Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Depreciation
Uploaded by
eunwink eunwinkOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Depreciation
Uploaded by
eunwink eunwinkCopyright:
Available Formats
Depreciation
Meaning - Depreciation may be defined as the permanent and continuing diminution in
the quality or the value of an asset.
Methods of Depreciation
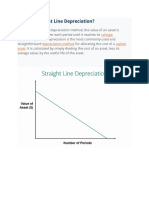
1. Straight line or Fixed Installment Method
A fixed or equal amount is to be charged as depreciation every year during the life time
of the asset. The amount of depreciation remains equal from year to year. The expected
lifetime of the asset is calculated and the cost of the asset is spread over its lifetime.
Depreciation expense per annum=Original cost/number of years of useful life
If the fixed asset is expected to have a scarp value at the end of its useful life, then
Depreciation expense per annum= (Original Cost-Estimated scrap value)/Number of
years of useful life.
2. Reducing Balance or Diminishing Balance Method
The value of asset goes on diminishing year after year, the amount of depreciation
charged every year also goes on declining. Every year a fixed percentage of the net
book value of the asset is reduced. For example 20% depreciation is charged. If the
asset has a value of $10000, the depreciation for the first year will be 20% of $10000
i.e. $4000. The book value for the next year will be now $6000. This year the
depreciation will be again 20% of the remaining value i.e. 20% of 6000=$1200. So the
remaining value of the asset is now $6000-$1200=$4800.
Straight line or Fixed Installment Method
Example – 1 X Ltd purchased a machine costing $ 10000 and residual value of
the machine was $ 2000 after the useful life of 5 years calculate the depreciation
as per straight line method and rate of depreciation.
Depreciation = Cost of the asset – Scrap value (Residual value)
Estimate useful life of the asset
10000-2000 = 1600
5
Rate of depreciation = Depreciation = 1600 X 100 = 16%
Cost of asset 10000
Reducing Balance or Diminishing Balance Method
Using the information in example no 1 calculating depreciation
1st year depreciation = 10000 x 16% = 1600
2nd year depreciation = (10000 – 1600) x 16% = 1344
3rd year depreciation = (10000-1600-1344) x 16% =1129
4 year depreiciation = (10000 -1600 – 1344 – 1129) x 16% = 948
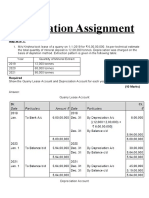
Q – 1 K Ltd purchased a machine on 1 Jan 2015 for $ 40 000 and another
machine purchased on 1 July 2015 for cash for same value. K Ltd charged
depreciation on machines at 10% per annum by straight line method. Books of K
Ltd ends on 31 December each year.
Required:
1. Prepare Machinery Account for the year 2015 ,2016 and 2017
2. Prepare provision for Depreciation on machine account
Q – 2 On 1st April 2012 Karma Ltd purchased two Machines from Hussain Ltd on cash
for $ 50 000 each. It was decided to write off depreciation on machines at 10% per
annum following Straight line method.
Karma Ltd books closed on 31st March of every year.
Required:
1. Prepare Machinery Account for three years.
2. Prepare provision for Depreciation on Machine Account
Q – 3 On 1st April 2012 X Ltd Ltd purchased two Machines for cash $ 90 000 each. It
was decided to write off depreciation on machines at 10% per annum following
diminishing balance method. Zen Ltd Ltd books closed on 31st March of every year.
Required:
Prepare Machinery Account for three years.
Prepare provision for Depreciation on Machine Account
Financial year – 1 April – 31st March
Calendar year = 1 Jan – 31 Dec
Current financial year 1 April 2020 – 31 st March 2021
Q – 4 On 1st April 2012 Puma Ltd purchased one Machine from XY Ltd by cheque for $
40 000 and on 1 july 2012 another machine purchased from P Ltd on credit for 45000. It
was decided to write off depreciation on machines at 10% per annum following
Diminishing balance method.
Puma Ltd books closed on 31st March of every year.
Required:
1. Prepare Machinery Account for three years.
2. Prepare provision for Depreciation on Machine Account
You might also like
- Depreciation O Level NotesDocument5 pagesDepreciation O Level NotesBijoy SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Unit III - DepreciationDocument5 pagesUnit III - Depreciationkailasbankar96No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Economic Evaluation of AlternativesDocument21 pagesChapter 3 - Economic Evaluation of Alternativessam guptNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Depreciation - 1675244829Document35 pagesChapter 7 Depreciation - 1675244829Hsu Lae NandarNo ratings yet
- IND-AS Tangible AssetDocument23 pagesIND-AS Tangible AssetsambhabdashcacsNo ratings yet
- Acc 308-Week3 - 3-2 Homework Chapter 11Document7 pagesAcc 308-Week3 - 3-2 Homework Chapter 11Lilian LNo ratings yet
- Classes Unit 4 Commerce DepreciationDocument25 pagesClasses Unit 4 Commerce Depreciationhappy lifeNo ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument25 pagesDepreciationArshad ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Depreciation Accounting-6Document19 pagesDepreciation Accounting-6rohitsf22 olypmNo ratings yet
- Plant Assets: Created by Ina IndrianaDocument23 pagesPlant Assets: Created by Ina IndrianadewiestiNo ratings yet
- Depreciation Lesson 8Document39 pagesDepreciation Lesson 8Charos Aslonovna100% (5)
- Lect 11a Depreciation (Part 1)Document18 pagesLect 11a Depreciation (Part 1)11Co sarahNo ratings yet
- Depreciation Method 160210070304Document14 pagesDepreciation Method 160210070304Ved PrakashNo ratings yet
- Accounting For DepreciationDocument6 pagesAccounting For DepreciationKaran GNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument51 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentBasavaraj OkkundNo ratings yet
- Depreciation: ConceptDocument6 pagesDepreciation: ConceptEdna OrdanezaNo ratings yet
- Depreciation Class WorkDocument5 pagesDepreciation Class WorkChaaru VarshiniNo ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument3 pagesDepreciationTheivanayaki M PSGRKCWNo ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument22 pagesDepreciationPrashantNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document27 pagesUnit 3v9510491No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Non-Current AssetsDocument25 pagesChapter 6 - Non-Current Assetswaronamphetlhe96No ratings yet
- What Is Straight Line Depreciation?: Salvage Value Depreciation Method Capital AssetDocument5 pagesWhat Is Straight Line Depreciation?: Salvage Value Depreciation Method Capital AssetErika ParadelaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Solution Week 06Document4 pagesTutorial Solution Week 06itmansaigonNo ratings yet
- 9 Depreciation 08-2022 Regular Ca FoundationDocument6 pages9 Depreciation 08-2022 Regular Ca FoundationjahnaviNo ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument7 pagesDepreciationkarthikrajan123No ratings yet
- Assignment Bba 4th SemDocument3 pagesAssignment Bba 4th SemShadaab MalikNo ratings yet
- Depreciation of Non Current Assets: Elizabeth - Accounting Privat ClassDocument28 pagesDepreciation of Non Current Assets: Elizabeth - Accounting Privat ClassSiti JulaehaNo ratings yet
- PPE Depreciaiton LectureDocument12 pagesPPE Depreciaiton Lecturecjorillosa2004No ratings yet
- Assignment On DepreciationDocument4 pagesAssignment On DepreciationNouman MujahidNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Disposal of Asset and Good Will Week 3Document28 pagesFinancial Accounting Disposal of Asset and Good Will Week 3Hania SohailNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 - PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT (v2)Document20 pagesCHAPTER 10 - PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT (v2)VerrelyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Replacement AnalysisDocument29 pagesChapter 5 - Replacement AnalysisUpendra ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document26 pagesChapter 11ENG ZI QINGNo ratings yet
- Edited Plant AssetsDocument12 pagesEdited Plant AssetsMesele AdemeNo ratings yet
- Mock - Econ - Exercise 4Document2 pagesMock - Econ - Exercise 4najib casanNo ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument15 pagesDepreciationYash AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Accounting of DepreciationDocument2 pagesAccounting of DepreciationAkshay KawadeNo ratings yet
- Capital and Revenue ExpenditureDocument22 pagesCapital and Revenue ExpenditureTimi Dele100% (1)
- Fixed AssetsDocument26 pagesFixed Assetssihlemooi3No ratings yet
- 3rd Examination Test in AccountingDocument23 pages3rd Examination Test in AccountingNanya BisnestNo ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument17 pagesDepreciationZAID BIN TAHIRNo ratings yet
- Accounting Long Questions II YearDocument10 pagesAccounting Long Questions II Yeararshad aliNo ratings yet
- Fixed Assets - Disposal and DepreciationDocument8 pagesFixed Assets - Disposal and DepreciationTeo Yu XuanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5. Depreciation, Bad Debts, Provision For Doubtful DebtsDocument32 pagesLecture 5. Depreciation, Bad Debts, Provision For Doubtful DebtsazizbektokhirbekovNo ratings yet
- Concept of Installment SystemDocument5 pagesConcept of Installment Systemshambhuling ShettyNo ratings yet
- Depreciation Methods: Submitted To Sir Rakesh KumarDocument4 pagesDepreciation Methods: Submitted To Sir Rakesh KumarSadaf HussainNo ratings yet
- Unit-I: DepreciationDocument4 pagesUnit-I: DepreciationEswari GkNo ratings yet
- Acc101 - Chapter 8: Accounting For Long-Term AssetsDocument18 pagesAcc101 - Chapter 8: Accounting For Long-Term AssetsMauricio Ace100% (1)
- AdditionalPracticalProblemPg.14.52 14Document1 pageAdditionalPracticalProblemPg.14.52 14Vijay KumarNo ratings yet
- CHP 6 A MS - MergedDocument14 pagesCHP 6 A MS - Mergedk.muhammed aaqibNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting IIDocument13 pagesFinancial Accounting IITimi DeleNo ratings yet
- LCTR 5 - Tangible Non Current Assets f3 2Document49 pagesLCTR 5 - Tangible Non Current Assets f3 2Kudakwashe MugwagwaNo ratings yet
- Fzb10 FR Module ADocument21 pagesFzb10 FR Module Aluckylover6543No ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document4 pagesChapter 10Mondy MondyNo ratings yet
- Depreciation Basic - Problem1Document2 pagesDepreciation Basic - Problem1Pallavi Ingale0% (1)
- 1st Semester Accounts Selected Question PDFDocument32 pages1st Semester Accounts Selected Question PDFVernon Roy100% (1)
- Fmswe6pZd1hEDocument32 pagesFmswe6pZd1hEsushmitakulkarni2480No ratings yet
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - BEC (Business Environment Concepts)From EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - BEC (Business Environment Concepts)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Write A Story Using The LineDocument1 pageWrite A Story Using The Lineeunwink eunwinkNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 4 Energy Resources and Transfers - Edexcel Physics IGCSEDocument3 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 4 Energy Resources and Transfers - Edexcel Physics IGCSEeunwink eunwinkNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - WISDOM (2nd Semester) : Sekolah Lentera KasihDocument1 pageGrade 9 - WISDOM (2nd Semester) : Sekolah Lentera Kasiheunwink eunwinkNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Algebra-Expressions and Equations: Answer The QuestionsDocument14 pagesGrade 7 Algebra-Expressions and Equations: Answer The Questionseunwink eunwinkNo ratings yet
- Book Review FormatDocument1 pageBook Review Formateunwink eunwinkNo ratings yet
- Book Review FormatDocument1 pageBook Review Formateunwink eunwinkNo ratings yet
- SLK Field Trip Grade 1-2 "Morin Jam Factory"Document2 pagesSLK Field Trip Grade 1-2 "Morin Jam Factory"eunwink eunwinkNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument17 pagesFinancial Managementcorpuzkrystal01No ratings yet
- ASEAN Capital Market Integration Issues and Challenges: Managing Director, Securities Commission of MalaysiaDocument13 pagesASEAN Capital Market Integration Issues and Challenges: Managing Director, Securities Commission of MalaysiaRizki HakimNo ratings yet
- AccountDocument2 pagesAccountSalih AkadarNo ratings yet
- Prospek Pengelolaan Hutan Berbasis Masyarakat Pada Taman Nasional Sebangau Melalui Usaha Pengembangan Tanaman Jelutung (Dyera Lowii)Document14 pagesProspek Pengelolaan Hutan Berbasis Masyarakat Pada Taman Nasional Sebangau Melalui Usaha Pengembangan Tanaman Jelutung (Dyera Lowii)abul_haitsam9764No ratings yet
- ETSY Short Report - Railroad Ranch 9.14.23Document7 pagesETSY Short Report - Railroad Ranch 9.14.23andrewNo ratings yet
- CPMI - Cross Border PaymentsDocument60 pagesCPMI - Cross Border PaymentsTarik IrrouNo ratings yet
- Chapte R: Dividend TheoryDocument19 pagesChapte R: Dividend TheoryArunim MehrotraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Merchandising Sector Student Version 4janDocument75 pagesChapter 10 Merchandising Sector Student Version 4janBình QuốcNo ratings yet
- Acon PtyDocument13 pagesAcon PtyTuba MirzaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 11 - ExcellDocument1 pageMODULE 11 - ExcellJulie Fulgar EstopaceNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesExam 1 Learning ObjectivesYingfanNo ratings yet
- Mergers Acquisitions and Other Restructuring Activities 8th Edition Depamphilis Test BankDocument32 pagesMergers Acquisitions and Other Restructuring Activities 8th Edition Depamphilis Test Bankwolfgangmagnusyya100% (27)
- Long Term Debt ProgramDocument10 pagesLong Term Debt ProgramSyarif Muhammad Hikmatyar100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Homework (April 22)Document6 pagesChapter 4 Homework (April 22)Sugim Winata EinsteinNo ratings yet
- Brief Description and Activities of Jibon Bima Corporation: OfficeDocument4 pagesBrief Description and Activities of Jibon Bima Corporation: OfficeMozaffor HossainNo ratings yet
- DUpont Case SummaryDocument4 pagesDUpont Case Summaryabhishekhrc0% (1)
- Chapter 2 Interest and DepreciationDocument32 pagesChapter 2 Interest and DepreciationJojobaby51714No ratings yet
- Installment SalesDocument5 pagesInstallment SalesMarianne LanuzaNo ratings yet
- Case Study - LBO Tata Tea and TetleyDocument4 pagesCase Study - LBO Tata Tea and TetleySumit RathiNo ratings yet
- Artículo para Poster Académico PDFDocument29 pagesArtículo para Poster Académico PDFDarío Guiñez ArenasNo ratings yet
- New Drone Ind AS 116Document13 pagesNew Drone Ind AS 116rajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document75 pagesChapter 11Maged AboelmagdNo ratings yet
- Binary Options e BookDocument74 pagesBinary Options e BookDaniel Santos100% (1)
- Schedule of List of Securities To Be Transition To T+1 Settlement Cycle Across ExchangesDocument234 pagesSchedule of List of Securities To Be Transition To T+1 Settlement Cycle Across ExchangesHans RajNo ratings yet
- 100 Percent Project Finance - The ProcessDocument3 pages100 Percent Project Finance - The Processnaz-sdeNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On The Credit Insurance ProductsDocument24 pagesA Presentation On The Credit Insurance ProductsAmresh SinhaNo ratings yet
- GST ChallanDocument2 pagesGST ChallanArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Annex A1 - Detailed Statement of Financial PositionDocument26 pagesAnnex A1 - Detailed Statement of Financial PositionwichupinunoNo ratings yet
- 1981 Stock Traders AlmanacDocument1 page1981 Stock Traders AlmanacCopy JunkieNo ratings yet
- New Reliane ProjectDocument197 pagesNew Reliane Projectggi2022.1888No ratings yet