0% found this document useful (0 votes)
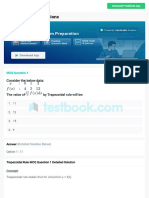
779 views9 pagesF (X, Y) Sin (Xy) + X LN (Y) Find F at (0, )
1. The document contains questions about calculus concepts such as derivatives, limits, continuity, Taylor series, and extremum values of functions.
2. It asks the reader to identify the correct answers for questions related to finding derivatives, limits, critical points, Taylor series expansions, and determining maximum/minimum values of functions.
3. The questions cover a wide range of calculus topics and concepts including Rolle's theorem, mean value theorem, Taylor's theorem, and determining extremum values using the second derivative test.
Uploaded by
muhammad abrarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
779 views9 pagesF (X, Y) Sin (Xy) + X LN (Y) Find F at (0, )
1. The document contains questions about calculus concepts such as derivatives, limits, continuity, Taylor series, and extremum values of functions.
2. It asks the reader to identify the correct answers for questions related to finding derivatives, limits, critical points, Taylor series expansions, and determining maximum/minimum values of functions.
3. The questions cover a wide range of calculus topics and concepts including Rolle's theorem, mean value theorem, Taylor's theorem, and determining extremum values using the second derivative test.
Uploaded by
muhammad abrarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd