshooting and Debug GuideDocument134 pagesHillstone All Series Device Troubleshooting and Debug GuideWAMS FILE100% (1)
- Jazzy Dumps V3 PDFDocument81 pagesJazzy Dumps V3 PDFAquadigNo ratings yet
- MCnew 2Document8 pagesMCnew 2Harvey EguilosNo ratings yet
- Hp0-Y12 Building Procurve Resilient, Adaptive NetworksDocument28 pagesHp0-Y12 Building Procurve Resilient, Adaptive NetworksMCP MarkNo ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument13 pagesFinal Examcristiaan_schipper_147263100% (5)
- How To Use PrepKingDocument429 pagesHow To Use PrepKingYoppi LisyadiNo ratings yet
- Structure of A Flask Project - Just LeptureDocument6 pagesStructure of A Flask Project - Just LeptureVenkata Vignesh RamNo ratings yet
- Various Communication Protocol A Comparative StudyDocument47 pagesVarious Communication Protocol A Comparative StudykailasamvvNo ratings yet
- As 2665-2001 Smoke Heat Venting Systems - Design Installation and CommissioningDocument8 pagesAs 2665-2001 Smoke Heat Venting Systems - Design Installation and CommissioningSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- H8 ManualDocument905 pagesH8 Manualapi-19479717No ratings yet
- sg2 User Manual (v04) PDFDocument267 pagessg2 User Manual (v04) PDFPedriosinho changomanNo ratings yet
- Anup Gupta: Email: Anupgupta@aol - in Contact No: - 91-9922945958Document3 pagesAnup Gupta: Email: Anupgupta@aol - in Contact No: - 91-9922945958Abhijit DuttaNo ratings yet
- Oracle Database 11g and 12c On IBM Power Systems Built With IBM POWER8 Processor TechnologyDocument16 pagesOracle Database 11g and 12c On IBM Power Systems Built With IBM POWER8 Processor TechnologyFélix David Mejía MejíaNo ratings yet
- Suruttappalli Shiva TempleDocument2 pagesSuruttappalli Shiva TempleNamasivayam MuthuthevarNo ratings yet
- Cisco Sge300Document1,053 pagesCisco Sge300Adeyvison SousaNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet GPDocument4 pagesTechnical Data Sheet GPdox4printNo ratings yet
- SdadsadasDocument3 pagesSdadsadasTwink Arcane 9No ratings yet
- Noises and CausesDocument16 pagesNoises and CausesAr Varun VermaNo ratings yet
- Smart Series Manual 02 SX 2000 90kWDocument348 pagesSmart Series Manual 02 SX 2000 90kWLalji Lunagariya0% (2)
- CEM PT HandbookDocument44 pagesCEM PT Handbook翹翹九九100% (2)
- Bridge Engineering MODULE 3Document9 pagesBridge Engineering MODULE 3Tantamco Joseph P.No ratings yet
- Timeline of ConcreteDocument6 pagesTimeline of Concretesmishra2222No ratings yet
- Solar ChimneysDocument30 pagesSolar ChimneysChandan KumarNo ratings yet
- Auditorium & Roof - PRSS 2020 Upd PDFDocument79 pagesAuditorium & Roof - PRSS 2020 Upd PDFSithesh RNo ratings yet
- Exposed Aggregate ConcreteDocument11 pagesExposed Aggregate ConcreteExposed Aggregate Concrete MelbourneNo ratings yet
- Freeradius On Debian 7Document4 pagesFreeradius On Debian 7Ahmad SofyanNo ratings yet
- VI in T24Document2 pagesVI in T24sureshNo ratings yet
- Brick Masonary - WatermarkDocument26 pagesBrick Masonary - WatermarkSohel PashaNo ratings yet
- Add 2 HSL Atm - Omd1 BSCDocument2 pagesAdd 2 HSL Atm - Omd1 BSCLaithAl-abbadiNo ratings yet
- Appendix DDocument14 pagesAppendix D蓉蓉No ratings yet
- Characterization of Eco-Efficient Acoustic Insulation MaterialsDocument8 pagesCharacterization of Eco-Efficient Acoustic Insulation MaterialsFloreaNo ratings yet