Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Valmed Patho
Uploaded by
Jez Rarang0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Original Title
VALMED PATHO
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views1 pageValmed Patho
Uploaded by
Jez RarangPATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
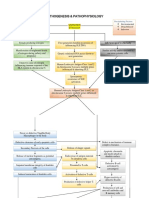
PREDISPOSING FACTOR PATHOPHYSIOLOGY PRECIPITATING FACTOR
Age, gender, heredity, race, Environment, drugs, infection,
hormones, history UNKNOWN lifestyle
ETIOLOGY
Female producing estrogen 1st generation familial possession Influencing agents in the body
of influencing SLE DNA
Increase level of estrogen Similar activity/structure to
Genetic relational DNA passes down to
our own systemic cell
ext generation
Unknown cause of estrogen
influencing immune response Human leukocyte antigen class 1 &2 in
of the human leukocyte system chromosome 6 possesses multiple
genes influencing in inheriting SLE
in chromosome 6
Occurrence of SLE
activation
Fewer or defective tangible body Defect in mechanism of
macrophages in the body immune complex
Human leukocyte antigen class 1
&2 in chromosome 6 posses clearance
multiple genes influenced in
inheriting SLE
Defective clearance of early
apoptotic cell Apoptic chromatin and
Release of danger signs nuclei attach to dendrite
Secondary necrosis of cell
Endocytose of antigen material by Defective B cell activation by
dendritic cell autoantigen
Release of nuclear fragments as
potential auto antigens
Presented to T cells Hyperactivity of defective B cell
Impaired membrane integrity of
dendrite cell
Activation of defective T cell Production of self and non-self
antibodies and B memory cells
Induced maturation of dendritic
cell Production of defective T
Negative abnormal B cell
cells contribution to already deficient
immune system
SYSTEMIC LUPUS
ERYTHEMATOSUS
You might also like
- Sle Concept Map Part 1Document1 pageSle Concept Map Part 1Vane UcatNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology Part 1Document1 pagePa Tho Physiology Part 1anonymous89ify100% (2)
- SLE Patogenesis & Patofisiologi PDFDocument8 pagesSLE Patogenesis & Patofisiologi PDFRIZQI IRFANSYAH100% (1)
- Pa Tho Physiology Sle, CompDocument5 pagesPa Tho Physiology Sle, CompHassan Bj MarabongNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematous: Precipitating Factors: Environmental Drug-Induced InfectionDocument10 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematous: Precipitating Factors: Environmental Drug-Induced Infectioninah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus PathophysiologyDocument8 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosus Pathophysiologykathy92% (24)
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus PathophysiologyDocument8 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosus PathophysiologySharmaineTaguitagOmli100% (1)
- Med 1.11 - SleDocument5 pagesMed 1.11 - SleZazaNo ratings yet
- Immunology-Serology: Autoimmunity: Compiled By: J.T Cayetano UST-MT 2019Document5 pagesImmunology-Serology: Autoimmunity: Compiled By: J.T Cayetano UST-MT 2019Joshua Ty CayetanoNo ratings yet
- SCIDDocument9 pagesSCIDgarimaupadhyay20002No ratings yet
- 18 IM 3.02 Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument8 pages18 IM 3.02 Systemic Lupus ErythematosusKaykie CalambaNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) : Genetic Factors Environmental FactorsDocument5 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) : Genetic Factors Environmental Factorsjoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase PTPN22 in Human AutoimmunityDocument9 pagesProtein Tyrosine Phosphatase PTPN22 in Human AutoimmunityAndrea AguirrePerezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 50 Assessment of Immune FunctionDocument12 pagesChapter 50 Assessment of Immune FunctionChan SorianoNo ratings yet
- Genetic Disorders - ReviewerDocument16 pagesGenetic Disorders - ReviewerDexcel concepcionNo ratings yet
- Biotech ReviewerDocument1 pageBiotech Reviewerdenmarkde22No ratings yet
- ImunitasDocument7 pagesImunitasdeeNo ratings yet
- Pertaining To Extracellular Fluid Such As Plasma and Lymph. The Term Humoral Immunity Is Used To Denote Antibody Mediated Immune ResponsesDocument4 pagesPertaining To Extracellular Fluid Such As Plasma and Lymph. The Term Humoral Immunity Is Used To Denote Antibody Mediated Immune ResponsesZhon CabitacNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lec - Week 2 - Topic 2Document3 pagesHistopath Lec - Week 2 - Topic 2Juren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Lupus: Earl Eugene Castro - Ab Biology 4 GeneticsDocument17 pagesLupus: Earl Eugene Castro - Ab Biology 4 GeneticsEARL CASTRONo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of SLEDocument16 pagesPathophysiology of SLESeff CausapinNo ratings yet
- I.S Transes Quiz 3Document23 pagesI.S Transes Quiz 3Nico LokoNo ratings yet
- LymphocytesDocument5 pagesLymphocytesLilyNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOHEMATOLOGYDocument126 pagesIMMUNOHEMATOLOGYmico guecoNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Diagnosis MechanismsDocument1 pageSystemic Lupus Erythematosus: Diagnosis MechanismsAndres DoblerNo ratings yet
- ApoptosisDocument2 pagesApoptosishihihi9898No ratings yet
- Chapter 29 Child With CancerDocument9 pagesChapter 29 Child With CancerMARCERA JERALDINE ALESSA P.No ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: ReviewDocument10 pagesPathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: ReviewAnia Scholastika PutriNo ratings yet
- Robbins Pathology - Chapter 6 TransDocument31 pagesRobbins Pathology - Chapter 6 Transnath nathNo ratings yet
- 3.5 - Genetic Modification and BiotechnologyDocument5 pages3.5 - Genetic Modification and BiotechnologyJulieta vazquezNo ratings yet
- Herpes Simplex Virus Infections: ReviewDocument6 pagesHerpes Simplex Virus Infections: ReviewUmmiNo ratings yet
- IMMUNE SYSTEM - MedSurgDocument5 pagesIMMUNE SYSTEM - MedSurgAdiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- IMMUNE SYSTEM Notes MidtermsDocument5 pagesIMMUNE SYSTEM Notes MidtermsAdiel Calsa100% (1)
- Introduction To Cellular AberrationDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Cellular AberrationAdiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- Esophagea L Cancer: By: Krizzia S. Bunagan-Legasi, RNDocument20 pagesEsophagea L Cancer: By: Krizzia S. Bunagan-Legasi, RNAnn SalvatierraNo ratings yet
- Study Stack - Immunology Final Table Review PDFDocument8 pagesStudy Stack - Immunology Final Table Review PDF장주연No ratings yet
- Nutrition and The Immune SystemDocument4 pagesNutrition and The Immune SystemMNo ratings yet
- ToleranceDocument39 pagesTolerancealka mehraNo ratings yet
- Robbins Pathology - Chapter 1 TransDocument11 pagesRobbins Pathology - Chapter 1 Transnath nathNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Otoimun Mkdu JoewonoDocument20 pagesKuliah Otoimun Mkdu JoewonoAyu Ratih PradnyaniNo ratings yet
- ImunoDocument16 pagesImunoLuan dos PNo ratings yet
- Principle and Classification of Auto-Immune DiseasesDocument42 pagesPrinciple and Classification of Auto-Immune Diseasesmanuel.mayin33No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Innate ImmunityDocument74 pagesChapter 4 Innate Immunity13701319477No ratings yet
- The Immune System in Health and DiseaseDocument30 pagesThe Immune System in Health and DiseaseApshar Munna100% (1)
- 4 Immunopathology (Page 131-168) .Kelik-2022Document38 pages4 Immunopathology (Page 131-168) .Kelik-2022Pola PhotographyNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Endterm Care of Clients With Problems in Cellular Aberrations Acute and ChronicDocument8 pagesNCM 112 Endterm Care of Clients With Problems in Cellular Aberrations Acute and ChronicApril FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Immune SystemDocument9 pagesDiseases of Immune SystemKhylle Camron LuzzieNo ratings yet
- ImmunoDocument49 pagesImmunoSharmaine L. LozanoNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 6 Infection and CytokinesDocument26 pagesLECTURE 6 Infection and Cytokinesxfxw5m5bczNo ratings yet
- Imunologi Tumor: Syarifuddin WahidDocument40 pagesImunologi Tumor: Syarifuddin WahidinhaNo ratings yet
- Sensory Neurons Link The Nervous System and Autoimmune DiabetesDocument3 pagesSensory Neurons Link The Nervous System and Autoimmune DiabetesGrigorina MitrofanNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOLOGY - 3 - Innate ImmunityDocument5 pagesIMMUNOLOGY - 3 - Innate ImmunityFelix NepumocenoNo ratings yet
- Signaling Comunication of Recognizing AntigenDocument17 pagesSignaling Comunication of Recognizing AntigenyulisaninasaraNo ratings yet
- The Immune System: Morphofunctional Peculiarities, Methods of Examination, Semiology of DiseasesDocument45 pagesThe Immune System: Morphofunctional Peculiarities, Methods of Examination, Semiology of DiseasesHIDE & ATTACKNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Factors Influencing Immune ResponseDocument4 pages4.1 Factors Influencing Immune Responsetinininiw69No ratings yet
- Epitope Spreading: Protection From Pathogens, But Propagation of Autoimmunity?Document7 pagesEpitope Spreading: Protection From Pathogens, But Propagation of Autoimmunity?carlosNo ratings yet
- STUDY GUIDE 2 (Operaña, Ellayza)Document4 pagesSTUDY GUIDE 2 (Operaña, Ellayza)OPERAñA ELLAYZA RB DECANONo ratings yet
- S.N. Characteristics Antigen Antibody: Antigen and Antibody Qno1. What Is Difference Between Antigen and Antibody?Document7 pagesS.N. Characteristics Antigen Antibody: Antigen and Antibody Qno1. What Is Difference Between Antigen and Antibody?maheen akramNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AuDocument3 pagesDrug Study AuJez RarangNo ratings yet
- Rarang Gina II-ADocument2 pagesRarang Gina II-AJez RarangNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: How Lupus Affects The BodyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: How Lupus Affects The BodyJez RarangNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesParacetamol Drug StudyJez RarangNo ratings yet
- Colon MassDocument1 pageColon MassJez RarangNo ratings yet
- Constipation HTP GeriaDocument6 pagesConstipation HTP GeriaJez RarangNo ratings yet
- TFNDocument2 pagesTFNJez RarangNo ratings yet
- TFNDocument2 pagesTFNJez RarangNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: NURSING CARE PLAN Functional Urinary IncontinenceDocument4 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: NURSING CARE PLAN Functional Urinary IncontinenceJez RarangNo ratings yet
- To Compare Rosuvastatin With Atorvastatin in Terms of Mean Change in LDL C in Patient With Diabetes PDFDocument7 pagesTo Compare Rosuvastatin With Atorvastatin in Terms of Mean Change in LDL C in Patient With Diabetes PDFJez RarangNo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport PowerpointDocument50 pagesCellular Transport PowerpointPortia EgkenNo ratings yet
- Hematology QuizDocument7 pagesHematology Quizsanwel80% (5)
- Final BiochemistryDocument6 pagesFinal BiochemistryHuyen Tram NguyenNo ratings yet
- Cells PowerpointDocument49 pagesCells Powerpointapi-272720493100% (1)
- SLM Number 4-Grade 7 Science - 2nd-Quarter - Plant - and - Animalcell-2Document16 pagesSLM Number 4-Grade 7 Science - 2nd-Quarter - Plant - and - Animalcell-2Maria Fe Vibar100% (5)
- Biology Introduction GuideDocument1 pageBiology Introduction GuideAna Lucia Lozada NoeNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Leukocyte-Platelet-Rich Plasma On Accelerated Orthodontic Tooth Movement in RabbitsDocument9 pagesThe Influence of Leukocyte-Platelet-Rich Plasma On Accelerated Orthodontic Tooth Movement in RabbitsMustafa AlsultanNo ratings yet
- Bootcamp's Step 1 Study ScheduleDocument8 pagesBootcamp's Step 1 Study Schedulecfqbcm5swbNo ratings yet
- Palmit072012slr PDFDocument22 pagesPalmit072012slr PDFGalina TodorovaNo ratings yet
- PROF ED. 213: Genetics: Cytological Bases of HeredityDocument40 pagesPROF ED. 213: Genetics: Cytological Bases of HeredityRonald DawalNo ratings yet
- Pea and Spinach Cell Fractionation and Differential CentrifugationDocument5 pagesPea and Spinach Cell Fractionation and Differential CentrifugationBrittany RockeyNo ratings yet
- Reti No IdesDocument15 pagesReti No IdesRobertoNo ratings yet
- CATCH Up Friday April 26, 2024 Poem BiomoleculesDocument2 pagesCATCH Up Friday April 26, 2024 Poem BiomoleculesAna Marie GanibanNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Free Response Questions Through 2010Document44 pagesAP Biology Free Response Questions Through 2010Bob100% (1)
- BIOL1040 Lecture NotesDocument50 pagesBIOL1040 Lecture NotesJonathanZhaoNo ratings yet
- NMAT BiologyDocument14 pagesNMAT Biologyerlymae100% (3)
- Chapter 9 NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 9 NotesjanetotheohNo ratings yet
- BCH 206 CholesterolDocument3 pagesBCH 206 CholesterolNewtonNo ratings yet
- BIOC4610 Continuous Assessment 2021Document4 pagesBIOC4610 Continuous Assessment 2021Rainbow HuiNo ratings yet
- Bas 121 Biochemistry 2 - 0 - 2 3 TheoryDocument1 pageBas 121 Biochemistry 2 - 0 - 2 3 Theoryjyotiraditya palNo ratings yet
- Transcription & Translation ColoringDocument2 pagesTranscription & Translation ColoringBesty MaranathaNo ratings yet
- Post-Lab Biochem 1aDocument5 pagesPost-Lab Biochem 1aOla Anna GamutinNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi MalariaDocument9 pagesPatofisiologi MalariaRasyid RidhaNo ratings yet
- Uji in Vitro Vaksin DNA Pengekspresi Ant PDFDocument9 pagesUji in Vitro Vaksin DNA Pengekspresi Ant PDFisvana dalailaNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication - PWDocument133 pagesDNA Replication - PWSantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Gene Linkage and Genetic MappingDocument32 pagesGene Linkage and Genetic MappingM Ian Benedict MaruyaNo ratings yet
- 01-Cell DivisionDocument21 pages01-Cell DivisionSENGUPTA CHANDANNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Idexx Procyte DX Hematology Analyzer Dot PlotsDocument4 pagesInterpreting Idexx Procyte DX Hematology Analyzer Dot PlotsWael SafwatNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of The EyeDocument38 pagesBiochemistry of The EyeYusuf Almalik SaputraNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument17 pagesUntitledrohit singhNo ratings yet