Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Evaluate 3 1 2
Uploaded by
irwansyah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesthanks
Original Title
2013CTMCRelayProblems
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentthanks
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesEvaluate 3 1 2
Uploaded by
irwansyahthanks
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
32 − 1
0 (a). Evaluate .
22
0 (b). Let t=TNYWR.
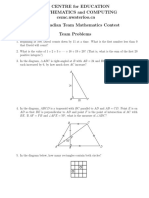
Determine the perimeter of the rectangle below.
2t+5
0 (c). Let t=TNYWR.
In the quadratic equation x2 − tx − 6t2 = 0, the positive root is a.
Determine the value of a.
1 (a). In the sequence, 1, 3, 5, 7, . . ., each term after the first is two larger than the
previous term.
What is the sum of the first 12 terms in this sequence?
1 (b). Let t=TNYWR.
The point (k, t) is on the line 3x − y − 6 = 0. Find the value of k.
1 (c). Let t=TNYWR.
A square with side length t is changed into a rectangle by adding k to its
length and subtracting k from its width. What is the smallest positive integer
value of k for which the new rectangle has area less than 2013?
2 (a). Evaluate
1
2 + 13
1 .
2 × 13
2 (b). Let t=TNYWR.
Peter lists the prime numbers in increasing order. Determine the average of
the 2tth and 2t + 1th numbers in his list.
2 (c). Let t=TNYWR.
In the diagram, D lies on side BC of 4ABC
with AD perpendicular to BC.
If AB = 35, BD = t and DC = 6, what is the
length of AC?
20A B
3 (a). In the sum + 1 3 A B , A and B are non-zero digits.
3B 0 8
Determine the value of A.
3 (b). Let t=TNYWR.
The lines x + y = k and x − ty = −8 intersect on the line y = x. Determine
the value of k.
3 (c). Let t=TNYWR.
In the diagram, the circle has centre O and
radius t. Square ABCD has side length t.
The overlapping area is shaded. What is the
positive difference between the unshaded area
of the square and the circle? Round your an-
swer to the nearest integer.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Answer Key For Team ProblemsDocument2 pagesAnswer Key For Team ProblemsirwansyahNo ratings yet
- Answer Key For Team ProblemsDocument2 pagesAnswer Key For Team ProblemsirwansyahNo ratings yet
- Answer Key For Team QuestionsDocument3 pagesAnswer Key For Team QuestionsirwansyahNo ratings yet
- Team Problems: 2013 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest (CTMC)Document3 pagesTeam Problems: 2013 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest (CTMC)irwansyahNo ratings yet
- 2014 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest: The Centre For Education in Mathematics and Computing Cemc - Uwaterloo.caDocument15 pages2014 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest: The Centre For Education in Mathematics and Computing Cemc - Uwaterloo.cairwansyahNo ratings yet
- The Centre For Education in Mathematics and Computing Cemc - Uwaterloo.ca 2014 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest Team ProblemsDocument4 pagesThe Centre For Education in Mathematics and Computing Cemc - Uwaterloo.ca 2014 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest Team ProblemsirwansyahNo ratings yet
- The Centre For Education in Mathematics and Computing Cemc - Uwaterloo.ca 2014 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest Individual ProblemsDocument2 pagesThe Centre For Education in Mathematics and Computing Cemc - Uwaterloo.ca 2014 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest Individual ProblemsirwansyahNo ratings yet
- @mathsbyramo @mathsbyramog: Channel GroupDocument12 pages@mathsbyramo @mathsbyramog: Channel GroupirwansyahNo ratings yet
- Answer Key For Team ProblemsDocument2 pagesAnswer Key For Team ProblemsirwansyahNo ratings yet
- Mensuration Solutions CGL Mains 2011-2018 by Deepak TyagiDocument38 pagesMensuration Solutions CGL Mains 2011-2018 by Deepak TyagiirwansyahNo ratings yet
- Time & Distance: Geometry Lecture-1Document10 pagesTime & Distance: Geometry Lecture-1irwansyahNo ratings yet
- SampleM 123Document4 pagesSampleM 123irwansyahNo ratings yet