Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Research Poster
Uploaded by
api-540836038Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Research Poster
Uploaded by
api-540836038Copyright:
Available Formats
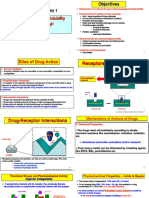
The Effect of Molecular Structure on the
Bioavailability of Pharmaceuticals
Jenny Van, Cindy Xu, Karen Zhang
University of Washington Department of Chemistry
Faculty Advisor: Dr. Brandi Cossairt
Introduction
The focus of our research is on analyzing molecular structure factors that affect oral
Factors Affecting Bioavailability Challenges in the Field of Bioavailability
bioavailability, which include rotatable bonds, polar surface area, electron affinity,
and aromaticity. We also consider current challenges in the field of bioavailability
and possible solutions to those challenges. Dielectric Effect Electron Affinity Polar Surface Area Aromaticity
Fig. 7. The intravenous route is set at 100%
bioavailability because the drug is injected directly
into the circulatory system. Oral bioavailability by
contrast is much lower because the drug has to
pass through the GI tract to reach the circulatory
system. The y-axis represents the drug’s Fig. 10. Electron affinity
Fig. 9. Polarized
concentration (mg/L). As concentration increases, vs. atomic number
atom
the rate of drug entering the system is greater than
the rate in which it exits and vice versa. Fig. 11. CHF3 Fig. 12. Benzene
Fig. 5. Molecular weight distribution for the 277-compound Goodman and Gilman
human oral bioavailability data set (left) and 1117-compound proprietary rat oral
bioavailability set (right).
Background Info on Drug Absorption
Fig. 3. From left to right, effect that dielectric capacity, electron affinity, polar surface
area, and aromaticity have on percent bioavailability.
Rotatable Bond Count
Fig. 6. Lipinski’s Rule of Five is used to identify orally active drugs.
Fig. 1-2. The longer the drug stays in the small intestine, which is the main location of
drug absorption, the greater its total absorption will be. Drugs are carried from the Fig. 13. Rotatable bonds in a molecule
blood supply directly to the liver through the portal vein when they reach the blood
vessels of the gastrointestinal tract. The liver is the main source of enzymes that
Other factors that affect bioavailability:
References
breaks down the drugs, so they must avoid being metabolized by those enzymes in
order to reach the circulatory system. Drugs that end up in blood vessels have to then ● Degree of ionization - pKa of 1. Pandey, Deepak S. Parul University. 2016.
molecule Fig. 4. Cluster diagram of drugs with over 2. Cooper GM. The Cell: A Molecular Approach. 2nd edition. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates; 2000.
be absorbed from those vessels via diffusion in order to reach their target site. 3. Turner, J.V., Maddalena, D.J. & Agatonovic-Kustrin, S. Bioavailability Prediction Based on Molecular Structure for a
● Chemical nature - size of molecule 20% bioavailability plotted against Diverse Series of Drugs. Pharmaceutical Research. 2004, 21(1), 68-82.
● Dosage form - affects disintegration rotatable bond count and polar surface 4. Lu, Jing J., et al. Influence of Molecular Flexibility and Polar Surface Area Metric on Oral Bioavailability in the Rat. J. Med.
Chem., 2004, 47(24), 6104–6107.
Fig. 3. The drug is absorbed across the and dissolution rate area. 5. Veber, Daniel F., et al. Molecular Properties That Influence the Oral Bioavailability of Drug Candidates. J. Med. Chem.
membrane of the stomach and intestines, ● Chemical stability - determines which 2002, 45(12), 2615-2623.
6. Chittimalla, S. K. Lipinski Rules.
which is made of phospholipids. The drug enzymes can metabolize the drug 7. Pharmacology in the Clinical Lab: Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Pharmacogenomics. LabCE.
has to be soluble in lipids in order to be Fig. 14. Different 8. Gavhane, Y.N., Yadav, A.V. Loss of orally administered drugs in GI tract.Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal, 2012, 20(4),
● Quality control - how the drug is
able to pass through the membrane. dosage forms. 331-344.
manufactured (e.g. inactive 9. Molecular Model of a Dielectric. Physics LibreTexts. 2018.
Molecules that are small and nonpolar are ingredients may be added to 10. Electron Affinity. Chemistry LibreTexts. 2018.
11. Chemical Bonding. Birdville Schools.
lipophilic, while large charged molecules influence the bioavailability) 12. Organic Chemistry: Aromatic Compounds. Ralph & Bev Shock.
are not. 13. Confab: rotatable bond detection. Open Babel. 2016.
14. https://www.dreamstime.com/royalty-free-stock-photography-dosage-form-drug-image26740087
You might also like
- Philippine National Formulary 8thED PDFDocument800 pagesPhilippine National Formulary 8thED PDFGio Mari Marcial100% (3)
- Pediatric Antibiotic Dosing ChartDocument1 pagePediatric Antibiotic Dosing Chartjimy babiNo ratings yet
- Fpgee Study Guide GurudattaDocument31 pagesFpgee Study Guide GurudattaWINSOMETAB33% (3)
- Polimero BiodegradableDocument16 pagesPolimero BiodegradableErika AriasNo ratings yet
- Orgmed Act 1 LabDocument3 pagesOrgmed Act 1 LabrlpmanglicmotNo ratings yet
- SihasoufuasoDocument10 pagesSihasoufuasosamitacalianNo ratings yet
- Lipids and Lipid-Processing Pathways in Drug Delivery and TherapeuticsDocument15 pagesLipids and Lipid-Processing Pathways in Drug Delivery and TherapeuticsVennyNo ratings yet
- Ijms 24 06970Document11 pagesIjms 24 06970y1ann1sNo ratings yet
- HERNANDEZ Assign3 PDFDocument3 pagesHERNANDEZ Assign3 PDFGrace HernandezNo ratings yet
- 2021-DD 01-IntroductionDocument36 pages2021-DD 01-IntroductionAlyamni AllNo ratings yet
- Molecular Properties That Influence The Oral Bioavailability of Drug CandidatesDocument10 pagesMolecular Properties That Influence The Oral Bioavailability of Drug Candidatesalifa ishmahdinaNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 PHARMACOLOGY - PrelimsDocument26 pagesNCM 106 PHARMACOLOGY - PrelimsKelsey Macaraig100% (3)
- 7 TargetedDocument17 pages7 Targeted5vz5qnfnsdNo ratings yet
- 01.25.01 Principles of Pharmacokinetics - Absorption and DistributionDocument10 pages01.25.01 Principles of Pharmacokinetics - Absorption and DistributionMikmik DGNo ratings yet
- Barry 2009Document9 pagesBarry 2009muammarNo ratings yet
- 1 Shifting: General Principles in Pharmacology: PharmacokineticsDocument4 pages1 Shifting: General Principles in Pharmacology: PharmacokineticsJustine Andrew RamirezNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 & 2Document14 pagesTopic 1 & 2Julianne Marie LacsentoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics - FINALDocument29 pagesChapter 3 - Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics - FINALAutumn Garofola100% (1)
- 46-Article Text-235-1-10-20111215Document5 pages46-Article Text-235-1-10-20111215Izza IsmahNo ratings yet
- Pesticide Biotransformation and Disposition Introduction To Pesticide Biotransformation and DispositionDocument3 pagesPesticide Biotransformation and Disposition Introduction To Pesticide Biotransformation and Dispositionpeli1494No ratings yet
- Medchemcomm: ReviewDocument14 pagesMedchemcomm: ReviewMehari AsratNo ratings yet
- Xenobiotic Metabolism and The Mechanism(s) of Benzene ToxicityDocument17 pagesXenobiotic Metabolism and The Mechanism(s) of Benzene ToxicitynurhalimahtrNo ratings yet
- My JournalDocument10 pagesMy JournalFelixNo ratings yet
- BDDCS Predictions, Self-Correcting Aspects of BDDCS Assignments, BDDCS Assignment Corrections, and Classification For More Than 175 Additional DrugsDocument10 pagesBDDCS Predictions, Self-Correcting Aspects of BDDCS Assignments, BDDCS Assignment Corrections, and Classification For More Than 175 Additional DrugsBagoes AsNo ratings yet
- 2015 Article 9845Document10 pages2015 Article 9845FelixNo ratings yet
- 5 - 2013 - Martinez - A Mechanistic Approach To Understanding The Factors Affecting DrugDocument24 pages5 - 2013 - Martinez - A Mechanistic Approach To Understanding The Factors Affecting DrugAHMAD ABDUL KHAFIDZNo ratings yet
- Med OrgDocument8 pagesMed OrgHannah Joy AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Reports: Gut Microbiota and Its Role in Metabolism of Common Drugs-A Short ReviewDocument6 pagesReports: Gut Microbiota and Its Role in Metabolism of Common Drugs-A Short ReviewwebcentrobioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PkokineticsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To PkokineticspdladvaNo ratings yet
- Toxicophores: Groups and Metabolic Routes Associated With Increased Safety RiskDocument13 pagesToxicophores: Groups and Metabolic Routes Associated With Increased Safety RiskMercedes ArmijosNo ratings yet
- Physicological Properties of Drug-1Document25 pagesPhysicological Properties of Drug-1Tanya SinghNo ratings yet
- Acsmedchemlett 9b00235Document4 pagesAcsmedchemlett 9b00235sarabindu_royNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Laboratory: Incompatibility: IncompatibiltyDocument2 pagesPharmacology Laboratory: Incompatibility: IncompatibiltyAlanis ApostolNo ratings yet
- Acer 13748Document70 pagesAcer 13748Mauricio FemeníaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacogenetics and PharmacogenomicsDocument25 pagesPharmacogenetics and PharmacogenomicsBogdan CoșmanNo ratings yet
- Target Drug Deliovery System UNIT - IVDocument18 pagesTarget Drug Deliovery System UNIT - IVS N A INSTITUTE OF PHARMACYNo ratings yet
- Environmental ToxicologyDocument65 pagesEnvironmental ToxicologyZulaikatu MustaphaNo ratings yet
- 4791-Article Text-13672-1-10-20210413Document6 pages4791-Article Text-13672-1-10-20210413Mohammed PhNo ratings yet
- Biopharm AssignmentDocument26 pagesBiopharm AssignmentPradhumn NamdeoNo ratings yet
- Chem in Everyday LifeDocument24 pagesChem in Everyday LifeSwapnil MandalNo ratings yet
- Molecules 21 00042Document31 pagesMolecules 21 00042amaliaNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Chemistry I 1435h: Drug Structure & Pharmacological ActivityDocument59 pagesMedicinal Chemistry I 1435h: Drug Structure & Pharmacological ActivityAbd ElraHman ElbahraWyNo ratings yet
- Kabanov Alexander V Pluronic Block Copolymers As Novel 2002Document24 pagesKabanov Alexander V Pluronic Block Copolymers As Novel 2002Francisco100% (1)
- The Role of BCS (Biopharmaceutics Classification System) and BDDCS (Biopharmaceutics Drug Disposition Classification System) in Drug Development Need To Be PrintedDocument9 pagesThe Role of BCS (Biopharmaceutics Classification System) and BDDCS (Biopharmaceutics Drug Disposition Classification System) in Drug Development Need To Be PrintedKimberly MccoyNo ratings yet
- Protein Drug BindingDocument26 pagesProtein Drug BindingBandita DattaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Cytotoxicity Studies of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide NanoparticlesDocument10 pagesComprehensive Cytotoxicity Studies of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide NanoparticlesDora PopescuNo ratings yet
- Ijn 257269 The Influence of Nanoparticle Properties On Oral BioavailabiDocument16 pagesIjn 257269 The Influence of Nanoparticle Properties On Oral BioavailabiLina WinartiNo ratings yet
- Amorphization 4Document10 pagesAmorphization 4Héctor PradoNo ratings yet
- Alqahtani 2021Document21 pagesAlqahtani 2021Karla SanchezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02. Molecular and Physicochemical Properties Impacting Oral Absorption of DrugsDocument21 pagesChapter 02. Molecular and Physicochemical Properties Impacting Oral Absorption of DrugsSava1988100% (1)
- Biochem Lec M-3Document13 pagesBiochem Lec M-3GE SalenNo ratings yet
- Lipid Nanoparticles: A Challenging Approach For Oral Delivery of BCS Class-II DrugsDocument15 pagesLipid Nanoparticles: A Challenging Approach For Oral Delivery of BCS Class-II DrugsnoviNo ratings yet
- Review of Stimuli-Responsive Polymers in Drug Discovery Development and DeliveryDocument16 pagesReview of Stimuli-Responsive Polymers in Drug Discovery Development and DeliveryЕгор Летов100% (1)
- PHARMA 02. PharmacodynamicsDocument11 pagesPHARMA 02. PharmacodynamicsCindy Mae MacamayNo ratings yet
- Art 00001Document8 pagesArt 00001Geo GeoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document6 pagesChapter 2FazeelaNo ratings yet
- Effect of PH and Ibuprofen On The Phospholipid Bilayer Bending ModulusDocument6 pagesEffect of PH and Ibuprofen On The Phospholipid Bilayer Bending ModulusJose Carlos Solis SuarezNo ratings yet
- Bp704t Ndds IVDocument18 pagesBp704t Ndds IVMILI G.No ratings yet
- Translational ADMET for Drug Therapy: Principles, Methods, and Pharmaceutical ApplicationsFrom EverandTranslational ADMET for Drug Therapy: Principles, Methods, and Pharmaceutical ApplicationsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Drug Design: Medicinal Chemistry: A Series of Monographs, Vol. 5From EverandDrug Design: Medicinal Chemistry: A Series of Monographs, Vol. 5E. J. AriënsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cell Surface Carbohydrate ChemistryFrom EverandCell Surface Carbohydrate ChemistryRobert E. HarmonNo ratings yet
- MDR-TB and XDR-TB: Ndoh 4 October 2006Document40 pagesMDR-TB and XDR-TB: Ndoh 4 October 2006Eta Calvin ObenNo ratings yet
- Nicolas, Krizha-Drug StudyDocument12 pagesNicolas, Krizha-Drug StudyKrizha Angela NicolasNo ratings yet
- DigoxinDocument2 pagesDigoxinIsabel Barredo Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy MCQs Practice Test 8Document4 pagesPharmacy MCQs Practice Test 8safa_sabaNo ratings yet
- Essentials of PharmacologyDocument26 pagesEssentials of PharmacologyCharlene DeleonNo ratings yet
- Handy Summary Chart Comparing The Main Medications For DepressionDocument2 pagesHandy Summary Chart Comparing The Main Medications For Depressionrowanpurdy100% (4)
- Formulary UpdatedDocument36 pagesFormulary UpdatedDipankar SahaNo ratings yet
- Usp 1151Document10 pagesUsp 1151Karnati PraveenaNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulant DrugsDocument7 pagesAnticoagulant DrugsNadia MohammadNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin ReviewDocument26 pagesVancomycin Reviewkhangsiean89No ratings yet
- Imp of Pharmacology: Batch: 2K19 Batch: 2K19 Batch: 2K19 Batch: 2K19 (HMT.) (HMT.) (HMT.) (HMT.)Document12 pagesImp of Pharmacology: Batch: 2K19 Batch: 2K19 Batch: 2K19 Batch: 2K19 (HMT.) (HMT.) (HMT.) (HMT.)movies linkNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Headache DisordersDocument2 pagesAssignment - Headache DisordersAyessa SalazarNo ratings yet
- Reconstitution and DilutionDocument337 pagesReconstitution and DilutionJaaydevNo ratings yet
- Abbreviation List Commonly Used in Medical Prescriptions (1507)Document1 pageAbbreviation List Commonly Used in Medical Prescriptions (1507)Muhannad AlshunaefNo ratings yet
- Podesta Military Tribunal Day Two - 4 May 2021Document3 pagesPodesta Military Tribunal Day Two - 4 May 2021Ronald Wederfoort100% (5)
- Empr Prescriber's EditionDocument420 pagesEmpr Prescriber's EditionPatel Pratyk100% (1)
- Certificate For COVID-19 Vaccination: Beneficiary DetailsDocument1 pageCertificate For COVID-19 Vaccination: Beneficiary DetailsManish VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Anticonvulsant DrugsDocument2 pagesAnticonvulsant Drugsshai padillaNo ratings yet
- PEDIATRIC Drug Formulary 2019-20Document56 pagesPEDIATRIC Drug Formulary 2019-20Eva Marie GonzalesNo ratings yet
- General Pharmacology - Sources of Drugs and Routes of AdministrationDocument48 pagesGeneral Pharmacology - Sources of Drugs and Routes of AdministrationDhriti Brahma78% (9)
- RA & Gout Case StudyDocument4 pagesRA & Gout Case StudyJossua RyanNo ratings yet
- Sustained and Controlled Release Drug Delivery SystemsDocument28 pagesSustained and Controlled Release Drug Delivery SystemsManisha Rajmane100% (2)
- MSN 571 Mid-Term Pharmacology QuestionsDocument13 pagesMSN 571 Mid-Term Pharmacology QuestionsNelson MandelaNo ratings yet
- Gentamicin SulfateDocument2 pagesGentamicin SulfateVlienkCruzNo ratings yet
- DepressionDocument10 pagesDepressionsalfaciNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pharmacokinetics: Deborah RobertsonDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacokinetics: Deborah RobertsonTheresa Tyra SertaniNo ratings yet
- Patient Information Leaflet Paediatric Paracetamol Elixir BP Paracetamol 120 mg/5 MLDocument4 pagesPatient Information Leaflet Paediatric Paracetamol Elixir BP Paracetamol 120 mg/5 MLmarhamatul laiyinahNo ratings yet
- Certificate For COVID-19 Vaccination: Beneficiary DetailsDocument1 pageCertificate For COVID-19 Vaccination: Beneficiary Detailspraharsh enuguriNo ratings yet