0% found this document useful (0 votes)
503 views25 pagesR Scatter Plot Guide for Analysts
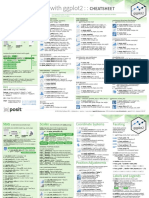
ggplot2 is an R package for data visualization, including creating scatter plots. This document provides examples of how to:
1) Create basic scatter plots and customize the appearance of points and lines using functions like geom_point() and geom_smooth().
2) Create scatter plots with multiple groups and change point colors, shapes, and sizes automatically or manually using scales.
3) Add elements like marginal rugs, 2d density estimations, ellipses, and rectangular bins to scatter plots using functions like geom_rug() and stat_ellipse().
Uploaded by
icen00bCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
503 views25 pagesR Scatter Plot Guide for Analysts
ggplot2 is an R package for data visualization, including creating scatter plots. This document provides examples of how to:
1) Create basic scatter plots and customize the appearance of points and lines using functions like geom_point() and geom_smooth().
2) Create scatter plots with multiple groups and change point colors, shapes, and sizes automatically or manually using scales.
3) Add elements like marginal rugs, 2d density estimations, ellipses, and rectangular bins to scatter plots using functions like geom_rug() and stat_ellipse().
Uploaded by
icen00bCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd