Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blood Glucose Stimulus Response Model SOLUTIONS
Uploaded by
fatimaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Blood Glucose Stimulus Response Model SOLUTIONS
Uploaded by
fatimaCopyright:
Available Formats
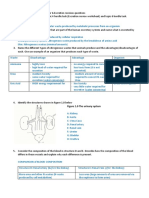
Regulation of Blood glucose levels stimulus response model solutions
When blood glucose levels rise after a meal.
STIMULUS RECEPTOR
Blood glucose levels rise above Stimulus is detected by islet
normal cells of the pancreas
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK
Blood glucose level
drops back to normal
MODULATOR
RESPONSE Beta cells of pancreas are
Body cells increase uptake of EFFECTOR stimulated to release the hormone
glucose from bloodstream. All body cells insulin into the blood. Alpha cells
Liver increases uptake glucose decrease glucagon release
and stores it as glycogen.
When blood glucose levels fall
STIMULUS RECEPTOR
Blood glucose levels drop below Stimulus is detected by islet
normal cells of the pancreas
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK
Blood glucose levels
increase to normal levels
MODULATOR
RESPONSE Alpha cells of the pancreas are
Liver breaks down glycogen EFFECTOR stimulated to release the hormone
stores and releases glucose into Liver cells glucagon into the blood. Beta cells
the blood. Feeling of hunger leads Brain & digestive decrease insulin release.
to ingestion of food. Digestion system
releases sugars.
You might also like
- Chemistry 12 Student WorkbookDocument291 pagesChemistry 12 Student WorkbookyutianzhaiNo ratings yet
- Module 5&6 Chemistry Notes (Created by Etho - X - BOS)Document25 pagesModule 5&6 Chemistry Notes (Created by Etho - X - BOS)noorNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Science OverviewDocument4 pagesYear 8 Science Overviewapi-3137245670% (1)
- Cell Division - Mitosis and The Cell CycleDocument43 pagesCell Division - Mitosis and The Cell CycleJomar CarabotNo ratings yet
- Biology PDFDocument178 pagesBiology PDFShubhamAuspiciosoGothwalNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Notes Biology AqaDocument94 pagesUnit 5 Notes Biology Aqa李超然No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument120 pagesUntitledJoe AmogusNo ratings yet
- Food Chain and Food Web PDFDocument6 pagesFood Chain and Food Web PDFA. ZNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Research TaskDocument4 pagesEndocrine System Research TaskShaheen AliNo ratings yet
- 16 Organ PDFDocument3 pages16 Organ PDFAya ZhNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument21 pagesBiologyTallyNo ratings yet
- Preliminary HSC Biology - Australian Biota NotesDocument13 pagesPreliminary HSC Biology - Australian Biota Notesamy_nomNo ratings yet
- AS Bio Unit 2 Chapter 3Document29 pagesAS Bio Unit 2 Chapter 3Aliya K100% (1)
- Oedipus The KingDocument3 pagesOedipus The Kingxray187No ratings yet
- Year 11 Maths AdvancedDocument14 pagesYear 11 Maths AdvancedKSB LightningNo ratings yet
- Science Essentials 9 For NSW Stage 5 Australian Curriculum EditionDocument3 pagesScience Essentials 9 For NSW Stage 5 Australian Curriculum Editionapi-374582387No ratings yet
- SURFING National Biology 4 Maitaing Internal Sample PDFDocument21 pagesSURFING National Biology 4 Maitaing Internal Sample PDFelamNo ratings yet
- AQA Biology Unit 1: Revision Notes: myrevisionnotes, #1From EverandAQA Biology Unit 1: Revision Notes: myrevisionnotes, #1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- C 1 1 2025 Topic Test MsDocument4 pagesC 1 1 2025 Topic Test MsRawanMazen SharifNo ratings yet
- c07ElementsCompoundsAndMixtures WEBDocument22 pagesc07ElementsCompoundsAndMixtures WEBDaniel WalshNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Homeostasis (Parts 1 and 2)Document19 pagesIGCSE Homeostasis (Parts 1 and 2)buhNo ratings yet
- Edrolo VCE Chemistry Units 34 - Textbook PDF v3Document530 pagesEdrolo VCE Chemistry Units 34 - Textbook PDF v3uyenkhuu06No ratings yet
- D4 Antacids (PH Regulation of The Stomach)Document3 pagesD4 Antacids (PH Regulation of The Stomach)Clare ChenNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Section 5 Lesson 1Document92 pagesIGCSE Biology Section 5 Lesson 1salmaNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes HSCDocument116 pagesBiology Notes HSCYuki SuzukiNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 1 Federal Board PDFDocument46 pagesBiology Chapter 1 Federal Board PDFMshoaibNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 U4Document3 pagesTopic 1 U4api-263323894No ratings yet
- Biology As A2 CombinedDocument253 pagesBiology As A2 CombinedKulsoom JawedNo ratings yet
- 2018 Year 11 Human Biology ATAR Course OutlineDocument21 pages2018 Year 11 Human Biology ATAR Course OutlineNessrynNo ratings yet
- Enzymes 2Document5 pagesEnzymes 2Ema Arroyo LopezNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Biology TestDocument10 pagesYear 10 Biology TestMichael Mc BrienNo ratings yet
- Kilbaha Edited ExamDocument28 pagesKilbaha Edited ExamfatimaNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Science Quiz Cells and Matter Quiz 6 Year 7 AnswerDocument14 pagesYear 7 Science Quiz Cells and Matter Quiz 6 Year 7 AnswerSithar DeviNo ratings yet
- C07chemicalreactions WEBDocument20 pagesC07chemicalreactions WEBAzman Bin KadirNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Properties of Matter PDFDocument30 pagesThe Structure and Properties of Matter PDFy9903061No ratings yet
- Task 3 - Student 2 ResponseDocument8 pagesTask 3 - Student 2 ResponsePradHvin RajaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Acid Neutralizing Capacity of Various Marketed Antacids in NepalDocument40 pagesDetermination of Acid Neutralizing Capacity of Various Marketed Antacids in NepalTshiva AryalNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Biology Mock Exam 1B - Dec 2018 - MARKSCHEMEDocument11 pagesYear 11 Biology Mock Exam 1B - Dec 2018 - MARKSCHEMEtechang1No ratings yet
- Drugs in Sports (Plasma Expanders)Document8 pagesDrugs in Sports (Plasma Expanders)Tharani GunasakaranNo ratings yet
- Scientific ReportDocument11 pagesScientific ReportDog DogNo ratings yet
- Biozone, DNA ReplicationDocument1 pageBiozone, DNA ReplicationNick BaderNo ratings yet
- Biology HSC Questions ARC 2006Document28 pagesBiology HSC Questions ARC 2006timeflies23No ratings yet
- SS2 ch3Document22 pagesSS2 ch3Eren SevinceNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Igcse TopicDocument1 pageDiabetes Igcse TopicDrRemyaranjith MenonNo ratings yet
- QATs Exam 2013 Units 3&4 PDFDocument57 pagesQATs Exam 2013 Units 3&4 PDFragsafgNo ratings yet
- HSC Biology Paper 2Document32 pagesHSC Biology Paper 2Calvin SywNo ratings yet
- M1 W14Document5 pagesM1 W14AmandaNo ratings yet
- VCE Biology 2019 Exam SolutionsDocument11 pagesVCE Biology 2019 Exam SolutionsMy Name is JeffNo ratings yet
- James Ruse 2021 Biology TrialsDocument40 pagesJames Ruse 2021 Biology TrialsHewadNo ratings yet
- Biology Dot Point SummaryDocument5 pagesBiology Dot Point SummaryRowan ScottNo ratings yet
- GCE A - AS Level Biology A Topic Test - Foundations in BiologyDocument26 pagesGCE A - AS Level Biology A Topic Test - Foundations in Biologyarfaat shah100% (1)
- Food ChemistryDocument21 pagesFood Chemistrylinm@kilvington.vic.edu.auNo ratings yet
- SS2 ch8Document26 pagesSS2 ch8Eren SevinceNo ratings yet
- Biology in Focus Prelim Sample ChapterDocument37 pagesBiology in Focus Prelim Sample ChapterLuke Vincent100% (1)
- NomenclatureDocument20 pagesNomenclatureViejay RegNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument3 pagesHormonesJason Ng100% (1)
- Relationships of Organisms With One Another Biology 5090 NotesDocument18 pagesRelationships of Organisms With One Another Biology 5090 NotesBalakrishnan MarappanNo ratings yet
- Doctor ZhivagoDocument3 pagesDoctor ZhivagoTaufiq XemoNo ratings yet
- GCSE Week 09 InheritanceDocument36 pagesGCSE Week 09 InheritanceFrankie BarnesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Pancreas: Regulate Blood Glucose - The Fuel ThatDocument2 pagesAnatomy of The Pancreas: Regulate Blood Glucose - The Fuel ThatSkyerex100% (1)
- Post Lab Question Experiment 5Document6 pagesPost Lab Question Experiment 5Skefadiuto100% (3)
- Chapter 1 QuickCheck & Chapter Review QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter 1 QuickCheck & Chapter Review QuestionsfatimaNo ratings yet
- Solutions To SAC 3 Excretion Revision WorksheetDocument6 pagesSolutions To SAC 3 Excretion Revision WorksheetfatimaNo ratings yet
- Osmoregulation HOMEOSTASIS Cut and Paste ActivityDocument2 pagesOsmoregulation HOMEOSTASIS Cut and Paste ActivityfatimaNo ratings yet
- Cornell Notes TemplateDocument2 pagesCornell Notes TemplatefatimaNo ratings yet