Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abstract Algebra: Cucbcss
Uploaded by
JibruOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Abstract Algebra: Cucbcss
Uploaded by
JibruCopyright:
Available Formats
School of distance education
CALICUT UNIVERSITY
SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION
ABSTRACT ALGEBRA
(V th sem BSc Mathematics, Core course)
CUCBCSS
Prepared by
Aboobacker P
Assistant Professor
WMO College, Muttil
QUESTION BANK
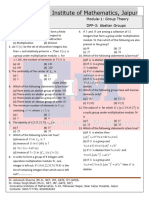
1. Which of the following is a binary structure ?
a. (a)(N , -) (b) ( Q, + )
b. ( c ) (Z, ÷ ) (d) None of these
2. Which of the following pairs are isomorphic binary structures
(a). (Q,+) and (R,+) (b)(R,+) and (R+, ×)
(c) (z,+) and (R,+) (d) None of these
3. Which of the following defines a binary operation on Z+ ?
(a) a b a b
(b) a b c , where c is the smallest integer greater than both a and b .
(c) a b c , where c is at least 5 more than a b .
(d) a b c , where c is the largest integer less than the product of a and b .
4. Let Z be a set of integers, then under ordinary multiplication (Z,*) is
(a) Group (b) Semi group
(c) Monoid (d) None of these
5. If b and c are the inverses of some element a in a group G then :
a. (a) b c (b) b c
b. (c) b kc forsome k N (d) None of these
6. Under which of the following binary operation, the set of positive integers is closed?
a. (a) b a b a/b ( b) a b a b
2
b. (c) ab= a b ( d) a b √ ab
7. On Q, which of the following does not define a binary operation?
a. ( a) a b | a | b (b) a b (a b)2
b. (c) a b √ ab (d) None of these
+
8. Let be defined on Q as a b ab/2 . Then identity for this binary operation is:
(a) 1 ( b) 2
Abstract Algebra Page 1
School of distance education
(c) 0 (d) None of these
9. The operation* on Q* of nonzero rational numbers defined by a*b= ab/2 is
(a) Not Commutative ( b) Not Associative
(c) Both commutative and associative (d) Neither commutative nor associative
10. The set of real numbers the operation addition is ……….
(a ) Not a group (b)Abelian but not cyclic
(c)Not Abelian but cyclic (d) A group but not abelian
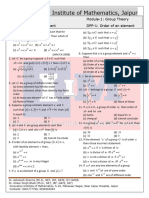
11. The order of the subgroup of Z4 generated by the element 3 is :
a. ( a) 3 (b) 4 (c) 2 (d) 1
12. Which of the following is a group?
(a) All n n diagonal matrices under addition
(b) All n n diagonal matrices under matrix multiplication
(c) All n n upper triangular matrices under matrix multiplication
(d) None of these
13. Let G be a group and let a b c e for a,b, c G . Then b c a equals :
(a) a ( b) e (c) b ( d) None of these
14. Let be the binary operation defined on Q+ as a b ab/2 . Then inverse of the element a is:
(a) 2 a (b) 4/a (c) a2 (d) None of these
15. Value of the product ( 11 ) ( - 4 ) in Z15 is :
(a) -1 (b) 1 (c) 0 (d) None of these
16. The set {1,2,3,4} is an abelian group under the operation………..
(a) Addition ( b)Addition modulo 5
( c)Multiplication modulo 4 ( d)Multiplication modulo 5
17. Which of the following set ,addition is not a binary operation?
(a) Complex numbers (b) Real numbers
(c) Non zero real numbers (d) Integers
18. How many binary operations can be defined on a set S with exactly n elements?
(a)nn (b) (c)n! (d)n2n
19. The set defined by {0 ,1,2,3,4,5} under the operation addition modulo 6 is……..
(a) (a group but not abelian ( b ) Both abelian and cyclic
(b) ( c )Not Abelian but cyclic (d) Abelian but not cyclic
20. Which of the following are true?
(1) A group may have more than one identity element
(2) Any two groups of three elements are isomorphic
(3) Every group of at most three elements is abelian
(a) 2&3 (b) 1&2 (c) 1&3 (d) All
21. The order of the symmetric group S3 is ………………….
(a) (a)3 (b)6 (c ) 12 (d)4
22. Let G= {1, -1, i, -i} where , be a set of four elements. Which of the following is a binary operation on
G? (1) a b a b (2) a b a.b
a. (a) Only 1 (b) Only 2 (c) Both (d) None of these
23. The order of 2 in the group (Z, + ) ,where Z is the set of integers is ………………..
a. (a )0 (b) 4 ( c)not defined ( d)infinity
24. Suppose a group G has an element x such that ax x for all a , then the number of elements in G is
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 5 (d) 7
25. How many non-trivial proper subgroups does the Klein 4-group have?
(a) (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3
Abstract Algebra Page 2
School of distance education
26. H and K are subgroup of a group G, then which of the following is a group?
( a) H U K (b) HK
(c )H ∩ K ( d)KH
27. Let G= C* ( non zero complex numbers). Which of the following are subgroups of G?
(1) All purely imaginary complex numbers under multiplication.
(2) All complex numbers with absolute value 1 under multiplication.
(b) (a) Only 1 (b) Both (c) Only 2 (d) None of these
28. Which of the following are true?
1) (Z6, +6 ) is a subgroup of (Z, + ).
(2 )Un (n th root of unity) is a subgroup of (C* , . )
(3) (Q+ , . ) is a subgroup of (R, +)
(a) Only 1 (b) Only2 (c) Only3 (d) All
29. The number of elements of order 2 in a cyclic group of even order is …………….
(a)1 (b) 2 (c)4 ( d)None of these
30. In a group G , a b)2 a2 b2 for all a,b G . This statement is:
(a) Always true (b) True if G is finite
(c) True if G is a multiplicative group (d) True if G is abelian
31. The number of elements in S3 satisfying the condition x2= e is…
(a)1 (b)2 (c)3 (d)4
32. Which of the following is not true?
( a)( Z,) is a proper subgroup of( R, ) ( b) ( Q+, . ), is a proper subgroup of (R+ ,.)
(c)( 3Z,) is a proper subgroup of( Z, ) (d) (Q+, ), is a proper subgroup of (R, )
33. If a group G is of order 31,then which of the following is false?
(a) (a) G is abelian (b) G is cyclic
(b) (c ) G is abelian but not cyclic (d) Both abelian and cyclic
34. Let k be a fixed positive integer and let kZ kn / n Z. Then :
(a) kZ, is a group which is isomorphic to R,
(b) kZ is not a group with respect to addition
(c) kZ, is a group which is isomorphic to Z,
(d) None of these
35. The Klein 4- group is isomorphic to __________
(a) Z2 Z4 (b) Z2 Z2 (c) Z4 (d) None of these
36. The elements of order 8 in the group (Z8 ,+8) is………………
( a)4 (b) 5 ( c)6 (d) 8
37. If G is a group of order four. Which of the following are not true?
(1) There exist a ԑ G such that a2= e
(2) There exist a ԑ such that a3 =e
(3) G is abelian
(a) Only 2 (b) 1&2 (c) Only 3 (d) All
38. Order of (2,2) in Z4× Z6 is …………………….
(a)2 (b) 6 ( c). 4 (d)12
39. Consider with the binary operation m* n = 2m + n. Which of the following are true?
(1) is commutative (2) is associative
(a) Only1 (b) Only2 (c)All (d) None of these
40. Let (G,* ) is a group. Which of the following are not always true?
(1)(a-1)-1= a (2) (a*b)-1 = b-1* a-1 for all a, b in G (3)(a*b) = (b*a) for all a, b in G
Abstract Algebra Page 3
School of distance education
(a) Only 1 (b) Only 3 (c) Only 2 (d) 1&2
41. If a and a2 are both generators of a cyclic group G of order n, then
a) n must be odd b) n must be even
c) n must be prime d)n must not be a prime
42. Which of the following is a non-abelian group with the property that each proper subgroup is
abelian?
(a) S3 (b) Z8 (c) S5 (d) None of these
43. The center of an abelian group G is:
a) {e} b) G c) A cyclic subgroup d) None of these
44. G is a group such that a2 = e , for all a in G then
(a) (a)G is cyclic (b) G is abelian
(b) ( c) G is finite (d)G has a subgroup which is not normal
45. Let G be a cyclic group of order 6. Then the number of elements g G such that G = < g > is :
( a) 5 (b) 3 (c) 2 (d) 4
46. G is a group of order n and a ԑ G,then am =e iff:
a)n divides m b)m divides n c)m is a power of n d)n is a power of m
47. Which of the following is true?
(a) Every cyclic group has a unique generator
(b) In a cyclic group, every element is a generator
(c) Every cyclic group has at least two generators
(d) None of these
48. If a, b are elements of a group G of order m then order of ab and ba are:
(a) same (b) Equal to m (c) unequal (d) None of these
49. Let G be a cyclic group of order 7. Then the number of elements g G such that G = < g > is :
(a) 5 (b) 3 (c) 7 (d) 6
50. G is a cyclic group of order 18, then which is true
(a )G has a subgroup of order 4 (b) G has a subgroup of order 6
(c ) G has a subgroup of order 5 (d)G has a subgroup of order 7
51. How many elements are there on the cyclic subgroup of Z30 generated by 25?
(a) 3 ( b) 6 ( c) 5 (d) None of these
52. Number of elements in the cyclic subgroup of the group of non-zero complex numbers under
multiplication, generated by, (1 i)/√2 is:
( a) 4 (b) 8 (c) 6 (d) None of these
53. Which of the following is a cyclic group with only one generator?
(a) Z2 (b) (Z,) ( c) Klein-4 group (d) None of these
54. Which of the following is a true statement?
(a) Every abelian group is cyclic (b) All generators of Z20 are prime numbers
(c) If G1 ,G2 are groups, then G1 G2 is a group (d) None of these
55. If a is a generator of a cyclic group G,then
(a) a2 is a generator (b) a-1 is a generator
(c )G has no other generators ( d)Every subgroup of G is generated by a
56. How many generators are there for an infinite cyclic group?
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 4 (d) Infinitely many
57. klien-4 group is
(a) A cyclic group (b) All its proper subgroup is cyclic
(c ) have only three proper subgroups (d )not abelian
58. Which of the following is an example for a cyclic group with four generators?
Abstract Algebra Page 4
School of distance education
(a) Z8 (b) Z6 (c) Z9 (d) Z,
59. The least common multiple of r,s Z is rs if and only if:
(a) r,s are relatively prime (b) One of them is a prime
(c) Both are prime (d) None of these
60. Which of the following is not true?
(a) Every cyclic group of order > 2 has at least two distinct generators
(b) If every proper subgroup of G is cyclic, then G itself is cyclic
(c) Every sub group of a cyclic group is cyclic
(d) None of these
61. G is a group of order pq, where p and q are prime numbers ,then
(a) G has a proper subgroup which is non cyclic ( b )G has a non abelian proper subgroup
( c)all its proper subgroup is cyclic ( d ) all its subgroups are noncyclic
62. How many elements are there in the subgroup generated by 4,6 , of the group Z12 ?
(a) 1 (b) 6 (c) 4 ( d) None of these
123456 7
63. The number orbits of the permutation is………..
2714635
(a)1 (b)2 ( c) 3 (d) 4
64. Which of the following is an order of a non abelian group
(a )19 (b)21 ( c)23 ( d) 25
123456
65. Which is the cyclic decomposition of the permutation
231465
(a)(231)(65) (b)(321)(56) ( c ).(123)(456) (d)(1234)(56)
123456
66. If = the order of the cyclic subgroup generated by is:
314562
(a) 6 (b) 12 (c) 4 (d) None of these
123456 6
67. Let = Then equals:
314562
123456 123456 123456
(a) (b) (c) (d) None of these (46)
314562 123456 314562
68. The product (1 3 6)(2 4) of two permutation is
123456 123456 123456 123456
(a ) ( ) ( b) . ( c). ( d).
346251 312546 235614 235461
123456
68. Let = , then the orbit of 1 under this permutation is:
241265
(a) 1,2,3,4 (b) 1,2,3,4,5 (c) 1,2,3, (d) None of these
69. Which of the following is a permutation function on R?
(a) f (x) x2 (b) f (x) ex (c) f (x)= x3 - 2x2 (d) f (x) x 1
70. Order of the permutation (4 5)(2 3 7) in S7 is
(a) 2 (b) 3 (c )5 (d)6
71. Which of the following is true?
(a) Every function is a permutation if and only if it is one to one.
(b) The symmetric group S3 is cyclic
(c) The symmetric group Sn is not cyclic for any n.
(d) Every function from a finite set onto itself must be one to one.
72. How many orbits are there for the permutation : Z Z , defined by (n) n 1 ?
(a) 2 (b) 1 (c) 3 (d) infinitely many
73. The set of of solution of x2-5x+6 =0 in Z12 is
(a ).{2,3,4} (b) {2,3} (c ) {.2,3,6} ( d){2,3,6,11}
74. How many orbits are there for the permutation : Z Z , defined by (n) n 2 ?
(a) 2 (b) 1 (c) 3 (d) infinitely many
Abstract Algebra Page 5
School of distance education
75. Legrange theorem is
(a) Every group of prime order is cyclic
(b) Order of the subgroup divides the order of the group
( c ) Order of an element divide the order of the group.
(d).None of these
76. Which of the following is an even permutation?
12345678 12345678 12345678
(a) (b) c) d) None of these
34516218 2 1 4 53 7 8 6 14352687
77. Which of the following is not true?
(a) Every cycle is a permutation (b) A3 is a commutative group
(c) A5 has 120 elements. (d) None of these
78. The order of ( 8, 10 ) in Z12 Z18 is:
(a) 9 ( b) 6 (c) 8 (d) None of these
79. Cayley’s theorem is
a). Order of the subgroup divides the order of the group
b).Every group is isomorphic to a group of permutations
C).Every group is isomorphic some cyclic group
d).Every group of prime order is cyclic
80. G= {1,ω , ω2 } ,where ω is the cube root of unity, then G under multiplication is
a). Not a group b). A group but not abelian
c). An abelian group but not cyclic d). Both abelian and cyclic
81. Index of the subgroup 5Z in (Z,+ ) is
a) 3 b).5 c)7 d)infinite
82. The number of cosets of the subgroup 3Z in (Z,+) is ……..
a)2 b).3 c) Infinite d)Cannot be determined
83. The order of ( 3, 10, 9 ) in Z4 Z12 Z15 is:
( a) 30 (b) 120 (c) 60 (d) None of these
84. What is the largest possible order of a cyclic subgroup of Z12 Z15 ?
(a) 60 (b) 30 (c) 180 (d) None of these
85. The cyclic subgroup of Z24 generated by 18 has order____________
(a) 4 (b) 6 ( c) 9 (d) None of these
86. If H is a subgroup of a group G. Then the index of H in G is
a)O(G) / O (H) b) O (H)/ OG) c) O(G) O(H) d) None of these
87.Suppose G is a group of order 29. Then which of the following is true?
(a) G is not abelian
(b) G has no subgroup other than (e) and G
(c) There is a group H of order 29 which is not isomorphic to G
(d) G is a subgroup of a group of order 30
88. In a non-abelian group the element a has order 108. Then the order of a 12 is:
(a) 54 (b) 27 (c) 18 (d) 9
89. If G is a group with no proper nontrivial subgroups, then G is:
( a) Not abelian (b) Cyclic (c) Isomorphic to Z, (d) An infinite group
90. How many automorphisms are there on the group Z12 ?
(a) 4 (b) 3 (c) 1 (d) None
91. How many subgroups are there for the group Z12 ?
(a) 6 (b) 2 (c) 4 (d) None of these
92.The inverse of the element 3 in the group (Z8 ,+8 ) is
a) 3 b).5 c)4 d)0
Abstract Algebra Page 6
School of distance education
93. Which of the following group has no proper non trivial subgroups?
(a) Z21 ( b) Z23 (c) Z, (d) Klein-4 group
94. Kernal of the homomorphism f: R* R* under multiplication is
a) {1} b).{-1,1} c) {0,1} d){-1,0 1}
95. How many cosets are there of the subgroup 4Z of 2Z ?
(a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 1
96. Which of the following is not a coset of the subgroup ( 4) of Z12 ?
(a) 1,5,9 (b) 2,6,10 (c) 0,4,8 ( d) None of these
97. The index of the subgroup ( 3) in Z24 ?
(a) 3 (b) 6 (c) 2 (d) 4
98 .f is a homomorphism f :( R,+) → (Z,×) such that f(2 )=3.then f(6) I is
a)6 b)9 c)18 d)27
99. If 1,2,4,53,6 , then the index of in S6 ?
(a) 120 (b) 160 ( c) 180 (d) None of these
100. f is a one one homomorphism from a group G1 to G2. Then Ker( f) is
a). G1 b) {e} c). have more than one element d)None of these
101. If 1,2,5,42,3 , then the index of in S5 ?
(a) 120 (b) 16 (c) 24 (d) None of these
102. Which of the following is not true?
(a) Every subgroup of every group has left cosets
(b) A subgroup of a group is a left coset of itself
(c) An is of index 2 in Sn for n > 1
(d) None of these
103. Let G be a group having elements a and b such that O(a) 4,O(b) 2 and a3 b ba . Then O(ab)
equals:
( a) 12 (b) 24 (c) 6 (d) 2
104. The number of elements of order 12 in the group Z12, ,12 )is:
(a) 4 (b) 6 (c) 12 (d) 2
105. Let G be any group and ϕ:G G, ϕ (g) g-1 g G. Then:
(a) is a homomorphism (b) is a homomorphism if g is a finite group
(c) is a homomorphism if g is abelian (d) is a homomorphism if and only if g is cyclic
106 . f is a homomorphism from a group G1 to a group G2,then which is false
a). f should be one one b) f may not be one one
c)f can be one one d) f may be onto
107. Let : Z Z7 be a homomorphism such that (1) 4 . Then Ker() equals:
(a) Z (b) 4Z (c) 7Z (d) None of these
108.What is the value of (25), where : Z Z7 be a homomorphism such that (1) 4 ?
(a) 0 (b) 2 (c) 4 (d) 7
109. How many homomorphisms are there of Z onto Z ?
(a) 2 (b) 1 (c) None (d) Infinitely many
110. Which of the following is true ?
(a) Every cyclic group has prime order (b) Every abelian group is cyclic
(c) Every group of prime order is cyclic (d) None of these
111. The sign of an even permutation is +1 and that of an odd permutation is -1. Let sgnn : Sn
1,1 be the homomorphism of Sn onto the multiplicative group defined by s ngn () = sign of .
Then kernel of is:
(a) Sn (b) An (c) { Identity permutation } (d) None of these
Abstract Algebra Page 7
School of distance education
112. How many elements are there in the factor group Z6 /( 3) ?
(a) 3 ( b) 2 ( c) 4 (d) 6
113. Which of the following is true?
(a) Every homomorphism is a one to one map
( b) A homomorphism may have an empty kernel
(c) For any two groups G and K, there exists a homomorphism of G into K
(d) For any two groups G and K, there exists an isomorphism of G onto K
114. How many elements of finite order are there in Z2 Z Z4 ?
(a) 4 ( b) 6 ( c) 8 (d) Infinitely many
115. Let U be the multiplicative group of complex numbers of modulus 1 and let :R, U be the
homomorphism defined as (x)= e2 i x , xR . Then the kernel of is:
(a) R (b) Z (c) 2Z (d)
116. If G is an infinite cyclic group, then how many generators are there for the group G?
(a) Exactly two (b) At least two (c) Infinitely many (d) Only one
117. G is a cyclic group of order 15, then which is true
a) G has a subgroup of order 4 b) G has a subgroup of order 6
c) G has a subgroup of order 5 d) G has a subgroup of order 7
118.A cyclic group with only one generator can have at most ------ elements
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) infinitely many
119.The set of nonzero real numbers the operation addition is ……….
a). Not a group b).Abelian but not cyclic
c).Not Abelian but cyclic d) A group but not abelian
120..The number of generators of the cyclic group of order 18 is.
(a) 4 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 6
121. Which of the following is a homomorphism of groups?
(a) : R Z ; (x) the greatest integer x .
(b) : R R ; (x) I x I under addition
(c) : Z9 Z2 ; (x) the remainder of x when divided by 2
(d) R+ R+ ; ( x) I x I under multiplication.
122. The set M2(R) of all 2×2 matrices with real entries have……………….
a)No zero divisors b)only two Zero devisors
c)Infinite number of zero divisors d)None of these
123. The ring of complex numbers is
a) not an integral domain b) an integral domain c).Ordered set d) none of these
124. How many units are there in the ring Z Q Z ?
(a) 4 (b) 6 (c) Infinitely many (d) none of these
125.The order of the ring M2 (Z2) of all 2 by 2 matricec with entries in Z2 is :
(a) 4 (b) 8 (c) 16 ( d) None of these
126. Let Z be the set of integers, then (Z,+,× ) is not a …………
a)Field b)Integral domain c)Commutative ring d)None of these
127.Characteristic of an intergral domain is
a) a prime number b)not a prime number c).Can be any number d) an even number
2
128. A solution for the quadratic equation x + x -6 0in the ring Z14 is:
(a) 3 (b) 7 (c) 6 (d) 4
129. How many units are there in the ring Z Z ?
(a) 2 (b) 4 (c) 1 (d) None of these
130. Which of the following is not a cardinality of a field?
Abstract Algebra Page 8
School of distance education
a)6 b)4 c)27 d)7
131. Which of the is true
a)(Z,+,×) is an integral domain b) (Z4 ,+4 , × 4) is an integral domain
c) (Z,+,×) is a field d)( R,+,×) is not an integral domain
132. Which of the following is not true?
(a) Every element in a ring has an additive inverse
( b) Multiplication in a field is commutative
(c) Addition in every ring is commutative
(d) Every ring with unity has at most two units
133. A solution for the quadratic equation x2 2 x 4 0 in the ring Z6 is:
(a) -2 (b) 3 (c) 2 (d) 1
134. Which of the following ring have a non zero characteristic?
( a) Z3 3Z (b) Z Z (c) 2Z ( d) None of these
135.What is true about M3( R ) of 3×3 matrices under matrix addition and multiplication
a)an integral domain b)a commutative ring with unity
c).a non commutative ring with unity d) a non commutative ring without unity.
136. Zero divisor is in (Z6, + 6 , ×6 ) are
a) {1,2,3} b){2,3} c) {2,3,4} d){2}
137. Th set of units in (Z6, + 6 , ×6 ) is
a){1, 5} b){1,2,3,4} c){1,2,3} d){2,3,4}
138. What is the characteristic of Z3 Z4 ?
(a) 12 (b) 4 (c) 3 (d) None of these
139. Which of the following is true?
(a) The characteristic of nZ is n. (b) nZ has zero divisors if n is not a prime
(c) As a ring , Z is isomorphic to nZ;n 1 (d) None of these
140. The solution for the equation 3x = 2 in the field Z7 is:
(a) 2 (b) 4 (c) 3 (d) 5
141. Which of the following is true
a) Every integral domain is a field b).Every field is an not an integral domain
c).Every finite integral domain is a field d) Every infinite integral domain is a field
142. How many ring homomorphisms are there from Z to Z?
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4
143.Which of the following is a zero divisor in the ring Z10 ?
(a) 3 (b) 5 (c) 7 (d) 9
144. Characteristic of the ring( Z, +, .) is
a)infinite b) 0 c) not exist d)none of these
145.Example of an integral domain which is not a field is
a)( R, +, .) b)(Q, + , .) c)(Z5 ,+5, ×5) d) (Z, +, .)
146. H is a subgroup of G such that aH = Ha, a in G. Then
a) H is normal subgroup b)H is cyclic c)H is abelian d) none of these
147.The numbe of elements in the coset of subgroup H of of a group G is
a)infinite b) same as order of H c) same as order of G d)none of these
148. R be a ring with unity, then characteristic of R is
a) same as order of 1 b)0 c)cannot be determined from given data d)None
149. Integral domain is :
a)a commutative ring with unity and with zero divisors
Abstract Algebra Page 9
School of distance education
b)a commutative ring with unity and no zero divisors.
c)May not be commutative ,must have zero divisors
d) May be commutative ,no zero divisors
150. Which is wrong about skew field ?
a)a commutative ring with unity
b)every filed is a skew field
c) Every nonzero element has multiplicative inverse
d)There exist some non zero element whose multiplicative inverse does not exist.
Answer Key
1.b 2.b 3.b 4.c 5.a 6. C 7.c 8. B 9. A 10. B 11.a 12. A 13.b 14.b 15.b 16.d 17.b
18.b 19.b 20.a 21.b 22.b 23.d 24.a 25.d 26.c 27.c 28.b 29.b 30.d 31.d 32.d 33.d 34.c
35.b 36.a 37.a 38.b 39.d 40.b 41.a 42.b 43.b 44.b 45.c 46.a 47.c 48.a 49.d 50.b 51.b
52.a 53.a 54.c 55.b 56.b 57.b 58.a 59.a 60.a 61.c 62.b 63.a 64.b 65.a 66.a 67.b 68.a
68.a 69. a 70. d 71.a 72.b 73.d 74.b 75.b 76.a 77.c 78.a 79. B 80. D 81.b 82.b 83.c
84.a 85.a 86.a 87.b 88.d 89.b 90.a 91.a 92.b 93.b 94.b 95.a 96.d 97. A 98.d 99.c 100.b
101.c 102.d 103.d 104.a 105.c 106.a 017.c 108.b 109.a 110.c 111.b 112.a 113.c 114.c
115.b 116.a 117.c 118.a 119.a 120.d 121.d 122.c 123.b 124.c 125.c 126.a 127.a 128.d
129.b 130.a 131.a 132.d 133.c 134.d 135.c 136.c 138.a 139.d 140.c 141.c 142.b 143.b 144.b
145.d 146.a 147.b 148.a 149.b 150.a
Abstract Algebra Page 10
You might also like
- DPP-3 Abelian GroupsDocument2 pagesDPP-3 Abelian GroupsTechnical IndiaNo ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics 18Mab302T - Discrete Matheamtics UNIT - IV: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 pagesDepartment of Mathematics 18Mab302T - Discrete Matheamtics UNIT - IV: Multiple Choice QuestionsNitish KumarNo ratings yet
- PPSC Paper 2011 (Lecturer in Mathematics)Document9 pagesPPSC Paper 2011 (Lecturer in Mathematics)saifoxford345No ratings yet
- Test Topology 2nd August BTCH JuneDocument1 pageTest Topology 2nd August BTCH JuneanamNo ratings yet
- 1 Problems On Group Theory (By Dr. J. G. Mehta)Document11 pages1 Problems On Group Theory (By Dr. J. G. Mehta)AkankshaNo ratings yet
- AlgebraDocument16 pagesAlgebraYoshuva0% (1)
- Check Your ProgressDocument9 pagesCheck Your Progresscloud.domain23No ratings yet
- ECAT MATHS MCQs PDFDocument2 pagesECAT MATHS MCQs PDFMUHAMMAD SHERJEEL100% (1)
- QB VSem Basic Mathematic AnalysisDocument15 pagesQB VSem Basic Mathematic AnalysisKANTHAVEL TNo ratings yet
- 150 Objective of GroupDocument18 pages150 Objective of GroupMantoo TariqNo ratings yet
- Mair24 Oct 2021Document3 pagesMair24 Oct 2021saifofqw0afNo ratings yet
- DPP-1 Order of An ElementDocument3 pagesDPP-1 Order of An ElementTechnical IndiaNo ratings yet
- Aa Test Unit IiDocument2 pagesAa Test Unit IiRupam dasNo ratings yet
- Maths 2Document16 pagesMaths 2Tech MasterNo ratings yet
- CS 1994Document14 pagesCS 1994VarshaNo ratings yet
- F.sc.I Math Question Bank CH# 1Document9 pagesF.sc.I Math Question Bank CH# 1Adnan FaizNo ratings yet
- Math PSC MCQ Sample Paper 1Document9 pagesMath PSC MCQ Sample Paper 1Adeel MajeedNo ratings yet
- Iit-Jam Mathematics Test: Modern Algebra Time: 60 Minutes Date: 08-10-2017 M.M.: 45Document6 pagesIit-Jam Mathematics Test: Modern Algebra Time: 60 Minutes Date: 08-10-2017 M.M.: 45Lappy TopNo ratings yet
- Module-V (QB)Document9 pagesModule-V (QB)sudheshNo ratings yet
- MCQ Us05cmth23Document8 pagesMCQ Us05cmth23John WickNo ratings yet
- MCQs Short Questions Math FSC Part1Document62 pagesMCQs Short Questions Math FSC Part1yumnaNo ratings yet
- Siri Krishana Math : Group Theory AssignmentDocument6 pagesSiri Krishana Math : Group Theory AssignmentGeo JosNo ratings yet
- T-1 CH#1,2Document4 pagesT-1 CH#1,2punjabcollegekwl5800No ratings yet
- PSC MCQ Sample Paper 1Document8 pagesPSC MCQ Sample Paper 1Sikandar KhanNo ratings yet
- Keshav Physics Sahodaya Oct 2021Document8 pagesKeshav Physics Sahodaya Oct 2021CVM-X11-4-GOPIKA PNo ratings yet
- Assignment A - Group TheoryDocument16 pagesAssignment A - Group Theoryakshat dwivediNo ratings yet
- Answer:c: Loop Loo PDocument37 pagesAnswer:c: Loop Loo PVivek CHOWDARYNo ratings yet
- PG Maths Materials 2Document4 pagesPG Maths Materials 2nandhini chandrasekarNo ratings yet
- MarktngDocument21 pagesMarktngjcshameerNo ratings yet
- ARGON Test 20.04.2022 Without AnsDocument4 pagesARGON Test 20.04.2022 Without AnsSHELESH GARGNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems Graph TheoryDocument4 pagesPractice Problems Graph Theoryedin ellieNo ratings yet
- Hyderabad Central University (Hcu) M.Sc. Mathematics Entrance - 2010Document8 pagesHyderabad Central University (Hcu) M.Sc. Mathematics Entrance - 2010Satyajit biswasNo ratings yet
- Etea Week 1 Xi EngineeringDocument9 pagesEtea Week 1 Xi EngineeringHamad KtkNo ratings yet
- DS (MCQ)Document4 pagesDS (MCQ)hiNo ratings yet
- Maths 2007Document21 pagesMaths 2007prasathkrp100% (2)
- MTH-241 Complex Variables PDFDocument7 pagesMTH-241 Complex Variables PDFSagar PatilNo ratings yet
- Hcu 2013Document9 pagesHcu 2013Ilir HoxhaNo ratings yet
- Modern Algebra (CH 10, Rings 1) RA Maths Test 27.5.2018Document2 pagesModern Algebra (CH 10, Rings 1) RA Maths Test 27.5.2018M Murugan100% (1)
- MCQ Xi Vol - 1Document55 pagesMCQ Xi Vol - 1AKASH KUMAR KOLEYNo ratings yet
- Subject:: Swami Sant Dass Public School Fi-Rst Periodic TEST (2020-21) Class-Viii Mathematics - TIME: 1 Hrs. M.M.: 50Document4 pagesSubject:: Swami Sant Dass Public School Fi-Rst Periodic TEST (2020-21) Class-Viii Mathematics - TIME: 1 Hrs. M.M.: 50GSSS udhopur barsalNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentMujtaba AbbasiNo ratings yet
- BC0039 Discrete Mathematics PAPER 1Document12 pagesBC0039 Discrete Mathematics PAPER 1SeekEducationNo ratings yet
- Nda Test Maths-2Document17 pagesNda Test Maths-2ROHIT YadavNo ratings yet
- ECAT MATHS MCQsDocument2 pagesECAT MATHS MCQsQazzafi Chandio83% (23)
- First Year Mathematics Important MCQS: Chapter # 1Document22 pagesFirst Year Mathematics Important MCQS: Chapter # 1Muhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Paper B - Matrices - 47Document6 pagesPaper B - Matrices - 47cristinaanghel512No ratings yet
- Questions: Abstract AlgebraDocument9 pagesQuestions: Abstract AlgebraAshish ShandilNo ratings yet
- Furman Math Tournament, Senior Exam 1998Document4 pagesFurman Math Tournament, Senior Exam 1998mnealNo ratings yet
- Practice Set3Document4 pagesPractice Set3dsreNo ratings yet
- BCA313Document4 pagesBCA313Riddhi GargNo ratings yet
- 11th Maths Term-1 PaperDocument4 pages11th Maths Term-1 PaperNehal GautamNo ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics MCQ'SDocument33 pagesDiscrete Mathematics MCQ'SGuruKPO100% (1)
- Sets - Proposition - UNIT - 1Document25 pagesSets - Proposition - UNIT - 1AKNo ratings yet
- Annual Exam 11th Math PrestigeDocument4 pagesAnnual Exam 11th Math PrestigeVarun PatilNo ratings yet
- SetsDocument2 pagesSetssushskyNo ratings yet
- Punjab Group of Colleges: 1 Quarter Test (Chapter 1, 2, 3)Document2 pagesPunjab Group of Colleges: 1 Quarter Test (Chapter 1, 2, 3)Qadir RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Number Theory MCQsDocument17 pagesNumber Theory MCQsZain Ul Abidin91% (11)
- Revision 1 XIDocument8 pagesRevision 1 XIMessi RonaldoNo ratings yet
- DPP-2 (Determinant)Document4 pagesDPP-2 (Determinant)Mahima FamousNo ratings yet
- Herstein Topics in Algebra Solution 2.13Document7 pagesHerstein Topics in Algebra Solution 2.13Under TakerNo ratings yet
- Mathematics HonoursDocument25 pagesMathematics HonoursPrachi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Manifolds, Tensor and Forms ( P. Rentein) PDFDocument170 pagesSolution Manual For Manifolds, Tensor and Forms ( P. Rentein) PDFAnonymous bZtJlFvPtpNo ratings yet
- Elementary Comutative AlgebraDocument121 pagesElementary Comutative AlgebraTobib MuhyidinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Basic Ring Theory: Matthew MacauleyDocument24 pagesChapter 13: Basic Ring Theory: Matthew MacauleyVale VanegasNo ratings yet
- Project On: Action On A Set: Submission Date 01/10/2019 Sub. Instructor To . (M.SC)Document11 pagesProject On: Action On A Set: Submission Date 01/10/2019 Sub. Instructor To . (M.SC)shambelNo ratings yet
- M402C10Document10 pagesM402C10SKETCHILY SEBENTENo ratings yet
- Ring (Mathematics) PDFDocument22 pagesRing (Mathematics) PDFDavidNo ratings yet
- How To Work With Quotient RingsDocument6 pagesHow To Work With Quotient RingsRustin AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 AssignmentDocument36 pagesUnit 10 Assignmentvatanemp 000100% (2)
- Abstract Algebra Exam 2016 Midsem-204-SolutionsDocument2 pagesAbstract Algebra Exam 2016 Midsem-204-SolutionsUllasRathodNo ratings yet
- Exam2 FeedbackDocument8 pagesExam2 Feedbackapi-542345721No ratings yet
- Homomorphisms of Groups 3Document65 pagesHomomorphisms of Groups 3JAHANZAIBNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Topology - Homology and Cohomology - Andrew H. WallaceDocument288 pagesAlgebraic Topology - Homology and Cohomology - Andrew H. WallacegeorgetacaprarescuNo ratings yet
- (Lecture Notes) Martyn R. Quick - MT5836 Galois Theory (2019)Document76 pages(Lecture Notes) Martyn R. Quick - MT5836 Galois Theory (2019)Ilir HoxhaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 Alg IIDocument3 pagesAssignment 5 Alg IISoumya Das guptaNo ratings yet
- B2bGroupTheoryHT11 Notes PDFDocument93 pagesB2bGroupTheoryHT11 Notes PDFTendai M Mudziiri ShumbaNo ratings yet
- Ideals, Homomorphisms and Factor RingsDocument5 pagesIdeals, Homomorphisms and Factor RingssarsaranNo ratings yet
- Theorem 4.25: Homomorphic Image Quotient GroupDocument2 pagesTheorem 4.25: Homomorphic Image Quotient GroupaliNo ratings yet
- Ring of Entire FunctionsDocument31 pagesRing of Entire Functionssan_kumar@ymail.commNo ratings yet
- Liouville's Theorem On Integration in Terms of Elementary FunctionsDocument26 pagesLiouville's Theorem On Integration in Terms of Elementary FunctionsVigen ChaltikyanNo ratings yet
- Quotient GroupsDocument4 pagesQuotient GroupsJuan Robinson100% (1)
- Tensores 2Document42 pagesTensores 2RickSantosNo ratings yet
- Pmath 336 ch2 PDFDocument34 pagesPmath 336 ch2 PDFMarlydTalakuaNo ratings yet
- 412notes6 PDFDocument10 pages412notes6 PDFmasrawy2010No ratings yet
- Linear Transformation On Strongly Magic SquaresDocument5 pagesLinear Transformation On Strongly Magic SquaresgomsonNo ratings yet
- Neutrosophic Rings IIDocument8 pagesNeutrosophic Rings IIMia AmaliaNo ratings yet
- TIFR Pamphlet On Algebraic TopologyDocument49 pagesTIFR Pamphlet On Algebraic TopologyRAMJANNo ratings yet