Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cardiac Output Blood Pressure: Methods To Elevate Parameter
Uploaded by
patra fadma100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
34 views1 pageOriginal Title
Hemodynamic-Values
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
34 views1 pageCardiac Output Blood Pressure: Methods To Elevate Parameter
Uploaded by
patra fadmaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
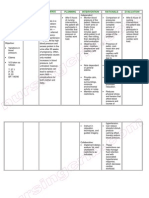
HEMODYNAMIC VALUES
METHODS TO ELEVATE PARAMETER METHODS TO DECREASE PARAMETER
CARDIAC OUTPUT BLOOD PRESSURE
CO=HR*SV (4-8L/min) CO*SVR
HEART RATE X STROKE VOLUME
60-100 bpm 60-120 mL/beat
Treat cause, parasympatholytic
(Atropine), sympathomimetic
(Epinephrine), pacemaker
Treat cause, antidysrhythmics,
Vagal electrical therapy
PRELOAD CONTRACTILITY AFTERLOAD
PAOP, CVP SVR
Fluids, blood Cardiac glycosides, Vasopressors
Sympathomimetics
Venous vasodilators, Beta blockers, Arterial vasodilators,
diuretics ace inhibitors, Ca channel blockers ACE inhibitors ARBs,
ARBs IABP
KEY HEMODYNAMIC VALUES (WITH EQUATIONS)
Cardiac Output (CO) HR x SV 4-8 L/min
Cardiac Index (CI) CO/BSA 2.5-4 L/min/m2
Central Venous Pressure (CVP) 2-6 mmHg
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) SBP+(2xDBP)/3 70-100 mmHg
Stroke Volume (SV) EDV - ESV 60-120 ml/beat
2
Stroke Volume Index (SVI) SV/BSA 30-65 ml/m2/beat
Pulmonary Artery Occlusion Pressure (PAOP) 8-12 mmHg
Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR) [MAP-RAP) x 80]/CI 800-1400 dynes/sec/cm-5
Central Venous Oxygen Saturation (ScvO2) 65-85%
Oxygen Delivery (DO2) CO x CaO2 x 10 900-1100 ml/min
NRSNG.com - “Tools and Confidence to Succeed in Nursing School.”
©2017 TazKai LLC | NRSNG.com - Reproduction Strictly Prohibited
Disclaimer information at NRSNG.com
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Medication Antidote Cheat SheetDocument1 pageMedication Antidote Cheat Sheetpatra fadmaNo ratings yet
- Doctors: Diagnosis: Allergies: History: Code StatusDocument1 pageDoctors: Diagnosis: Allergies: History: Code Statuspatra fadmaNo ratings yet
- Nurse Report SheetDocument1 pageNurse Report Sheetpatra fadmaNo ratings yet
- Care Pland Sheet01Document2 pagesCare Pland Sheet01patra fadmaNo ratings yet
- Maternity PediatricDocument65 pagesMaternity Pediatricpatra fadmaNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- National Stroke Thrombolysis Guideline Template v9 5-12-13 FINAL 2Document15 pagesNational Stroke Thrombolysis Guideline Template v9 5-12-13 FINAL 2Muhammad FauziNo ratings yet
- TOFPA: A Surgical Approach To Tetralogy of Fallot With Pulmonary AtresiaDocument24 pagesTOFPA: A Surgical Approach To Tetralogy of Fallot With Pulmonary AtresiaRedmond P. Burke MD100% (1)
- SCI9 Q1M2 PNHSDocument30 pagesSCI9 Q1M2 PNHSsai deveraNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in OtorhinolaryngologyDocument22 pagesRecent Advances in OtorhinolaryngologyInderdeep Arora100% (1)
- Anesthetic Consideration in Hypertensive PatientDocument11 pagesAnesthetic Consideration in Hypertensive PatientYosiAsmaraNo ratings yet
- The Endovascular Management of Ruptured Abdominal Aortic AneurysmsDocument12 pagesThe Endovascular Management of Ruptured Abdominal Aortic AneurysmsDiilNo ratings yet
- ACLS MedicationsDocument31 pagesACLS MedicationsDrNorNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Issues in Women With Atrial Septal Defect: April 2012Document9 pagesPregnancy Issues in Women With Atrial Septal Defect: April 2012Dara Dasawulansari SyamsuriNo ratings yet
- Transport in Humans: Test Yourself 8.1 (Page 140)Document3 pagesTransport in Humans: Test Yourself 8.1 (Page 140)lee100% (3)
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyDocument3 pages"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano50% (2)
- Psihountas V Jewish Hospital Et Al Complete FileDocument102 pagesPsihountas V Jewish Hospital Et Al Complete FilePeter M. HeimlichNo ratings yet
- Phlebitis and ThrombophlebitisDocument27 pagesPhlebitis and ThrombophlebitisSushant SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Positioning ClientsDocument2 pagesPositioning ClientsROBERT C. REÑA, BSN, RN, MAN (ue)100% (13)
- Simpo 14 Sept 19Document71 pagesSimpo 14 Sept 19Henry SNo ratings yet
- Acute Management of StrokeDocument19 pagesAcute Management of StrokeBKGUBIONo ratings yet
- Aorto Iliac DiseaseDocument58 pagesAorto Iliac Diseasejhk0428100% (1)
- Learn The Anatomy of The HeartDocument3 pagesLearn The Anatomy of The Heartash vldnbrNo ratings yet
- Varicose VeinsDocument7 pagesVaricose VeinsTarran PhagooNo ratings yet
- Sample ReportDocument3 pagesSample ReportRobeants Charles PierreNo ratings yet
- Echocardiogram: Echocardiogram, Also Known As Echocardiography, or Heart Ultrasound Is ADocument23 pagesEchocardiogram: Echocardiogram, Also Known As Echocardiography, or Heart Ultrasound Is AKarl RobleNo ratings yet
- Ecmo Basic ConceptsDocument37 pagesEcmo Basic Conceptskhoniker bondhuNo ratings yet
- Mortality RateDocument5 pagesMortality RateAlquino Heart RubioNo ratings yet
- Management If Intra-Arterial Injection, ATOTW 2023Document6 pagesManagement If Intra-Arterial Injection, ATOTW 2023Ali AftabNo ratings yet
- Medication - ALT-Template - AmlodipineDocument1 pageMedication - ALT-Template - AmlodipineNancyAmissahNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Peripheral Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Peripheral Tissue PerfusionRosalie Delfin90% (10)
- Nursing Care Plan Pregnancy Induced Hypertension (PIH Preeclampsia and Eclampsia)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan Pregnancy Induced Hypertension (PIH Preeclampsia and Eclampsia)deric91% (78)
- Chest X - RayDocument49 pagesChest X - RayLyk TiglaoNo ratings yet
- Usg 16054Document9 pagesUsg 16054Nikita NanwaniNo ratings yet
- Heart - WikipediaDocument215 pagesHeart - WikipediaUviweNo ratings yet
- Tips Vs BrtoDocument11 pagesTips Vs BrtoCsiszár MártonNo ratings yet