Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tof Care Plan
Tof Care Plan
Uploaded by
JennyDaniel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesOriginal Title
362858171-Tof-Care-Plan
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesTof Care Plan
Tof Care Plan
Uploaded by
JennyDanielCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
NURSING CARE PLAN
Tetralogy of Fallot
ASSESSMENT NURSING SCIENTIFIC PLANNING RATIONALE IMPLEMENTATION EVALUA-TION
DIAGNOSES ANALYSIS
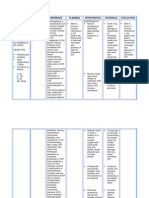
Cyanosis Risk for Tetralogy fallot After 4 hours of nursing If the patient experience cardiac Assessed and record the vital sign. Objective evaluation:
dyspnea Decreased results in low intervention the pt, will output he cardiac and respiratory rate Administered cardiac drugs as Baby's condition was
delay in growth cardiac output oxygenation of have adequate cardiac will increase and bp will decrease. ordered. improved
and development related to blood due to output as evidenced by Cardiac drugs are given to increase Assessed dypsnea,exertion skin
blue anoxia structural mixing of cardiac rate within the strength of cardiac contractions. color during rest and when active.
attacks abnormalities of oxygenated and normal range. Indicates hypoxia and increase Avoided allowing the infant to cry
the heart. de oxygenated Assess and record the oxygen need. for a long period of time, use soft
blood in the left vital sign. Conserves energy,cross cut nipple nipple when feeding.
ventricle Administer cardiac requires less energy for infant to
through the drugs as ordered. feed.
VSD and Assess
preferential low dypsnea,exertion skin
of both color during rest and
oxygenated and when active.
deoxgenated Avoid allowing the
blood from the infant to cry for a long
ventricles period of time,use soft
through the nipple when feeding
aorta because of
obstruction to
flow through
the pulmonary
valve.
ASSESSMENT NURSING SCIENTIFIC PLANNING RATIONALE IMPLEMENTATION EVALUA-TION
DIAGNOSES ANALYSIS
Objective: Impaired gas Congenital 1. Establish good To gain both trust and Established good trusting Objective evaluation:
exchange related Heart Disease trusting relationship cooperation relationship with the patient the baby condition
-V/S: to altered oxygen refers to a with the patient and was improved
and significant others
supply as
BP:80/50 problem with significant others Monitored respiratory
evidenced by Indicators of adequacy of
mmHg dyspnea, the hearts 2. Monitor respiratory rate/depth, use of accessory
respiratory function or degree of
tachypnea, structure and rate/depth, use of compromise and therapy muscles, areas of cyanosis.
PR: 124 bpm tachycardia, and function due to accessory muscles, needs/effectiveness Auscultated breath sounds,
fatigue secondary abnormal heart areas of cyanosis. noting presence or absence
RR: 28 cpm to Congenital Development of atelectasis and
development 3. Auscultate breath and adventitious sounds.
Heart Disease t/c sounds, noting stasis of secretion can impair gas
Temp: 37.1 C
Tetralogy of Before birth. It exchange
presence or absence Monitored vital signs; note
-with O2 fallot can disrupt the
normal flow of and adventitious changes in cardiac rhythm.
inhalation @ sounds.
blood to the Compensatory changes in vital Compensatory.
2lpm via nasal different parts signs and development of Helped with breathing
cannula as of the body thus 4. Monitor vital signs; dysrhythmias reflect effects of exercises. Pursed lip
ordered affecting the note changes in impaired gas exchange
exchange of breathing.
cardiac rhythm.
-circumoral gasses Helps improve oxygen inspiration Elevated head of bed to
Compensatory.
cyanosis noted of the lungs moderate or high back rest.
5. Help with breathing
exercises. Pursed lip Helps the lung expand and aids in
breathing. the relaxation of the muscles
6. Elevate head of bed decreasing the oxygen demand of
to moderate or high the body
back rest.
ASSESSMENT NURSING SCIENTIFIC PLANNING RATIONALE IMPLEMENTATION EVALUA-TION
DIAGNOSES ANALYSIS
Objectives: Ineffective tissue Due to 1. Monitor skin colour Cool, blanched, mottled skin Monitored skin colour and Objective evaluation:
perfusion narrowing of and temp. every and cyanosis may indicate temp. every 2hours. the baby condition
-bluish the artery which 2hours. Assess for tissue perfusion was improved
Assessed for signs of skin
discoloration on (cardiopulmonary small amount of signs of skin Decrease heart rate and
oxygenated breakdown.
lips noted ) blood pressure may
blood can pass breakdown. Monitored and documented
indicateincreased
-clubbing of Related to through the 2. Monitor and arteriovenousexchange,whic patients vital signs every
finger noted decrease oxygen systemic documented patients h leads to decrease tissue hour..
cellular exchange circulation vital signs every perfusion Kept patient warm
-nasal flaring Which the hour.. Warmth aids
secondary to Elevated lower extremities.
patient 3. Keep patient warm vasodilation,which improve
-use of accessory congenital heart experience tissue perfusion
Changed position regularly
disease t/c 4. Elevate lower and inspect skin every shift.
muscle noted difficulty in To increase arterial blood
tetralogy of fallot breathing extremities.
supply and improve tissue
-with capillary 5. Change position
perfusion.
refill time of 3 regularly and inspect To avoid decrease in tissue
seconds skin every shift. perfusion and risk of skin
breakdown.
-with O2 of 2 lpm
via nasal cannula
as ordered
-body weakness
noted(allways on
bed)
You might also like
- CMS Neuro 1 AnswersDocument13 pagesCMS Neuro 1 AnswersKomal Menon100% (14)
- Pathophysiology of Tetralogy of FallotDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Tetralogy of FallotMark James Melendres100% (12)
- Child - Bronchiolitis NCPDocument2 pagesChild - Bronchiolitis NCPjoeti80% (5)
- Schema TherapyDocument5 pagesSchema TherapyATHINA METAXANo ratings yet
- NCP AsthmaDocument2 pagesNCP Asthmaissaiahnicolle0% (1)
- Hepatitis A Case Study 1Document20 pagesHepatitis A Case Study 1Gerome Valderama100% (1)
- Case Presentation On TOFDocument19 pagesCase Presentation On TOFJay PaulNo ratings yet
- NCP FORM For TetralogyDocument3 pagesNCP FORM For TetralogyGraceMelendres100% (3)
- Tetralogy of Fallot Case PresentationDocument32 pagesTetralogy of Fallot Case PresentationUday Kumar50% (2)
- Case Study Tetralogy of FallotDocument15 pagesCase Study Tetralogy of FallotBenjamin Leonzon100% (2)
- Tetralogy of Fallot Lesson PlanDocument25 pagesTetralogy of Fallot Lesson PlanUday Kumar100% (1)
- NCP HydrocephalusDocument3 pagesNCP HydrocephalusCazze SunioNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On RHD PDFDocument18 pagesLesson Plan On RHD PDFSAYMABANU80% (5)
- NCP RHDDocument7 pagesNCP RHDHenry Roque Tagalag80% (5)
- Pediatrics Care Plan Kawasaki Disease Final Draft and CorrectedDocument9 pagesPediatrics Care Plan Kawasaki Disease Final Draft and CorrectedValencia Vickers50% (4)
- NCP Preeclampsia and EclampsiaDocument14 pagesNCP Preeclampsia and EclampsiaBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Buergers Disease NCPDocument5 pagesBuergers Disease NCPNikko Dela Cruz100% (2)
- D DDocument26 pagesD DMela MarieNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of Fallot NCPDocument6 pagesTetralogy of Fallot NCPHarlene Joyce ReyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Acyanotic Heart DiseaseDocument55 pagesNursing Care Plan For Acyanotic Heart DiseaseDeepikaxena John79% (14)
- NCP HydrocephalusDocument6 pagesNCP HydrocephalusgopscharanNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosis Pathophysiolog Y Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosis Pathophysiolog Y Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharina Aubrey100% (3)
- Pda Case StudyDocument27 pagesPda Case Studykreny10100% (9)
- Bronchopneumonia Care PlanDocument6 pagesBronchopneumonia Care PlanAbhijit Soundade0% (1)
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument5 pagesTetralogy of FallotCharity OaniaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanBhie DizonNo ratings yet
- 1.case Presentation CHDDocument23 pages1.case Presentation CHDDHARM MEENA0% (1)
- NCP For EclampsiaDocument3 pagesNCP For EclampsiaFatma Nor Aljanna Macog100% (1)
- Nursing Careplan For TofDocument17 pagesNursing Careplan For Tofanamika sharmaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document4 pagesNursing Care Plan 1Johndelle Banlasan Hernan100% (1)
- Case Study On Obstructive HydrocephalusDocument57 pagesCase Study On Obstructive HydrocephalusGayLah Momblanco67% (9)
- Tetralogy of Fallot CASE STUDYDocument12 pagesTetralogy of Fallot CASE STUDYMaricel Agcaoili GallatoNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Cystic Fibrosis: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Cystic Fibrosis: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- NCP1 Knowledge DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP1 Knowledge DeficitNOslipperyslope100% (1)
- NCP - LeprosyDocument3 pagesNCP - LeprosyKevin DareNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument43 pagesCase Presentationkayal100% (1)
- New Born NCPDocument8 pagesNew Born NCPCarl Vincent Marrion Rejuso100% (1)
- H-Mole NCPsDocument7 pagesH-Mole NCPsJoevence Gazo CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- CASE-STUDY Myocardial InfarctionDocument77 pagesCASE-STUDY Myocardial Infarctionjuodie100% (1)
- NCP Hydrocephalus-Delayed Growth and DevelopmentDocument4 pagesNCP Hydrocephalus-Delayed Growth and DevelopmentCazze Sunio100% (3)
- Patent Ductus ArteriosusDocument49 pagesPatent Ductus Arteriosusarchana vermaNo ratings yet
- NCP Preeclampsia and EclampsiaDocument16 pagesNCP Preeclampsia and EclampsiaBiway Regala100% (1)
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Patent Ductus Arteroisus (PDA)Document2 pagesPathophysiology of Patent Ductus Arteroisus (PDA)Rodel Yacas100% (1)
- NCP For CHDDocument2 pagesNCP For CHDMonica Rivera100% (1)
- Final NCPDocument21 pagesFinal NCPkoringring100% (1)
- Care of Patients With Mechanical VentilatorDocument4 pagesCare of Patients With Mechanical VentilatorIman Bee Sanayon0% (1)
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument22 pagesTetralogy of FallotHusna Aje100% (1)
- Case Presentation: HydrocephalusDocument22 pagesCase Presentation: HydrocephalusNina100% (2)
- Congenital Heart Disease - ASDDocument36 pagesCongenital Heart Disease - ASDAuni Akif Aleesa100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN PneumoniaDocument38 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN PneumoniaLuna JadeNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument31 pagesTetralogy of FallotAnditha Namira RS100% (1)
- NCP For EclampsiaDocument6 pagesNCP For EclampsiaXtine Soliman Zamora100% (3)
- Assisting in Intravenous InfusionDocument4 pagesAssisting in Intravenous InfusionEloise Pateño33% (3)
- NCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingDocument3 pagesNCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingVerajoy DaanNo ratings yet
- Defect (VSD) Occurs: Decreased Cardiac Output Related To IndependentDocument5 pagesDefect (VSD) Occurs: Decreased Cardiac Output Related To IndependentPrincess GarciaNo ratings yet
- Kez NCPDocument12 pagesKez NCPShizuka Marycris AmaneNo ratings yet
- CASE SCENARIO and NCPDocument14 pagesCASE SCENARIO and NCPBeverly PagcaliwaganNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPWendy Escalante100% (1)
- NCP Week 6 Nrg301 ValenzonaDocument3 pagesNCP Week 6 Nrg301 ValenzonaJoshennaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveFreisanChenMandumotanNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - JayDocument8 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - JayJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic College of Davao Del Sur, Inc.: Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesPolytechnic College of Davao Del Sur, Inc.: Nursing Care PlanDwight DiazNo ratings yet
- Palliative CystectomyDocument20 pagesPalliative CystectomymostafaNo ratings yet
- John Woods - Boys Who Have Abused - Psychoanalytic Psychotherapy With Victim Perpetrators of Sexual Abuse (Forensic Focus) (2003) PDFDocument242 pagesJohn Woods - Boys Who Have Abused - Psychoanalytic Psychotherapy With Victim Perpetrators of Sexual Abuse (Forensic Focus) (2003) PDFFelipe Concha AquevequeNo ratings yet
- Adhd Research PaperDocument5 pagesAdhd Research Paperafeeotove100% (1)
- Evidence Based Clinical Practice Update PracticeDocument14 pagesEvidence Based Clinical Practice Update PracticeYoni ZarkhNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Approaches To The Treatment of DepressionDocument6 pagesAyurvedic Approaches To The Treatment of DepressionSN WijesinheNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Skin and Parasitic DiseasesDocument14 pagesNursing Management of Skin and Parasitic Diseasesyer tagalajNo ratings yet
- A) A/E of Moclobemide SNATCH: A) Pharmacology 1) Anti-DepressantsDocument10 pagesA) A/E of Moclobemide SNATCH: A) Pharmacology 1) Anti-DepressantsNur Atiqah Mohd AzliNo ratings yet
- 1998 SpringDocument8 pages1998 Springturner_amberNo ratings yet
- Fresher Teacher ResumeDocument1 pageFresher Teacher ResumeRoxanne L. JayloNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of A Shared Psychotic DisorderDocument2 pagesDiagnosis of A Shared Psychotic DisorderTalia SchwartzNo ratings yet
- Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy For DepressionDocument10 pagesMindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy For DepressionCMValmaNo ratings yet
- WrarfDocument7 pagesWrarfRonel ViolantaNo ratings yet
- Essential Falls Management Series: Falls and People With Intellectual & Developmental Disabilities (Tideiksaar Excerpt)Document9 pagesEssential Falls Management Series: Falls and People With Intellectual & Developmental Disabilities (Tideiksaar Excerpt)Health Professions Press, an imprint of Paul H. Brookes Publishing Co., Inc.No ratings yet
- Clinical Pathway in Emergency MedicineDocument648 pagesClinical Pathway in Emergency MedicineUtari100% (1)
- Procedure Rabbit Blood CollectionDocument4 pagesProcedure Rabbit Blood CollectionryzeepotNo ratings yet
- Apriladi Hypnosis For Cancer A Hypnotists Guide To Helping Those in NeedDocument13 pagesApriladi Hypnosis For Cancer A Hypnotists Guide To Helping Those in NeedApriladi Putra Pegagan100% (2)
- OT With Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Major Role!: Waad Aljurayed/ Asma Almutairi/ Manar AlmutairiDocument1 pageOT With Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Major Role!: Waad Aljurayed/ Asma Almutairi/ Manar Almutairiwaad100% (1)
- Unit 1, Part 4 Clin. PKDocument11 pagesUnit 1, Part 4 Clin. PKshammaNo ratings yet
- Duterte Open To Legalization of Medical MarijuanaDocument3 pagesDuterte Open To Legalization of Medical MarijuanaTreblif AdarojemNo ratings yet
- Difficult Airway Management During Anesthesia A Review of The Incidence and SolutionsDocument6 pagesDifficult Airway Management During Anesthesia A Review of The Incidence and SolutionsSudar Pecinta ParawaliNo ratings yet
- A. Ward Round IPS Example FINALDocument5 pagesA. Ward Round IPS Example FINALEzra Ledya Sevtiana SinagaNo ratings yet
- Zivorad - Influences - Instantaneous Method For Discreating TraumasDocument5 pagesZivorad - Influences - Instantaneous Method For Discreating Traumassoribo67% (3)
- Bipolar DisorderDocument10 pagesBipolar DisorderJimmy100% (1)
- Working Student 4Document6 pagesWorking Student 4Ruvilyn EsplanaNo ratings yet
- Adherence To Potent Antiretroviral TherapyDocument5 pagesAdherence To Potent Antiretroviral TherapyGabrieela SiguiNo ratings yet
- Initial TemplateDocument8 pagesInitial TemplateZuj PayNo ratings yet
- Philia: As A Summary, Management IncludeDocument3 pagesPhilia: As A Summary, Management IncludeMarissa AsimNo ratings yet