Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Porter's Five Forces of Competitive Position: New Market Entrants, Eg
Uploaded by
Nasir Bashir0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageOriginal Title
portersfiveforcesdiagram
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pagePorter's Five Forces of Competitive Position: New Market Entrants, Eg
Uploaded by
Nasir BashirCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
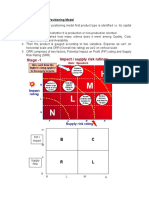
Porter’s Five Forces of
Competitive Position New Market Entrants, eg:
entry ease/barriers
geographical factors
incumbents resistance
new entrant strategy
routes to market
Supplier Power, eg: Competitive Rivalry, eg: Buyer Power, eg:
brand reputation number and size of firms buyer choice
geographical coverage industry size and trends buyers size/number
product/service level quality fixed v variable cost bases change cost/frequency
relationships with customers product/service ranges product/service importance
bidding processes/capabilities differentiation, strategy volumes, JIT scheduling
Product and Technology
Development, eg:
alternatives price/quality
market distribution changes
fashion and trends
legislative effects
You might also like
- Porter's Five ForcesDocument4 pagesPorter's Five ForcesRahman MashukNo ratings yet
- Porter'sfiveforcesdiagramDocument1 pagePorter'sfiveforcesdiagramapi-3756651No ratings yet
- Porter'SfiveforcesdiagramDocument1 pagePorter'SfiveforcesdiagramArdian SetiadiNo ratings yet
- Porters Five Forces DiagramDocument1 pagePorters Five Forces Diagramyiah100% (2)
- Value Chain Analysis and Five Force AnalysisDocument22 pagesValue Chain Analysis and Five Force Analysisreagan blaireNo ratings yet
- Porter's 5 Force Analysis: Competitive Advantage of Nations - Part of The Environmental Analysis ProcessDocument10 pagesPorter's 5 Force Analysis: Competitive Advantage of Nations - Part of The Environmental Analysis ProcessvibinwalesNo ratings yet
- Porter'S Five Forces:: Force Sample DriversDocument5 pagesPorter'S Five Forces:: Force Sample DriversMd AsaduzzamanNo ratings yet
- Industry Analysis: DR - Debjani BanerjeeDocument13 pagesIndustry Analysis: DR - Debjani BanerjeeSamNo ratings yet
- Porter'SfiveforcesdiagramDocument1 pagePorter'Sfiveforcesdiagramch_suresh1000No ratings yet
- Porter'SfiveforcesdiagramDocument1 pagePorter'Sfiveforcesdiagrambey_dbNo ratings yet
- Identification of Investment OpportunitiesDocument14 pagesIdentification of Investment OpportunitiesMrityunjayChauhanNo ratings yet
- Porter's Five Forces: Understand competitive forces and stay ahead of the competitionFrom EverandPorter's Five Forces: Understand competitive forces and stay ahead of the competitionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Category Factors Political: PESTLE and SWOT AnalysisDocument3 pagesCategory Factors Political: PESTLE and SWOT AnalysisNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Porters Five Forces DiagramDocument1 pagePorters Five Forces DiagramabollatiNo ratings yet
- Porter'SfiveforcesdiagramDocument1 pagePorter'SfiveforcesdiagramGlenda De FreitasNo ratings yet
- Competitve Forces - Cosmetics IndustryDocument6 pagesCompetitve Forces - Cosmetics IndustryShiblee RahmanNo ratings yet
- Me - G - II We - Sawula - (Cor)Document6 pagesMe - G - II We - Sawula - (Cor)Alazer Tesfaye Ersasu TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Porters Five Forces - Content, Application, and CritiqueDocument9 pagesPorters Five Forces - Content, Application, and CritiqueJosé Luís NevesNo ratings yet
- BBP712S 2Document48 pagesBBP712S 2nafisa anjumNo ratings yet
- Porters Five Forces ModelDocument17 pagesPorters Five Forces ModelJerry GayonNo ratings yet
- New Venture DevelopDocument10 pagesNew Venture Developabdul rizaNo ratings yet
- Strat Man Chapter 2 PPTDocument18 pagesStrat Man Chapter 2 PPTRhea Mae CatipayNo ratings yet
- Competitive Structure of IndustriesDocument4 pagesCompetitive Structure of IndustriesPooja SheoranNo ratings yet
- External EnvironmentDocument23 pagesExternal EnvironmentHimanshu SahdevNo ratings yet
- PESTEL FrameworkDocument13 pagesPESTEL FrameworkFatima AliNo ratings yet
- Porter Analysis ReportingDocument5 pagesPorter Analysis ReportingMinini NestNo ratings yet
- External Environment AnalysisDocument23 pagesExternal Environment AnalysisMarc Eric RedondoNo ratings yet
- IUBAV - Lecture 2 - Module 1 and Module 2 Market Structure and Competitive Analysis and Positioning (S2 2023 2024Document15 pagesIUBAV - Lecture 2 - Module 1 and Module 2 Market Structure and Competitive Analysis and Positioning (S2 2023 2024Vũ Trần Nhật ViNo ratings yet
- Porter Five Forces of Nano by RVDocument14 pagesPorter Five Forces of Nano by RVRahul VermaNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report - Strategic ManagementDocument3 pagesNarrative Report - Strategic ManagementFrederick BacangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document27 pagesChapter 3Roseanne YumangNo ratings yet
- External Environment in The Asia Pacific RegionDocument23 pagesExternal Environment in The Asia Pacific RegionFatimah Binte AtiqNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id3192207Document22 pagesSSRN Id3192207DivaNo ratings yet
- Threat of New EntrantsDocument5 pagesThreat of New EntrantsJAY MARK TANONo ratings yet
- Market StructuresDocument27 pagesMarket StructuresRosemarie DiquentoNo ratings yet
- Michelle Morrissey - CHRDocument16 pagesMichelle Morrissey - CHRShell Morrissey100% (1)
- Marketing EnvironmentDocument23 pagesMarketing EnvironmentajayzxNo ratings yet
- PorterDocument5 pagesPorterVijitha VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Porter's Five Forces AnalysisDocument8 pagesPorter's Five Forces AnalysisRoyce WijayaaNo ratings yet
- How Competitive Forces Shape StrategyDocument11 pagesHow Competitive Forces Shape StrategyErwinsyah RusliNo ratings yet
- 4 Porter 5 Force Analysis JainDocument12 pages4 Porter 5 Force Analysis Jainmanohard12No ratings yet
- Business Core PurposeDocument10 pagesBusiness Core PurposeUjjwal GuptaNo ratings yet
- "Five Competitive Forces That Shape StrategyDocument32 pages"Five Competitive Forces That Shape StrategySahrish TahirNo ratings yet
- Jeremiah PorterDocument8 pagesJeremiah PorterB ChuckNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Assiment-04Document3 pagesStrategic Management Assiment-04Amal ChandraNo ratings yet
- Porters 5 Forces AnalysisDocument6 pagesPorters 5 Forces AnalysisRobi MatiNo ratings yet
- Michael Porters Model For Industry and Competitor AnalysisDocument9 pagesMichael Porters Model For Industry and Competitor AnalysisbagumaNo ratings yet
- Industry Life CycleDocument4 pagesIndustry Life CycleTANISHA KUMARI 1912177No ratings yet
- Michael Porter's "Five Forces" ModelDocument8 pagesMichael Porter's "Five Forces" ModelArpan ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- External Environment Analysis: BY Prasad KulkarniDocument15 pagesExternal Environment Analysis: BY Prasad KulkarniPreeti ShettyNo ratings yet
- Five Forces That Shape Industry Competition: Rivalry Among Existing CompetitorsDocument14 pagesFive Forces That Shape Industry Competition: Rivalry Among Existing CompetitorsNISHANT BANKANo ratings yet
- Porters 5 ForcesDocument3 pagesPorters 5 Forcesjabbimuhammed50No ratings yet
- 5 Forces NotesDocument9 pages5 Forces NotesKshitij LalwaniNo ratings yet
- Porter's Five Forces AnalysisDocument6 pagesPorter's Five Forces AnalysisChandni SheikhNo ratings yet
- Porter 5 Forces ModelDocument24 pagesPorter 5 Forces ModelKumen22100% (1)
- Applied Economics Week 2. q2Document4 pagesApplied Economics Week 2. q2Rica ParillaNo ratings yet
- Strategy Related MaterialsDocument76 pagesStrategy Related MaterialsRaman Sharma100% (1)
- Untitled Document-35Document2 pagesUntitled Document-35Yashika KhanNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document14 pagesPresentation 1skratkiniNo ratings yet
- Question No 1 Final SiftedDocument5 pagesQuestion No 1 Final SiftedNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Class Work SheetDocument4 pagesClass Work SheetNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Question 4Document3 pagesQuestion 4Nasir BashirNo ratings yet
- SCM Riphah Finalterm F 2020Document3 pagesSCM Riphah Finalterm F 2020Nasir Bashir0% (1)
- Q2, SAP - 20401 - Nasir - Bashir - SC - Final ExamDocument11 pagesQ2, SAP - 20401 - Nasir - Bashir - SC - Final ExamNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Case Teaching NotesDocument95 pagesCase Teaching NotesRishu SinghNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Workplace Environment That Affect Employee's Performance in Private Hospitals of Hyderabad, PakistanDocument6 pagesThe Impact of Workplace Environment That Affect Employee's Performance in Private Hospitals of Hyderabad, PakistanNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Category Factors Political: PESTLE and SWOT AnalysisDocument3 pagesCategory Factors Political: PESTLE and SWOT AnalysisNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document83 pagesLec 2Nilesh NeemaNo ratings yet
- Exhaustive Question List Final-V1.0Document5 pagesExhaustive Question List Final-V1.0Nasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Chart Title: Joan Alcide 32 16 4 2 E F, G, H H IDocument7 pagesChart Title: Joan Alcide 32 16 4 2 E F, G, H H INasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Final Paper. ARM Group B. MS PMDocument2 pagesFinal Paper. ARM Group B. MS PMNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Category Factors Political: PESTLE and SWOT AnalysisDocument3 pagesCategory Factors Political: PESTLE and SWOT AnalysisNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Workplace Environment That Affect Employee's Performance in Private Hospitals of Hyderabad, PakistanDocument6 pagesThe Impact of Workplace Environment That Affect Employee's Performance in Private Hospitals of Hyderabad, PakistanNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Final Paper. ARM Group B. MS PMDocument2 pagesFinal Paper. ARM Group B. MS PMNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- E396 PDFDocument19 pagesE396 PDFNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- E396 PDFDocument19 pagesE396 PDFNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- ZaraDocument8 pagesZaraNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Final - ARM Assignment - SAP#20401 - Nasir - Bashir - MSPM - Spring 2020, 31 MayDocument29 pagesResearch Paper Final - ARM Assignment - SAP#20401 - Nasir - Bashir - MSPM - Spring 2020, 31 MayNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Workplace Environment That Affect Employee's Performance in Private Hospitals of Hyderabad, PakistanDocument6 pagesThe Impact of Workplace Environment That Affect Employee's Performance in Private Hospitals of Hyderabad, PakistanNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Hanan - ARM Final PaperDocument12 pagesHanan - ARM Final PaperNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- ZaraDocument8 pagesZaraNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Final Paper - Amjad-SAP-11297 Section B, ARMDocument13 pagesFinal Paper - Amjad-SAP-11297 Section B, ARMNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Identification of Risk Management in Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) Project PeshawarDocument13 pagesIdentification of Risk Management in Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) Project PeshawarNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Hanan - ARM Final PaperDocument12 pagesHanan - ARM Final PaperNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Final Paper - Amjad-SAP-11297 Section B, ARMDocument13 pagesFinal Paper - Amjad-SAP-11297 Section B, ARMNasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Comments. Assingment 3Document15 pagesComments. Assingment 3Nasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Comments. Bisma Nasir (22004) Section A - Second Submission (Abstract+Introduction)Document13 pagesComments. Bisma Nasir (22004) Section A - Second Submission (Abstract+Introduction)Nasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Comments. Bisma Nasir (22004) Section A QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesComments. Bisma Nasir (22004) Section A QuestionnaireNasir BashirNo ratings yet