Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1
Uploaded by
dsureshcivilOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Uploaded by
dsureshcivilCopyright:
Available Formats
17
In contrast to the old model, in which dose is averaged over the bone. the currant model
contains separate calculations of the dose equivalent to the active haematopoietic tissue within the
cavities of trabccular bone, and to osteogenic c&s, in particular those on the endoatcal surfaces of
bone.
Developing blood cells are found in various stages of maturation within the rod marrow, which
is therefore of concern with rcspcct to the radiation induction of leukemia. The need to limit the
dose to this tissue was rccogniscd in Publication 2, but was not explicitly addressed in developing
the recommendations for bone-seeking radionuclidcs.
The osteogenic cells are the precursors of cells involved in the formation of new bone
(ostcoblasts) and in the resorption of bone (osteoclasts), and arc of concern with rcspcct to
carcinogenisis in bone. The location of the osteogenic cells in the skeleton is not well dcfincd; for
the purpose of calculating the dtrivcd guides. the average dose cquivaknt is determined over a
IO pm thick layer of soft tissue adjacent to the surface of the bone. The following discussion is
limitcd to the example of particulate (alpha and beta) irradiation of et&steal tissues.
Energy deposition in endosteal tissues is averaged over a layer of cells near the bone surfacer,
the mass m of which is taken to bc 120 g. We distinguish bctwccn radionuclidcs that r&de on
bone surfaces and those that are distributed throughout the bone volume. The specific effective
energy for endosteal tissue from a radionuclidc distributed uniformly on bone surface may be
expressed as
SEES(BS-Bone) - [F?CB) AF?BS-CB)+ F?TB) AfiBS-TB) ]Q E/ m , (13
where
E is the energy emitted per disintegration;
Fs(CB) and Fa(TB) denote the fractions of activity in the skeleton residing on the surfacer
(‘) of cortical bone (CB) and trabccular bone (TB), and Fa(CB) + Fs(TB) - 1.
Cortical and trabccular bone are defined as bone with a surface/volume ratio lus than
and greater than 60 cm2 cm-‘, respectively.
AFa(BS - CB) and AmBS - TB) are the fractions of the energy emitted from the
surfaces of cortical and trabccular bone that are absorbed by the endoateal tiuue at the
bone surface (BS). AfiBS - CB) is normally smaller than AFa(BS - TB) bccausc of
the greater absorption of radiation by the bone itself.
A corresponding equation can be written for SEEV(BS - Bone) for radionuclidcs that dcpoait
within bone volume (“); F”(CB) would then be the fraction of activity that is dispersal evenly
throughout cortical bone, and so on.
Values of parameters for the above formulation arc contained in ICRP 30 (see Chapter 5 of
ICRP 1979a). The quality factor Q for alpha radiation is taken to be 20, rather than IO as in
ICRP 2, and the ‘relative damage factor’ n is no longer used.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- 3Document1 page3dsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Absorption and Lung Clearance ClassesDocument1 pageGastrointestinal Absorption and Lung Clearance ClassesdsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1dsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2dsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1dsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- Iii. Changes in The Models For Derived Guides: SolubleDocument1 pageIii. Changes in The Models For Derived Guides: SolubledsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1dsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1dsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- Output 1 11 PDFDocument1 pageOutput 1 11 PDFdsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- Output 1 8 PDFDocument1 pageOutput 1 8 PDFdsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- Output 1 9 PDFDocument1 pageOutput 1 9 PDFdsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- Output 1 12Document1 pageOutput 1 12dsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1dsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1dsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- Output 1 11Document1 pageOutput 1 11dsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- BT Fkext: Tissue Dose Cquivcalcnt Conversion Factor, E//cctive Dose Equivalent Conversion FactorDocument1 pageBT Fkext: Tissue Dose Cquivcalcnt Conversion Factor, E//cctive Dose Equivalent Conversion FactordsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- Output 1 12Document1 pageOutput 1 12dsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- Output 1 10Document1 pageOutput 1 10dsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- Output 1 8Document1 pageOutput 1 8dsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- Output 1 10Document1 pageOutput 1 10dsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- Output 1 9 PDFDocument1 pageOutput 1 9 PDFdsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- Control of Cracking Due To End Restraint: Input Parameters Symbol Unit ValueDocument1 pageControl of Cracking Due To End Restraint: Input Parameters Symbol Unit ValuedsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- Control of Cracking Due To End Restraint: Input Parameters Symbol Unit ValueDocument1 pageControl of Cracking Due To End Restraint: Input Parameters Symbol Unit ValuedsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- Eatc-3-Crack - 2Document1 pageEatc-3-Crack - 2dsureshcivil100% (1)
- Risk and Control of Cracking Due To Continuous Edge RestraintDocument1 pageRisk and Control of Cracking Due To Continuous Edge RestraintdsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- Risk and Control of Cracking Due To Continuous Edge RestraintDocument1 pageRisk and Control of Cracking Due To Continuous Edge RestraintdsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- Output 1 7Document1 pageOutput 1 7dsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- H Aoj Uuywq JkabjkfDocument6 pagesH Aoj Uuywq JkabjkfdsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- Do Oho B JBF PDFDocument1 pageDo Oho B JBF PDFdsureshcivilNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- 2019 MakeX Courageous Traveler Techinical Guide V1.1Document66 pages2019 MakeX Courageous Traveler Techinical Guide V1.1Yair XolalpaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - EU Institutions and Comparative Political System - 2023springDocument10 pagesSyllabus - EU Institutions and Comparative Political System - 2023springreif annieNo ratings yet
- Phy 111 - Eos Exam 2015Document7 pagesPhy 111 - Eos Exam 2015caphus mazengeraNo ratings yet
- SIGA Monitoring ToolDocument3 pagesSIGA Monitoring ToolMhalou Jocson EchanoNo ratings yet
- Substation Automation HandbookDocument454 pagesSubstation Automation HandbookGiancarloEle100% (6)
- PTE - Template - Essay All TypesDocument8 pagesPTE - Template - Essay All TypeskajalNo ratings yet
- 18.443 MIT Stats CourseDocument139 pages18.443 MIT Stats CourseAditya JainNo ratings yet
- Socrates 8dDocument8 pagesSocrates 8dcarolinaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Ebook Ebook PDF Oracle 12c SQL 3rd Edition by Joan Casteel PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Ebook Ebook PDF Oracle 12c SQL 3rd Edition by Joan Casteel PDFdaniel.morones654100% (35)
- Xerox University Microfilms: 300 North Zeeb Road Ann Arbor, Michigan 48106Document427 pagesXerox University Microfilms: 300 North Zeeb Road Ann Arbor, Michigan 48106Muhammad Haris Khan KhattakNo ratings yet
- Physical Fitness Test Score CardDocument4 pagesPhysical Fitness Test Score CardChing DialomaNo ratings yet
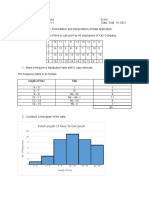
- Cedrix James Estoquia - OLLC Lesson 4.6 Presentation and Interpretation of Data ApplicationDocument4 pagesCedrix James Estoquia - OLLC Lesson 4.6 Presentation and Interpretation of Data ApplicationDeuK WR100% (1)
- Guardian Brand Book - 042019Document15 pagesGuardian Brand Book - 042019FTU.CS2 Nguyễn Việt HưngNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Synopsis & Dissertation-DefenseDocument10 pagesGuidelines For Synopsis & Dissertation-DefenseRajni KumariNo ratings yet
- A Phenomenological Research Design IllustratedDocument15 pagesA Phenomenological Research Design IllustratedMATEI100% (1)
- PR1 Module 2Document12 pagesPR1 Module 2Ervin GonzalesNo ratings yet
- ABB Softstarters, Type PSR, PSS, PST/PSTBDocument50 pagesABB Softstarters, Type PSR, PSS, PST/PSTBElias100% (1)
- John Constantine Rouge Loner Primordial Orphan Paranormal DetectiveDocument4 pagesJohn Constantine Rouge Loner Primordial Orphan Paranormal DetectiveMirko PrćićNo ratings yet
- Sistem Informasi Geografis Pemetaan Lahan PertaniaDocument12 pagesSistem Informasi Geografis Pemetaan Lahan PertaniaRizal Nurrahman HabibNo ratings yet
- DLL in Science 5 Q1 W1Document3 pagesDLL in Science 5 Q1 W1Rhinalyn Andaya Barberan100% (2)
- Work Text INGE09: Understanding The SelfDocument24 pagesWork Text INGE09: Understanding The SelfFrancis Dave MabborangNo ratings yet
- Modular Kitchen AnalysisDocument3 pagesModular Kitchen AnalysisGhanithan SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Dream Drills for High Hardened SteelDocument8 pagesDream Drills for High Hardened SteelPuneeth KumarNo ratings yet
- Time May Not Exist - Tim Folger in DiscoverDocument3 pagesTime May Not Exist - Tim Folger in DiscoverTrevor Allen100% (5)
- Autodesk Revit 2014 ContentDocument6 pagesAutodesk Revit 2014 ContentGatot HardiyantoNo ratings yet
- A Minimal Core Calculus For Java and GJDocument15 pagesA Minimal Core Calculus For Java and GJpostscriptNo ratings yet
- PROPOSED ARFF BUILDINGDocument27 pagesPROPOSED ARFF BUILDINGDale Bryan S DalmacioNo ratings yet
- The School and The Community: Prepared By: Sen Xiao Jun Mohana Sundra Segaran Kaviyanayagi PonuduraiDocument26 pagesThe School and The Community: Prepared By: Sen Xiao Jun Mohana Sundra Segaran Kaviyanayagi PonuduraiKaviya SKTDSNo ratings yet
- Fif-12 Om Eng Eaj23x102Document13 pagesFif-12 Om Eng Eaj23x102Schefer FabianNo ratings yet
- 8D Form - LongDocument6 pages8D Form - LongmaofireNo ratings yet