Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The National College Toba Tek Singh Operating System Bs 5
Uploaded by
hasan raza habi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views4 pageshello world
Original Title
Operating
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenthello world
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views4 pagesThe National College Toba Tek Singh Operating System Bs 5
Uploaded by
hasan raza habihello world
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
The National College Toba TEk Singh
Operating system BS 5th
Total Marks: 60 Time: 60 ` Name:
1. Data cannot be written to secondary storage unless written within a ______
a) File b) swap space c) directory d) text format
2. File attributes consist of ____________
a) Name b) type c) identifier d) all
3. The information about all files is kept in ____________
a) Swap space b) operating system c) seperate directory structure d) none
4. A file is a/an _______ data type.
a) abstract b) primitive c) public d) private
5. The operating system keeps a small table containing information about all open
files called ____________
a) system table b) open-file table c) file table d)
directory table
6. In UNIX, what will the open system call return?
a) pointer to the entry in the open file table
b) pointer to the entry in the system wide table
c) a file to the process calling it d) none of the mentioned
7. System wide table in UNIX contains process independent information such as
a) location of file on disk b) access dates c) file size d) all
8. The open file table has a/an _______ associated with each file.
a) file content b) file permission c) open count d) close count
9. Which of the following are the two parts of the file name?
a) name & identifier b) identifier & type
c) extension & name d) type & extension
10. The UNIX sytem uses a/an ________ stored at the beginning of a some files to indicate
roughly the type of file.
a) identifier b) extension c) virtual number d) magic number
11. The larger the block size, the ______ the internal fragmentation.
a) greater b) lesser c) same d) none of the mentioned
12. In the sequential access method, information in the file is processed ____________
a) one disk after the other, record access doesnt matter b) one record after the other
c) one text document after the other d) none of the mentioned
13. Sequential access method ______ on random access devices.
a) works well b) doesnt work well c) both a & b d) none
14. The direct access method is based on a ______ model of a file, as _____ allow random
access to any file block.
a) magnetic tape, magnetic tapes b) tape, tapes c) disk, disks d)
all
15. For a direct access file ____________
a) there are restrictions on the order of reading and writing
b) there are no restrictions on the order of reading and writing
c) access is restricted permission wise
d) access is not restricted permission wise
16. A relative block number is an index relative to ____________
a) the beginning of the file b) the end of the file
c) the last written position in file d) none of the mentioned
17. The index contains ____________
a) names of all contents of file b) pointers to each page
c) pointers to the various blocks d) all of the mentioned
18. For large files, when the index itself becomes too large to be kept in memory?
a) index is called b) an index is created for the index file
c) secondary index files are created d) all of the mentioned
19. In UNIX, what is a link?
a) a directory entry b) a pointer to another file or subdirectory
c) implemented as an absolute or relative path name d) all of the mentioned
20. The operating system _______ the links when traversing directory trees, to preserve the
acyclic structure of the system.
a) considers b) ignores c) deletes d) none of the mentioned
21. The deletion of a link ________ the original file.
a) deletes b) affects c) does not affect d) none
22. When keeping a list of all the links/references to a file, and the list is empty, implies that
a) the file has no copies b) the file is deleted c) the file is hidden d) none
23. When a cycle exists, the reference count maybe non zero, even when it is no longer
possible to refer to a directory or file, due to _______
a) the possibility of one hidden reference b) the possibility of two hidden references
c) the possibility of self referencing d) none of the mentioned
23. What is the mount point?
a) an empty directory at which the mounted file system will be attached
b) a location where every time file systems are mounted
c) is the time when the mounting is done d) none of the mentioned
24. When a file system is mounted over a directory that is not empty then _____________
a) the system may not allow the mount b) the system must allow the mount
c) the system may allow the mount and the directory’s existing files will then be made
d) all of the mentioned
25. In UNIX, exactly which operations group members and other users can execute is
definable by _____________
a) the group’s head b) the file’s owner c) the file’s permissions d) all
26. A process _____ lower the priority of another process if the same own both
a) must b) can c) cannot d) none
27. In distributed file system ________________ directories are visible from the local
machine.
a) protected b) local c) private d) remote
27. In the world wide web, a ____ is needed to gain access to the remote files, and separate
operations are used to transfer files.
a) laptop b) plugin c) browser d) player
28. Anonymous access allows a user to transfer files _____________
a) without having an account on the remote system
b) only if he accesses the system with a guest account
c) only if he has an account on the remote system d) none of the mentioned
29. The machine containing the files is the _______ and the machine wanting to access the
files is the ______
a) master, slave b) memory, user c) server, client d) none
30. Distributed naming services/Distributed information systems have been devised to
a) provide information about all the systems
b) provide unified access to the information needed for remote computing
c) provide unique names to all systems in a network d) all of the mentioned
31. Domain name system provides _____________
a) host-name-to-network-address translations for the entire internet
b) network-address-to-host-name translations for the entire internet
c) binary to hex translations for the entire internet
d) all of the mentioned
32. To recover from failures in the network operations _____________ information may be
maintained.
a) ip address b) state c) stateless d) operating system
33. The series of accesses between the open and close operations is a _____________
a) transaction b) procedure c) program d) file session
34. Reliability of files can be increased by _____________
a) keeping the files safely in the memory b) making a different partition for
the files
c) by keeping them in external storage d) by keeping duplicate copies of the file
35. Protection is only provided at the _____ level.
a) lower b) central c) higher d) none
36. What is the main problem with access control lists?
a) their maintenance b) their length c) their permissions d) all
37. Many systems recognize three classifications of users in connection with each file (to
condense the access control list).
a) Owner b) Group c) Universe d) All
38. All users in a group get _______ access to a file.
a) different b) similar c) same d) none
39. Universe consists of _____________
a) all users that aren’t included in the group or owners b) all users that are not owners
c) all users in the system d) none of the mentioned
40. In UNIX, groups can be created and modified by?
a) superuser b) any user c) a programmer only d) the people in the group
41. To control access the three bits used in UNIX are represented by _____________
a) r b) w c) x d) all of the mentioned
42. If each access to a file is controlled by a password, then what is the disadvantage?
a) user will need to remember a lot of passwords b) it is not reliable
c) it is not efficient d) all of the mentioned
43. What will happen in a multi level directory structure?
a) the same previous techniques will be used as in the other structures
b) a mechanism for directory protection will have to applied
c) the subdirectories do not need protection once the directory is protected
d) none of the mentioned
44. In UNIX, the directory protection is handled _________ to the file protection.
a) different b) similar c) it is not handled at all d) none
45. Disks are segmented into one or more partitions, each containing a file system or ______
a) left ‘raw’ b) made into swap space
c) made into backup space d) left ‘ripe’
46. The three major methods of allocating disk space that are in wide use are _____________
a) contiguous b) linked c) indexed d) all of the mentioned
47. In contiguous allocation _____________
a) each file must occupy a set of contiguous blocks on the disk
b) each file is a linked list of disk blocks
c) all the pointers to scattered blocks are placed together in one location
d) none of the mentioned
48. In linked allocation _____________
a) each file must occupy a set of contiguous blocks on the disk
b) each file is a linked list of disk blocks
c) all the pointers to scattered blocks are placed together in one location
d) none of the mentioned
49. In indexed allocation _____________
a) each file must occupy a set of contiguous blocks on the disk
b) each file is a linked list of disk blocks
c) all the pointers to scattered blocks are placed together in one location
d) none of the mentioned
50. On systems where there are multiple operating system, the decision to load a particular
one is done by _____________
a) boot loader
b) bootstrap
c) process control block
d) file control block
51. The VFS (virtual file system) activates file system specific operations to handle local
requests according to their _______
a) size b) commands c) timings d) file system types
52. What is the real disadvantage of a linear list of directory entries?
a) size of the linear list in memory b) linear search to find a file
c) it is not reliable d) all of the mentioned
53. Contiguous allocation of a file is defined by _____________
a) disk address of the first block & length b) length & size of the block
c) size of the block d) total size of the file
54. One difficulty of contiguous allocation is _____________
a) finding space for a new file b) inefficient c) costly d) time taking
55. _______ and ________ are the most common strategies used to select a free hole from the
set of available holes.
a) First fit, Best fit b) Worst fit, First fit
c) Best fit, Worst fit d) None of the mentioned
56. The first fit and best fit algorithms suffer from _____________
a) internal fragmentation b) external fragmentation c) starvation d) all
57. To solve the problem of external fragmentation ________ needs to be done periodically.
a) compaction b) check c) formatting d) replacing memory
58. If too little space is allocated to a file _____________
a) the file will not work b) the file cannot be extended
c) there will not be any space for the data, as the FCB takes it all d) the file cannot be opened
59.A machine in Network file system (NFS) can be ________
a) client b) server c) both a & b d) none
60. A _________ directory is mounted over a directory of a _______ file system.
a) local, remote b) remote, local c) local, local d) none
61.The mount mechanism ________ a transitive property.
a) exhibits b) does not exhibit c) may exhibit d) none
62. A mount operation includes the _____________
a) name of the network
b) name of the remote directory to be mounted
c) name of the server machine storing it
d) all of the mentioned
63. The mount request is mapped to the corresponding __________ and is forwarded to the
mount server running on the specific server machine.
a) IPC b) System c) CPU d) RPC
BEST OF LUCK
You might also like
- Final Dbs MCQDocument30 pagesFinal Dbs MCQapi-370530810100% (1)
- System and Network Administration MCQs - ITEC3123Document24 pagesSystem and Network Administration MCQs - ITEC3123sultanfateh748No ratings yet
- Quiz of Debian Linux by Zubair BarkatDocument10 pagesQuiz of Debian Linux by Zubair BarkatZubair BarkatNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper-1 Answers and ExplanationsDocument5 pagesSample Paper-1 Answers and Explanationsdebu000No ratings yet
- Database StructureDocument6 pagesDatabase StructurejattakcentNo ratings yet
- Semester: 8 Sem Subject: DOS Quiz BankDocument92 pagesSemester: 8 Sem Subject: DOS Quiz BankSAI RAMANNo ratings yet
- 8th Sem DOS Quiz Bank: 50 Questions on Distributed Operating SystemsDocument7 pages8th Sem DOS Quiz Bank: 50 Questions on Distributed Operating SystemsSAI RAMANNo ratings yet
- MCQ LISTDocument25 pagesMCQ LISTsidduNo ratings yet
- Linux Administration MCQ GuideDocument6 pagesLinux Administration MCQ GuidepmullapudishaNo ratings yet
- Linux QuestionsDocument5 pagesLinux QuestionsBhaskar SinNo ratings yet
- File Path and Directory Structure OS FundamentalsDocument53 pagesFile Path and Directory Structure OS FundamentalsQQQQQQQQQQQAQNo ratings yet
- TestBank ch10Document12 pagesTestBank ch10aimen_riyadhNo ratings yet
- Answers Unix TRPDocument7 pagesAnswers Unix TRParunkareerNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 18 UNIX ProgrammingDocument18 pagesPage 1 of 18 UNIX Programmingaraghav_23100% (1)
- Os QB 23-24Document8 pagesOs QB 23-24janhavizambre2023No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Practice Questions on Printers and LinuxDocument58 pagesMultiple Choice Practice Questions on Printers and LinuxBhumi ranaNo ratings yet
- OS Concepts Test QuestionsDocument20 pagesOS Concepts Test QuestionsRavi100% (1)
- Guide To Computer Forensics and Investigations 5Th Edition Bill Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument32 pagesGuide To Computer Forensics and Investigations 5Th Edition Bill Test Bank Full Chapter PDFkieraquachbs2ir100% (10)
- Unix MCQDocument12 pagesUnix MCQbabjeereddyNo ratings yet
- Guide To Computer Forensics and Investigations 5th Edition Bill Test BankDocument11 pagesGuide To Computer Forensics and Investigations 5th Edition Bill Test Bankshelleyrandolphikeaxjqwcr100% (30)
- UNIX Shell and Process FundamentalsDocument6 pagesUNIX Shell and Process FundamentalsakragnarockNo ratings yet
- CompTIA Linux+ Guide To Linux Certification 4th Edition Eckert Test Bank 1Document11 pagesCompTIA Linux+ Guide To Linux Certification 4th Edition Eckert Test Bank 1miles100% (31)
- UNIXDocument48 pagesUNIXArijit MaityNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4Document1 pageQuiz 4Richard RoqueNo ratings yet
- Quiz-4: FormsDocument1 pageQuiz-4: FormsRichard RoqueNo ratings yet
- BE Computer and IT Advanced Unix Programming, Artificial Intelligence and Expert SystemDocument41 pagesBE Computer and IT Advanced Unix Programming, Artificial Intelligence and Expert SystemJ DNo ratings yet
- Eos MCQDocument189 pagesEos MCQshruti patilNo ratings yet
- Data Processing SS 2Document2 pagesData Processing SS 2akpowowomarvelousNo ratings yet
- T.Y.B.Sc.I.T. Sem V Advanced Web ProgrammingDocument12 pagesT.Y.B.Sc.I.T. Sem V Advanced Web ProgrammingFouzan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- OS Sheet (5) SolutionDocument8 pagesOS Sheet (5) Solutionhussienboss99No ratings yet
- This Set of Linu1Document8 pagesThis Set of Linu1Printesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Screening QuestionsDocument7 pagesScreening Questionsvernon_hill1No ratings yet
- Display DOS Commands Files DirectoriesDocument9 pagesDisplay DOS Commands Files DirectoriesAlefiya bai SunelwalaNo ratings yet
- Mod 8 Self AssessDocument1 pageMod 8 Self AssessstudydatadownloadNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemsDocument7 pagesOperating SystemsIT8109No ratings yet
- OS FileSystem MCQsDocument2 pagesOS FileSystem MCQsAruna RaoNo ratings yet
- MC0070-Operating Systems With Unix Model Question PaperDocument23 pagesMC0070-Operating Systems With Unix Model Question Paperprac87No ratings yet
- B.A CS-II Midterm Paper OBJDocument2 pagesB.A CS-II Midterm Paper OBJSameer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Design of UNIX Operating System M.J Bach MCQ UNIT - IIDocument5 pagesDesign of UNIX Operating System M.J Bach MCQ UNIT - IIPrakashRameshGadekar67% (3)
- QUIZ Answer MergedDocument31 pagesQUIZ Answer MergedPiyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ilp Pat Test UnixDocument6 pagesIlp Pat Test Unixsahoo_deb6837No ratings yet
- OSSSC Group C Computer Model PaperDocument6 pagesOSSSC Group C Computer Model PaperSudamNo ratings yet
- 2_FYBCA-203-OS1-MCQBANK_2020-2021Document3 pages2_FYBCA-203-OS1-MCQBANK_2020-2021rupeshpawar0086No ratings yet
- PCO CrosswordDocument2 pagesPCO CrosswordElson RealistaNo ratings yet
- File Handling in CDocument7 pagesFile Handling in CAurangzaib BhattiNo ratings yet
- File 2022-1Document9 pagesFile 2022-1سيناء الحبيبةNo ratings yet
- Dos MCQ SetDocument26 pagesDos MCQ SetNisha MateNo ratings yet
- BC0042 Operating Systems Paper 1Document16 pagesBC0042 Operating Systems Paper 1SeekEducationNo ratings yet
- Secu5101 Computer Forensics & Cybercrime 08-09Document11 pagesSecu5101 Computer Forensics & Cybercrime 08-09David MusokeNo ratings yet
- Computer-1 (Q) With AnsDocument2 pagesComputer-1 (Q) With AnsRajuNo ratings yet
- Course: Field Training Faculty of Computers and Information Assiut University 2019/2020 - Spring 2020 Assiut UniversityDocument11 pagesCourse: Field Training Faculty of Computers and Information Assiut University 2019/2020 - Spring 2020 Assiut UniversityGDSC Assuit UniversityNo ratings yet
- Linux Question Bank With AnswersDocument39 pagesLinux Question Bank With Answerskirancha77No ratings yet
- BC A Linux FinalDocument7 pagesBC A Linux FinalsampurnakumarNo ratings yet
- TYBSC Computer Science SEM VI UG CS 321 Operating SystemDocument47 pagesTYBSC Computer Science SEM VI UG CS 321 Operating SystemPriyanka MahajanNo ratings yet
- BC0042 Operating SystemsDocument11 pagesBC0042 Operating SystemsSeekEducationNo ratings yet
- OPrating System QUASTIONDocument14 pagesOPrating System QUASTIONYohannes GeremewNo ratings yet
- BT0036 OPERATING SYSTEM PAPER 1 (BSciIT SEM 2)Document16 pagesBT0036 OPERATING SYSTEM PAPER 1 (BSciIT SEM 2)SeekEducationNo ratings yet
- Best Free Open Source Data Recovery Apps for Mac OS English EditionFrom EverandBest Free Open Source Data Recovery Apps for Mac OS English EditionNo ratings yet
- Free Open Source Linux OS For Data Recovery & Data Rescue Bilingual Version UltimateFrom EverandFree Open Source Linux OS For Data Recovery & Data Rescue Bilingual Version UltimateNo ratings yet
- Business Continuity Generaly Accepted Practices GAP v2.1 (Disaster Recovery Journal 2015) PDFDocument140 pagesBusiness Continuity Generaly Accepted Practices GAP v2.1 (Disaster Recovery Journal 2015) PDFducuhNo ratings yet
- Key Differences Between Natural Sciences and Social SciencesDocument6 pagesKey Differences Between Natural Sciences and Social SciencesAshenPerera60% (5)
- BW Query GuidelinesDocument10 pagesBW Query GuidelinesyshriniNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference To Psychotropic Medications: AntidepressantsDocument2 pagesQuick Reference To Psychotropic Medications: AntidepressantsNaiana PaulaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Pages 109-112 2 PDFDocument4 pagesGrammar Pages 109-112 2 PDFSteve SernaNo ratings yet
- JSMSC - TDv3 6 20Document251 pagesJSMSC - TDv3 6 20Jason20170% (1)
- Annual Reading Plan - Designed by Pavan BhattadDocument12 pagesAnnual Reading Plan - Designed by Pavan BhattadFarhan PatelNo ratings yet
- Product Catalog Encoders en IM0038143Document788 pagesProduct Catalog Encoders en IM0038143Eric GarciaNo ratings yet
- Get TRDocDocument209 pagesGet TRDoc10131No ratings yet
- All About Bearing and Lubrication A Complete GuideDocument20 pagesAll About Bearing and Lubrication A Complete GuideJitu JenaNo ratings yet
- Power Fresh 16Document3 pagesPower Fresh 16M. Ardi PrediyanaNo ratings yet
- TC-21FJ30LA: Service ManualDocument33 pagesTC-21FJ30LA: Service ManualRajo Peto alamNo ratings yet
- Distillation Lab ReportDocument6 pagesDistillation Lab ReportSNo ratings yet
- CS Sample Paper 1Document10 pagesCS Sample Paper 1SpreadSheetsNo ratings yet
- Year 5 Reasoning Test Set 3 Paper A: Q Marks Answer Notes 1a 1b 7 6 4Document2 pagesYear 5 Reasoning Test Set 3 Paper A: Q Marks Answer Notes 1a 1b 7 6 4Amina Zeghar BNo ratings yet
- Viennot - 1979 - Spontaneous Reasoning in Elementary DynamicsDocument18 pagesViennot - 1979 - Spontaneous Reasoning in Elementary Dynamicsjumonteiro2000No ratings yet
- Operational Readiness Guide - 2017Document36 pagesOperational Readiness Guide - 2017albertocm18100% (2)
- Q3 SolutionDocument5 pagesQ3 SolutionShaina0% (1)
- EPON ONU with 4FE+WiFi EONU-04WDocument4 pagesEPON ONU with 4FE+WiFi EONU-04WAndres Alberto ParraNo ratings yet
- BRTU-2000 Remote Terminal Unit for High Voltage NetworksDocument2 pagesBRTU-2000 Remote Terminal Unit for High Voltage NetworksLaurentiuNo ratings yet
- Super BufferDocument41 pagesSuper Bufferurallalone100% (1)
- Invoice Request for Digitize Global InovasiDocument1 pageInvoice Request for Digitize Global InovasiAsa Arya SudarmanNo ratings yet
- MOA of Actuarial Societ of BangladeshDocument22 pagesMOA of Actuarial Societ of BangladeshActuarial Society of BangladeshNo ratings yet
- SW - Simulation - Product MatrixDocument2 pagesSW - Simulation - Product Matrixsamar2011No ratings yet
- Rectangle StabbingDocument49 pagesRectangle StabbingApurba DasNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Stock ExchangeDocument11 pagesProject Report On Stock Exchangebhawna33% (3)
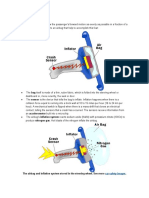
- Airbag Inflation: The Airbag and Inflation System Stored in The Steering Wheel. See MoreDocument5 pagesAirbag Inflation: The Airbag and Inflation System Stored in The Steering Wheel. See MoreShivankur HingeNo ratings yet
- Barcode BasicsDocument3 pagesBarcode Basicsnikhilbajpai_88No ratings yet
- Quiz Chapter 1 Business Combinations Part 1Document6 pagesQuiz Chapter 1 Business Combinations Part 1Kaye L. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- A Review of High School Economics Textbooks: February 2003Document27 pagesA Review of High School Economics Textbooks: February 2003Adam NowickiNo ratings yet