2019-10-31
Purpose
• Establish baseline status
Hand Evalua*on • Validate progress
• Professional communica=on
• Research
History General Informa=on
• Demographic data • Medical history
• Diagnosis, Date of onset • Social history
• Mechanism of injury • Occupa=on
• Past medical history • Hobbies & interests
• Main complaints
• Pa=ent’s goals & expecta=ons
1
� 2019-10-31
Subjec=ve Complaints Observa=on
• ANtude towards injury
• Complaints of pain
• Appearance
• Sensa=on • Colour/Circula=on
• How func=on is impaired • Sudomotor func=on
• Atrophy
• Posture of digits
Observa=on Palpa=on
• Edema
• Areas of tenderness
• Fascial cords/
nodules/callous
2
� 2019-10-31
Equipment for Examina=on Assessment of Edema
• Goniometer
• Two-point caliper
• Semmes-Weinstein monofilaments
• Dynamometer
• Pinch gauge
• Tape measure, volumeter
l Circumferen=al
l Volumetric
Assessment of ROM Recording ROM Measurements
• Use standardized
goniometric
measurements • AROM PIP Ext/Flex
30/75 30-75
• 0 degree neutral
star=ng posi=on • PROM PIP Ext/Flex
• Documenta=on – 10/85 10-85
frequent
• Factors affec=ng ROM
3
� 2019-10-31
Tendon Status EIP & EDM Test
• EDC test
EPL Test Flexor Tendons
FDS Test FDP Test
4
� 2019-10-31
Tendon Func=on
To Assess Extrinsic Muscle-Tendon Unit
Tightness, the Wrist Posi=on is the Key
Tendon Excursion
Extrinsic Flexor Tightness
To Assess Extrinsic Muscle-Tendon Unit
Tightness, the Wrist Posi=on is the Key
• With wrist
• Occurs from origin extended, finger
to inser=on extension is limited
• Most prominent
• With wrist flexed,
joint crossed by the
muscle-tendon unit Finger extension
is the key to assess improves
=ghtness
5
� 2019-10-31
Extrinsic Flexor Tightness Extrinsic Extensor Tightness
• With wrist flexed,
finger flexion is
limited
• With wrist
extended, finger
flexion improves
Evalua=on of Ar=cular/Periar=cular
Extensor Tightness
Tightness
• Goniometric
measurements remain
unchanged
irrespec=ve of the
wrist posi=on
6
� 2019-10-31
Ar=cular/Periar=cular Tightness Intrinsic Tightness
• The MCP posi=on is
the key to assess the
intrinsic =ghtness
Intrinsic Tightness Oblique Re=nacular Ligament
Tightness
• The PIP joint posi=on
is the key to assess
the oblique
re=nacular =ghtness
7
� 2019-10-31
Web Space Contracture Neuro-Muscular Func=on
• Radial Nerve Func=on
– Posterior Interosseous Nerve
• Median Nerve Func=on
– Anterior Interosseous Nerve
• Ulnar Nerve Func=on
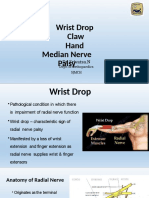
Radial Nerve Lesion Radial Nerve
• Closed injuries – differen=al diagnosis
• Open Injuries – essen=al to assess proximal vs distal trauma
assessment simpler
• Saturday Night Palsy
• Findings obvious
• Loss of wrist & digital • Mid shae humeral fractures
extension
• Loss of BR, Supinator,
Ticeps func=on
8
� 2019-10-31
Posterior Interosseous Nerve Posterior Interosseous Nerve
• Fibrilla=on of Supinator – proximal trauma
• Entrapment at • Classic radial devia=on in extension with loss
proximal & distal
of digital extension
edges of supinator -
Arcade of Froshe • Par=al paralysis – Loss of 4th & 5th MCP
extension, at =mes loss of 3rd & 4th MCP
• Involvement of EDC,
extension
EDM,ECU, EPL & B,
and EIP
R
F OSHE
RADIAL NERVE
Median Nerve Lesion Comparison of Findings
• Entrapment at superficialis arch
distally, ligament of Struthers,
lacertus fibrosus and deep head
of pronator teres
• Carpal tunnel syndrome
• Anterior interosseous syndrome
• Differen=al diagnosis – for
proximal vs distal lesions
9
� 2019-10-31
Classic Tests – Median Nerve
Anterior Interosseous Syndrome
Lesions
• Acute demyelina=on
• Denerva=on of FPL, FDP – D2 & D3, and
• Phalen’s test pronator quadratus
• Reverse Phalen’s • Benedic=on Sign – Posi=ve
• Tinel’s • Anastomo=c varia=on – Mar=n Gruber
Anastomosis
Ulnar Nerve Lesions Nerve Lesion - Elbow
• Lesions - Cubital Tunnel, • Denerva=on of FCU,
Arcade of Struthers, profundii – D4 & D5,
tendinous origin of FCU, and muscles supplied by
fracture disloca=ons, ulnar nerve distally
Guyon’s canal • No or minimal clawing
• Lesions proximal to elbow • Wartenburg’s sign -
– Cervical foramina, and posi=ve
Thoracic Outlet
UTHERS
STR
ULNAR NERVE
10
� 2019-10-31
Nerve Lesion – Distal to Elbow Classic Tests – Ulnar Nerve Lesions
Egawa Froment’s
• Denerva=on of
Palmar & Dorsal
Interooseii, intrinsic
muscles of the small
finger, adductor
Cross Finger
pollicis, and deep
fibers of FPB
• Clawing profound
Provoca=ve Tests Strength
• Ar=cular Status – OA • Measurement of grip & pinch strength
• Posi=onal Tests – Nerve & Tendon Status important once adequate mobility is restored
• Resisted Mo=on Tests – Nerve & Tendon • Strength measurements offer a gross
Status assessment of pa=ent’s power & precision
• Resisted/Loading Tendon Tests – handling
Inflammatory process tendons • Many factors can influence measurements
11
� 2019-10-31
Grip Strength Pinch Strength
Func=onal/ADL Assessment Sensibility
• Minnesota rate of • Normal sensibility is a
manipula=on test prerequisite to normal
hand func=on
• Jebson-Taylor hand
• Hypersensi=vity vs
func=on test desensi=zed
• Purdue pegboard • Important to ini=ate
test appropriate
• Other therapeu=c
techniques
12
� 2019-10-31
Sensibility Tes=ng Conclusion
• Protec=ve sensa=on
• Vibra=on – 30 cps, 256, cps In-depth understanding of anatomy and
• Moving touch assessment is pre-requisite to the
• 2 Point discrimina=on management of all common hand
• Semmes-Weinstein Monofilament disorders
• Localiza=on
• Func=onal-Moberg Pickup Test
13