Professional Documents
Culture Documents
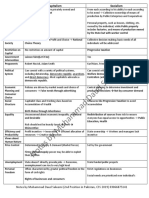
Advantages and Disadvantages of Capitalism
Advantages and Disadvantages of Capitalism
Uploaded by
Zafar ArshadCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Advantages and Disadvantages of Capitalism
Advantages and Disadvantages of Capitalism
Uploaded by
Zafar ArshadCopyright:
Available Formats
Criticism of Capitalism
1. A threat to Democracy and Freedom
Capitalism creates very large concentrations of money and property in the hands of a relatively small minority
of the human population (the elite or the "power elite"). "Corporate capitalism" and "inverted totalitarianism"
are terms used to criticize this aspect of capitalism. Corporate capitalism has been criticized for the amount of
power and influence corporations and large business interest groups have over government policy, including
the policies of regulatory agencies and influencing political campaigns of the elected politicians. The existence
of large corporations seems to circumvent the principles of democracy, which assumes equal power relations
between all individuals in a society.
Governments listen to big business and banks because they fund their election campaigns. They listen to big
newspaper barons because they know that they can influence public opinion.
References:
NRA (National Rifle Association) in USA
Military Industrial Complex in USA
2. Exploitation of Workers
Critics of capitalism view the system as inherently exploitative.
Reference: Marx’s Labor Theory of Value
Since capitalists control the means of production (e.g. factories, businesses, machinery and so on) and workers
control only their labor, the worker is naturally coerced into allowing their labor to be exploited. Critics argue
that exploitation occurs even if the exploited consents, since the definition of exploitation is independent of
consent. In essence, workers must allow their labor to be exploited or face starvation. Since some degree of
unemployment is typical in modern economies, Marxists argue that wages are naturally driven down in free
market systems. Hence, even if a worker contests their wages, capitalists are able to find someone from
the reserve army of labor who is more desperate.
3. Imperialism and Wars (Neo – Colonialism)
Critics of capitalism argue that the system is responsible for not only economic exploitation, but also imperialist
and colonial wars. Large corporations have had a long history of interference in and distortion of the policies
of sovereign nation states through high-priced legal lobbying and bribes.
Vladimir Lenin claimed that state use of military power to defend capitalist interests abroad was an inevitable
corollary of monopoly capitalism. He argued that capitalism needs imperialism in order to survive and monopoly
Notes by Muhammad Daud Saleemi (2nd Position CSS 2019) - 03066875141
capitalists influence state policy to carve up the world into spheres of interest. These trends led states to defend
their capitalist interests abroad through military power.
Reference:
The military–industrial complex, mentioned in Dwight D. Eisenhower's presidential farewell address,
appears to play a significant role in the American capitalist system. It may be one of the driving forces of
American militarism and intervention abroad.
Many of the wars fought in recent years have been over profit. In Iraq, the war was largely funded by oil
barons, and it was private firms who handled most of the security after the initial invasion. In Libya,
western forces intervened when the civil war caused oil supplies to be cut off. They only sided with the
rebels because they thought they were the most likely to win. In Iran, military intervention is being
threatened over the blocking of trading routes to transport oil.
The military–industrial complex (MIC) is an informal alliance between a nation's military and the arms
industry which supplies it, seen together as a vested interest which influences public policy. The driving factor
behind this relationship between the government and defense-minded corporations is that both sides
benefit—one side from obtaining war weapons, and the other from being paid to supply them. In US context,
Congress is also part of this relationship forming a triangle of relationships influenced by political
contributions, political approval for military spending and loose regulations of the industry.
4. Market Instability and Recessions
Critics of capitalism, particularly Marxists, identify market instability as a permanent feature of capitalist
economy. Marx believed that the unplanned and explosive growth of capitalism does not occur in a smooth
manner, but is interrupted by periods of overproduction in which stagnation or decline occur (i.e. recessions).
This process is referred to as “Boom and bust cycles”. Capitalist economies have a tendency to booms and
busts with painful recessions and mass unemployment
Financial institutions such as Banks and Investment Firms make risky and greedy investments to maximize
profit which may lead to instability and recession. During a long recession, people can lose their jobs, have
their houses foreclosed and suffer a decline in their living standards.
Reference:
The Great Depression
Financial Crisis of 2007-2008
5. Monopolization
Notes by Muhammad Daud Saleemi (2nd Position CSS 2019) - 03066875141
A capitalist economic system allows enough freedom for property holders to establish their influence in the
markets become all-powerful without much restriction on the extent of this spread. This leads to
monopolization of markets by one or a few major players. This permits a handful of firms to dominate the
market and govern prime factors like prices, quantity supplied and quality of the product without any
opposition from other competitors.
This also creates barriers to entry for other players in the market due to a high degree of control being
exercised by the firms monopolizing the markets.
Reference:
Google controls 90% of the Web Search Market.
6. Economic and Social Inequality
Critics argue that capitalism is associated with the unfair distribution of wealth and power; a tendency
towards various forms of economic and social inequalities, and repression of workers. Capitalism does not
focus on furthering equality among various income groups. Critics, such as Ravi Batra, argue that the capitalist
system has inherent biases favoring those who already possess greater resources. The rich continue to make
large sums of money due to the conducive environment in the economy while the lower income groups have
to make do with fixed monthly wages. Hence, the gap between the rich and poor continues to broaden
without any help from government regulations.
Statistics:
This has been highlighted through the figure given below which shows the skewed income distribution in USA
in the year 2010. Such inequality in distribution of wealth and power in the economy leads to societal
imbalance which has immediate and often extreme reactions from the masses.
Notes by Muhammad Daud Saleemi (2nd Position CSS 2019) - 03066875141
One study shows that in the United States 43.35% of the people in the Forbes magazine "400 richest
individuals" list were already rich enough at birth to qualify.
Reasons:
Right to Private Property and Inheritance
Capitalist society is based on the legal right to private property and the ability to pass on wealth to future
generations. Capitalists argue that a capitalist society is fair because you gain the rewards of your hard work.
But, often people are rich, simply because they inherit wealth or are born into a privileged class. Therefore,
capitalist society not only fails to create equality of outcome but also fails to provide equality of opportunity.
Access to Better Opportunities
Children of rich people have access to better opportunities to grow. For example, in the absence of a quality
public education system funded by state, rich people are in a position to give their children a better education
. This is results in a continuous cycle of poverty for the poor who aren’t able to compete and change their
fortunes due to lack to opportunities.
Notes by Muhammad Daud Saleemi (2nd Position CSS 2019) - 03066875141
7. Causes Conflict in Society
Increasing Economic Inequalities may lead to social inequalities and resentment among classes, which is
dangerous for the fabric of society. (Conflict Theory)
8. Alienation
9. Social Evils
A capitalist society does not consider the social needs of the nation as its primary objective. Stimulus to
economic growth is the prime purpose of such a market setup. This overlooking of the needs of the masses
leads to problems like
a) Ignorance of Worker Rights
Labor unions are squashed and the general needs of the workers could be overlooked in a capitalist setup.
b) Selfishness and Greed
The majority of criticisms against the Profit Motive are centered on the idea that the profit motive encourages
selfishness and greed, rather than altruism and serving the public good, or necessarily creating an increase in
net wealth. Critics of the profit motive contend that companies disregard morals or public safety in the pursuit
of profits.
c) Threat to Environment
A profit maximizing capitalist firm is likely to ignore negative externalities, such as pollution from
production. Environmentalists have argued that capitalism requires continual economic growth and that it will
inevitably deplete the finite natural resources of Earth and cause mass extinctions of animal and plant life. Such
critics argue that while this neoliberalism or contemporary capitalism has indeed increased global trade,
environmental indicators indicate massive environmental degradation since the late 1970s after Free Trade
exploded.
d) Privatization of Basic Human Necessities such as Education, Water, Health Care, etc. (Exclusive Rights
to Natural Resources)
e) Creation of False Needs
Notes by Muhammad Daud Saleemi (2nd Position CSS 2019) - 03066875141
f) Global Poverty (Dependency Theory, South-East Economic Disparity due to extraction and flow of
resources), and Human Rights Abuses by MNCs in 3rd World Countries
Advantages of Capitalism
1. Increased Competition and Incentive to Work Hard
Competition is a natural benefit and consequence of capitalism. While some may think of increased
competition as a disadvantage of the system, it is advantageous because increased competition produces
increased quality and decreased prices to the consumer. Capitalism tends to reward the business that
produces the highest quality item for the lowest price, resulting in increased market share for that
producer.
More competitors mean better quality products and lower prices. At the same time, these companies will
have to hire more workers and pay them better wages.
Under capitalism people have to work hard if they want to survive which is not possible in case of socialist
economy where government provides amenities to people.
2. Economic growth
Capitalism allows the economy to grow exponentially. It is a basic fact of economics that the more money
a firm makes, the more it can invest in production, and the more it invests in production, the more money
it makes. So long as no unfortunate events befall the firm, this growth can, obviously, continue
indefinitely.
Historically, capitalism has an ability to promote economic growth as measured by gross domestic
product (GDP), capacity utilization or standard of living. This argument was central, for example, to Adam
Smith's advocacy of letting a free market control production and price and allocate resources. Many
theorists have noted that this increase in global GDP over time coincides with the emergence of the
modern world capitalist system.
New Businesses: It encourages entrepreneurship because people can set up easily their own business
under this as compared to other economic system.
Notes by Muhammad Daud Saleemi (2nd Position CSS 2019) - 03066875141
3. Benefit of Society at large: Capitalism and the Invisible Hand
The invisible hand is a term used by Adam Smith is his book “Wealth of the Nations” to describe the
unintended social benefits of individual self-interested actions. . He argued that self-interested individuals
operating through a system of mutual interdependence in capitalism tend to promote the general benefit of
society at large.
The theory is that the Invisible Hand states that if each consumer is allowed to choose freely what to buy and
each producer is allowed to choose freely what to sell and how to produce it, the market will settle on a
product distribution and prices that are beneficial to all the individual members of a community, and hence to
the community as a whole.
How?
a. Efficient Allocation of Resources
Competition ensures that resources are distributed according to consumer preferences since Consumer’s
choice is given full weight under Capitalism. Firms are not rewarded for producing goods people don’t want.
b. Efficient Methods of Production and Creative Destruction
In a market system, firms have incentives to be productively efficient – cutting costs to improve
competitiveness, productivity and maximize profit. If firms don’t remain productive and efficient they will go
out of business.
J. Schumpeter argued a powerful influence in capitalism was the idea of ‘creative destruction’. If firms
become inefficient and outdated, they go out of business. This leads to short-term problems – unemployment.
However, it allows resources – capital and labor to shift to new, more innovative and efficient industries.
Example:
Uber, Careem in Pakistan (Death of Auto-rickshaw industry)
c. Capitalism encourages Innovation
Most important for economic growth is capitalism's intrinsic reward for innovation. This includes innovation in
more efficient production methods. Companies must find profitable ways to produce high-quality innovative
new products that consumers want to buy.
As Steve Jobs said, "You can't just ask customers what they want and then try to give that to them. By the time
you get it built, they'll want something new."
Notes by Muhammad Daud Saleemi (2nd Position CSS 2019) - 03066875141
How?
Businesses invest into research and development to create better products.
Employees focus on improving their best practices so they can remain as productive as possible.
Services are improved to solve more problems.
d. Improved Quality and Wide Range of Goods and Services
People have unique problems which must be solved. This wide array of needs allows for businesses to find a
niche so they can exist. If there is value in the goods or services being offered, defined as being able to solve a
problem, then it will continue to operate. That results in a society that offers a wider range of products or
services than those that operate with government interference or mandate.
4. Limited Government Intervention
In capitalist economies, governments play a minimal role in deciding what to produce, how much to produce,
and when to produce it, leaving the cost of goods and services to market forces. When entrepreneurs spot
openings in the marketplace, they rush in to fill the vacuum. Because markets distribute the factors of
production (land, labor, capital and entrepreneurship) in accord with supply and demand, the government can
limit itself to enacting and enforcing rules of fair play.
In a capitalist system, the government does not prohibit private property or prevent individuals from working
where they please. The government does not prevent firms from determining what wages they will pay and
what prices they will charge for their products.
Exceptions:
However, many countries have minimum wage laws and minimum safety standards. Under some versions of
capitalism, the government carries out a number of economic functions, such as issuing money, supervising
public utilities and enforcing private contracts. Many countries have competition laws that prohibit monopolies
and cartels from forming. Government agencies regulate the standards of service in many industries, such as
airlines and broadcasting as well as financing a wide range of programs.
5. Relationship to Political Freedom
In his book The Road to Serfdom, Friedrich Hayek asserts that the economic freedom of capitalism is a
requisite of political freedom. He argues that the market mechanism is the only way of deciding what to
produce and how to distribute the items without using coercion. Friedman claimed that centralized economic
Notes by Muhammad Daud Saleemi (2nd Position CSS 2019) - 03066875141
operations are always accompanied by political repression. In his view, transactions in a market economy are
voluntary and that the wide diversity that voluntary activity permits is a fundamental threat to repressive
political leaders and greatly diminish their power to coerce.
The tendency with governments that own production and set prices is that it often leads to political control
beyond what people expect – often including many other aspects of life.
6. Capitalism promotes self-regulation of market
Businesses in a Capitalistic society only have power because consumers allow them to have it. If buyers are
not interested in the goods or services that are offered by an organization, then that business will not
continue to exist. This means businesses must create goods or services that are desired by the society and this
helps to serve the needs of individuals and households.
By encouraging the production of desirable goods and discouraging the production of unwanted or
unnecessary ones, the marketplace self-regulates, leaving less room for government interference and
mismanagement.
7. It encourages Free Trade and International Harmony (Theory of Economic Interdependence)
Capitalist nations promote free trade allowing more nations to cooperatively work together for economic prosperity.
This will likely mitigate disputes between nations.
8. Compatible with Human Nature
One of the most common arguments that capitalists use is that capitalism works perfectly with human nature,
which is based on following self-interest. Self-interest is rewarded duly with large amounts of money and the
entire economy is fuelled by people working hard to furnish their own needs. In addition, it causes
competition, which is an essential part of advancing the human race. The power of competition is shown
during wars, where huge technological achievements are made. For example, the Jeep was invented by the
Allies during WWII. Though this ruthless competition often damages society, one cannot deny that these traits
have contributed greatly in the progress mankind at a rapid pace and have been successful in delivering.
However, other aspects of human nature like altruism, patience and kindness have their place, too, in the
capitalist world. There are tens of thousands of registered charities providing not-for-profit activities. Centrally
planned altruism is actually unnecessary and, in fact, limits what people would otherwise give on their own
initiative.
Notes by Muhammad Daud Saleemi (2nd Position CSS 2019) - 03066875141
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5811)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Full Download Ebook Ebook PDF Microeconomics 16th Canadian Edition by Christopher T S Ragan PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Ebook Ebook PDF Microeconomics 16th Canadian Edition by Christopher T S Ragan PDFdanny.wainer321100% (43)
- Fertigrow Business Plan Group 3Document69 pagesFertigrow Business Plan Group 3Elaiza May PatigayonNo ratings yet
- Women in Ancient IndiaDocument13 pagesWomen in Ancient IndiaBhoomejaa SKNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Economics Self Assessment Exam Style Question's Answers - Section 1Document4 pagesIGCSE Economics Self Assessment Exam Style Question's Answers - Section 1DesreNo ratings yet
- Annex-7 - 6.6 KV Breakers Testing ReportDocument20 pagesAnnex-7 - 6.6 KV Breakers Testing ReportZafar ArshadNo ratings yet
- Carlinsoskice Solutions ch02Document10 pagesCarlinsoskice Solutions ch02Clara Lustosa100% (1)
- Massey - Spatial Divisions of Labor - Social Structures and The Geography of Production PDFDocument410 pagesMassey - Spatial Divisions of Labor - Social Structures and The Geography of Production PDFMaruclaNo ratings yet
- Theory of AlienationDocument8 pagesTheory of AlienationZafar ArshadNo ratings yet
- Capitalism Vs Socialism ComparisonDocument2 pagesCapitalism Vs Socialism ComparisonZafar ArshadNo ratings yet
- Presidential Vs Parliamentary System in Pakistan - S ContextDocument3 pagesPresidential Vs Parliamentary System in Pakistan - S ContextZafar ArshadNo ratings yet
- Western Political ThoughtDocument1 pageWestern Political ThoughtZafar ArshadNo ratings yet
- Political Science Topics and QuestionsDocument3 pagesPolitical Science Topics and QuestionsZafar ArshadNo ratings yet
- Annex-5 - 132 KV Breakers Testing Report PDFDocument42 pagesAnnex-5 - 132 KV Breakers Testing Report PDFZafar ArshadNo ratings yet
- Transitional Devices: Connecting Words)Document2 pagesTransitional Devices: Connecting Words)Zafar Arshad100% (1)
- Paragraph B PDFDocument1 pageParagraph B PDFZafar ArshadNo ratings yet
- How To Crack Compulsory PapersDocument5 pagesHow To Crack Compulsory PapersZafar ArshadNo ratings yet
- Coherence: Repetition of A Key Term or PhraseDocument3 pagesCoherence: Repetition of A Key Term or PhraseZafar ArshadNo ratings yet
- SRO 492 of 2009 For Temporary Importation For ExportDocument5 pagesSRO 492 of 2009 For Temporary Importation For ExportZafar ArshadNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart - Production SystemDocument30 pagesFlow Chart - Production Systemmatthew mafaraNo ratings yet
- Entreprenuership Notes 2020 by Kimuli Fred ST Henry's College Gangu PDFDocument334 pagesEntreprenuership Notes 2020 by Kimuli Fred ST Henry's College Gangu PDFkhami PETERSON83% (6)
- Human Resources For HealthDocument11 pagesHuman Resources For Healthperpustakaan pusatNo ratings yet
- سعد رزاق ناصحDocument10 pagesسعد رزاق ناصحعبدالمحسن علي ENo ratings yet
- Reading StrategiesDocument57 pagesReading StrategiesAl Cheeno AnonuevoNo ratings yet
- 16 - Problem Set #7-1 PDFDocument3 pages16 - Problem Set #7-1 PDFHasham DaqiqNo ratings yet
- VU Lesson 25 Introduction To Macroeconomics MacroeconomicsDocument3 pagesVU Lesson 25 Introduction To Macroeconomics MacroeconomicsSusheel KumarNo ratings yet
- Issues and Trends in HR in South AfricaDocument7 pagesIssues and Trends in HR in South Africasammie celeNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics: National Income AccountingDocument26 pagesMacroeconomics: National Income AccountingShakib AhmmedNo ratings yet
- A2 Economics Chapter 9Document200 pagesA2 Economics Chapter 9Wu JingbiaoNo ratings yet
- Be Advised, The Template Workbooks and Worksheets Are Not Protected. Overtyping Any Data May Remove ItDocument11 pagesBe Advised, The Template Workbooks and Worksheets Are Not Protected. Overtyping Any Data May Remove ItGreen XchangeNo ratings yet
- Aging The Individual and Society 10th Edition Hillier Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument34 pagesAging The Individual and Society 10th Edition Hillier Test Bank Full Chapter PDFJustinSweeneyyomr100% (14)
- Essentials To Entrepreneurship Chap14 McqsDocument67 pagesEssentials To Entrepreneurship Chap14 McqssheheryarNo ratings yet
- Port Management and Logistics: Topic 6: Establishing A Port's Competitive EdgeDocument11 pagesPort Management and Logistics: Topic 6: Establishing A Port's Competitive EdgeChris PaynalNo ratings yet
- PDF Microeconomic Theory Basic Principles and Extensions 12E Walter Nicholson Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Microeconomic Theory Basic Principles and Extensions 12E Walter Nicholson Ebook Full Chapterrodney.mccown591100% (3)
- Power of Productivity LewisDocument12 pagesPower of Productivity LewissnegcarNo ratings yet
- Block 3 MCO 5 Unit 2Document27 pagesBlock 3 MCO 5 Unit 2Tushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineers Code of Ethics Essential RolesDocument11 pagesCivil Engineers Code of Ethics Essential RolesJOHN IAN M. SUBILNo ratings yet
- JB APUSH Unit 2 Topic 2.4Document11 pagesJB APUSH Unit 2 Topic 2.4Graham NicholsNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument252 pagesUntitledJuan BorgatelloNo ratings yet
- Industrial Relations & Labour Welfare - 1915318 - Question BankDocument21 pagesIndustrial Relations & Labour Welfare - 1915318 - Question BankbalajipikachuNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Bread Labour: StructureDocument9 pagesUnit 5 Bread Labour: StructureShobhit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Econ 1740 EportfolioDocument5 pagesEcon 1740 Eportfolioapi-269480516No ratings yet
- Chapter 11, The Conversion Business Process Chapter 11, The Conversion Business ProcessDocument6 pagesChapter 11, The Conversion Business Process Chapter 11, The Conversion Business ProcessSibusisoNo ratings yet