Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antimicrobials Antibiotics
Uploaded by
JULIE ANNE TAN100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
22 views2 pagesAntibiotics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAntibiotics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
22 views2 pagesAntimicrobials Antibiotics
Uploaded by
JULIE ANNE TANAntibiotics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
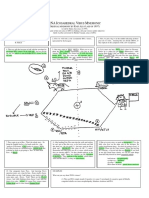
BACTERIOLOGY WEEK 4: ANTIMICROBIALS
ANTIMICROBIALS (ANTIBIOTICS) 5. Quinolones
- Chemical substances produced by a 6. Bacitracin
microorganism with the capacity to inhibit other 7. Metronidazole
microorganisms
- Destroy/kill the organism
MINIMAL INHIBITORY MINIMAL LETHAL
CONCENTRATION (MIC) CONCENTRATION (MLC)
NARROW SPECTRUM BROAD SPECTRUM - Is the lowest - Is the lowest
concentration of a concentration of drug
- Effective against a - Destroy different kinds
drug that inhibits that kills bacterial
limited number of of organism
bacterial growth growth
pathogens 1. Ampicillin
1. Bacitracin 2. Cephalosporin
2. Clindamycin 3. Chloramphenicol
3. Dapsone 4. Ciprofloxacin THERAPEUTIC INDEX
4. Erythromycin 5. Rifampicin - Is the ratio of the toxic dose to the therapeutic
5. Gentamicin 6. Sulfonamines dose
6. Isoniazid 7. Trimethoprim - The higher the therapeutic index, the more
7. Polymyxin B 8. Tetracycline effective the chemotherapeutic agent
8. Vancomycin - (CARST)
- (PIGBEDCV)
QUALITIES OF A GOOD AMA
KILL or INHIBIT pathogens
CLASSIFICATION OF BROAD SPECTRUM Selective toxicity (cause NO damage to the host)
a. Natural - Produced by bacteria or NON allergenic
drugs fungi Stable
1. Ampoterecin B Remain in specific tissues of the body
2. Erythromycin, Kill pathogens before they mutate / resistant
3. Kanamycin
4. Neomycin
5. Nystatin ACTION OF ANTIMICROBIALS
6. Rifampicin 1. Inhibiting cell wall synthesis
7. Streptomycin 2. Inhibiting CHON synthesis
8. Tetracycline 3. Inhibiting N.A synthesis
9. Vancomycin 4. Destroying the cell membrane
10. Bacitracin 5. Inhibiting essential metabolites
11. Gentamicin
12. Polymyxin
13. Griseofulvin
CELL WALL INHIBITORS
14. Penicillin
15. Cephalosphorin BACTERICIDAL
b. Semi- - Chemically modified natural 1. Basitracin
synthetic drugs with added extra 2. Cephalosporin
drugs chemical groups 3. Ampicillin
1. Ampicillin, 4. Imipenem
2. Carbenicillin 5. Vancomycin
3. Methicillin 6. Isoniazid
4. Synthetic - Chemically produced drugs - acts only on growing cells (stati/cidal)
drugs 1. Sulfonamides 7. Carbenicillin
2. Trimethoprim 8. Methicillin resembles D-alanyl-D-
3. Chloramphenicol PENICILIN
9. Penicillin alanineof the
4. Cifrofloxacin Beta lactamase resistant peptidoglycansubunits
Broad spectrum penicillin
5. Isoniazid penicillin
1. Pen G inactivated by stomach
6. Dapsone 1. Cloxacilin 1. Amoxicillin
acids, (parenterally)
2.2. Penicillin
Dicloxacillin
V 2. resistant
acid Ampicillin(orally)
3. Mehcillin 3. Piperacillin
3.4. Penicillinase resistant penicillin
BACTERIOSTATIC BACTERICIDAL Nafcillin 4. Carbenicillin
1. Methicillin
AGENTS AGENTS 5. Oxacillin 5. Ticarcillin
2. Nafcillin
1. Chloramphenicol 1. Aminoglycosides Key points: 3. Oxacillin
2. Dapsone a. gentamicin 4. Cephalosporins
Cell growths stops and death often follows
1. Cephalotin
3. Erythromycin b. amikacin Most selective antibiotics with high therapeutic
4. Clindamycin c. streptomycin index 2. Cefoxitin
5. Isoniazid 2. Beta-lactams 3. Ceftriazone
Inhibits transpeptidation enzymes
6. Rifampicin a. ceftriazone 4. Cephalexine
7. Sulfonamides b. imipenem
5. Cefixime
8. Tetracyclines c. penicillin INHIBIT PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
d. cefotaxime 30’S Ribosomes Inhibitors 6. Ribosomes
50’s Cefoperazone
3. Glycopeptides 5. Ampicillin acidInhibitors
stable, effective for
a. vancomycin 1. Tetracycline G+,1.G- Chloramphenicol-
4. Isoniazid 6. Vancomycin
-BACTERIOSTATIC cup-shaped molecule
BACTERIOSTATIC
drug; teicoplanin drug
7. Carbenicillin Acid stable,
Pseudomonas and
Proteus
2. Aminoglycosides- 2. Macrolide DRUG RESISTANCE
BACTERICIDAL a. Erythromycin – Intrinsic resistance Extrinsic resistance
a. Streptomycin, BACTERIOSTATIC - Lack specific target - Cannot bind to bacterial
Kanamycin Amikacin OR CIDAL site ( mycoplasma) cell ( mutation)
Gentamicin b. Clindamycin- - Unable to reach its - Cannot pass through the
b. Tobramycin BACTERIOSTATIC site of action cell membrane
Neomycin/Netilmicin OR CIDAL ( ribosome) ( mutation-cell membrane
c. Fusidic acid c. Lincomycin permeability)
Key points: - Destroyed by the enzyme
Binds with 30s subunit resulting to misreading of ( beta lactamase)
mRNA and interferes with aminoacyl-tRNA binding PENICILLINASES and
Binds with 50s subunit resulting to inhibition of CEPHALOSPORINASE
peptidyl transferase and inhibits peptide chain 1) BETA lactam
elongation INHIBITOR with BETA
High dosage of tetracycline may lead to live and LACTAM antibiotic
kidney damage and yellowing the teeth of children 2) CLAVULANIC ACID
Chloramphenicol may cause temporary or with AMOXICILLIN
permanent depression of bone marrow leading to ( AUGMENTIN)
aplastic anemia and leukemia (toxic side effect) 3) SULBACTAM with
Aminoglycosides Macrolide antibiotics AMPICILLIN
1. Gentamicin 1. erythromycin ( UNASYN)
2. Kanamycin 2. clindamycin - Pump out of the cell
3. Neomycin 3. azithromycin before it can damage or
4. streptomycin Chloramphenicol and kill cell ( MDR pump)
5. tobramycin erythromycin
- they have cyclohexane - bind to 23s rRNA
ring and may cause on the 50s
deafness and loss of ribosomal unit
balance (toxic)
INHIBIT NUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS
1. RIFAMPIN
2. MITOMYCIN
3. METRONIDAZOLE –disruption if DNA, for
anaerobic
4. NOVOBIOCIN
5. NITROFURANTOIN
6. QUINOLONES and FLUROQUINOLONES
a. CIPROFLOXACIN
b. NALIDIXIC ACID
c. NORFLOXACIN
d. LEVOFLAXIN-
- Interfere with the DNA gyrase and replication
- Highly effective for enteric bacteria E.coli
7. BACTERICIDAL
INHIBIT ENZYME ACTIVITY /METABOLITES
INHIBITORS
FOLIC ACID INHIBITORS
SULFONAMIDES inhi. Folic acid metabolism,
high there. index
TRIMETHOPRIM blocks tetrahydrofolate
synthesis
SXT ( trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole)
= co-trimoxazole
DAPSONE interferes F.A. synthesis
Others:
- Anti-TB drugs = S-I-R-E
- Inhibits synthesis of Cord factor (mycolicacid)
DISRUPT CELL MEMBRANE
Cell Membrane Inhibitors Anti- fungal agents
- Polymixin B (g-bacteria - Polyenes
Pseudomonas)) ( amphotericin B)
- Polymixin E (Colistin)- - Azole (Clotrimazole,
ointment Ketoconazole,
- BACTERICIDAL Fluconazole)
You might also like
- Mechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingFrom EverandMechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingH. RaškováNo ratings yet
- RNA I V M: Cosahedral Irus NemonicDocument2 pagesRNA I V M: Cosahedral Irus NemonicAnonymous 9xheGVRM1No ratings yet
- Mind Maps in Biochemistry - (Metabolism of Proteins)Document22 pagesMind Maps in Biochemistry - (Metabolism of Proteins)Gus LionsNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Library BooksDocument24 pagesPharmacy Library BooksJaved Noor Muhammad GabaNo ratings yet
- Pharma FinalADocument33 pagesPharma FinalAvaegmundigNo ratings yet
- Apoptosis, GENERAL PATHOLOGYDocument16 pagesApoptosis, GENERAL PATHOLOGYAhmad100% (1)
- Additional ProtozoanDocument2 pagesAdditional ProtozoanMary ChristelleNo ratings yet
- Kamal KV 500 Q CollectionsDocument13 pagesKamal KV 500 Q CollectionsBeta ReaderNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of The EyeDocument8 pagesPharmacology of The EyeRahul IyerNo ratings yet
- General PharmaDocument43 pagesGeneral PharmaAhmed El SharkawyNo ratings yet
- Intro To TDM and ToxicologyDocument46 pagesIntro To TDM and ToxicologyAl-hadad AndromacheNo ratings yet
- PharmecogenomicsDocument21 pagesPharmecogenomicsRatan Ratan100% (1)
- UW (Step 1) Biochemistry - Educational ObjectivesDocument41 pagesUW (Step 1) Biochemistry - Educational ObjectivesUsama BilalNo ratings yet
- Vicks Drug of Choice ListDocument17 pagesVicks Drug of Choice Listethank211No ratings yet
- Epidemiology MarkerDocument29 pagesEpidemiology Markerdrsanty100% (3)
- Cholinergic Anticholinergic DrugsDocument60 pagesCholinergic Anticholinergic DrugsMD. RASEL MAHMUD MIMNo ratings yet
- مذكرة فارماكولوجي روعةDocument56 pagesمذكرة فارماكولوجي روعةKomang Gede Suwija Negara100% (1)
- Cancer Drugs Drugs Indication Adverse Effects Interaction and ContraindicationDocument5 pagesCancer Drugs Drugs Indication Adverse Effects Interaction and ContraindicationOndari gisemba OSINDENo ratings yet
- Tetracyclines, Macrolides & OthersDocument3 pagesTetracyclines, Macrolides & OthersJaybee SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Recall QuestionsDocument2 pagesRecall QuestionsAymen BekirNo ratings yet
- Secondary Hemostasis FibrinolysisDocument8 pagesSecondary Hemostasis FibrinolysisSean MatthewNo ratings yet
- Lab Diagnosis of NeoplasiaDocument14 pagesLab Diagnosis of Neoplasiasapphiresia100% (6)
- Presenation Fibrous Cavernous Tuberculois Teachers VersionDocument49 pagesPresenation Fibrous Cavernous Tuberculois Teachers VersionĆux 天主好 OkereNo ratings yet
- Toxicology and TDMDocument121 pagesToxicology and TDMteppie0917No ratings yet
- Adrenergic Agonists 2020 PDFDocument65 pagesAdrenergic Agonists 2020 PDFAlaa NaserNo ratings yet
- Pathologyq'sDocument358 pagesPathologyq'sNick JacobNo ratings yet
- Certifying DeathDocument8 pagesCertifying DeathDaniel LimNo ratings yet
- Azathioprine DrugDocument18 pagesAzathioprine DrugteritohahaNo ratings yet
- SE ContentOutlineandSampleItemsDocument167 pagesSE ContentOutlineandSampleItemsKatina CamposNo ratings yet
- 800 QuestionsDocument77 pages800 QuestionsAtif DogarNo ratings yet
- Ahmed Samir - Step 1 Experience - 251Document16 pagesAhmed Samir - Step 1 Experience - 251Mohamed LoaiNo ratings yet
- Microbiology 19 PDFDocument6 pagesMicrobiology 19 PDFLyka Villagracia AsiloNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic CMU 2557 ORC Shared View PDFDocument60 pagesAntibiotic CMU 2557 ORC Shared View PDFSitthikorn StrikerrNo ratings yet
- Pathology Questions PDFDocument67 pagesPathology Questions PDFDhruva PatelNo ratings yet
- This Set of Microbiology Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pagesThis Set of Microbiology Multiple Choice QuestionsMinh AnhNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry & Genetics Important Concepts Q&as DR Kumar Ponnusamy & Jegathambigai RN, Biochemistry & Genetics, International Medical University (IMU) / AIMST University School of Medicine, MalaysiaDocument60 pagesBiochemistry & Genetics Important Concepts Q&as DR Kumar Ponnusamy & Jegathambigai RN, Biochemistry & Genetics, International Medical University (IMU) / AIMST University School of Medicine, MalaysiaDr Kumar Ponnusamy100% (3)
- Dma PharmaDocument12 pagesDma PharmaYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- KAPS Pharmacist Syllabus The PharmapediaDocument3 pagesKAPS Pharmacist Syllabus The PharmapediaSanam ThahaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions Section: Choose The Most Appropriate Single AnswerDocument3 pagesMultiple Choice Questions Section: Choose The Most Appropriate Single Answersepanta2002No ratings yet
- GonadoDocument32 pagesGonadoshailendra meena50% (2)
- 7959fad152da0a5 PDFDocument410 pages7959fad152da0a5 PDFDrgame MedNo ratings yet
- NORADRENALINE (Norepinephrine) : Presentation DescriptionDocument3 pagesNORADRENALINE (Norepinephrine) : Presentation DescriptionMutiaraNo ratings yet
- Block H Pre Proff KGMC 2022 SolvedDocument17 pagesBlock H Pre Proff KGMC 2022 SolvedF ParikhNo ratings yet
- Repro Costanzo NotesDocument11 pagesRepro Costanzo NotesAbeebs SalahouNo ratings yet
- Chapter 43 - Beta-LactamDocument7 pagesChapter 43 - Beta-LactamErika De JesusNo ratings yet
- 2018.docx Version 1Document92 pages2018.docx Version 1Afsal Ur FriendNo ratings yet
- First Aid Pharmacology AntimicrobialsDocument23 pagesFirst Aid Pharmacology AntimicrobialsLaura Lopez RocaNo ratings yet
- GP at Orientation PDocument28 pagesGP at Orientation PasiyazaidiaNo ratings yet
- PhisioDocument15 pagesPhisiojohnNo ratings yet
- SPMC - Microbiology Case StudyDocument9 pagesSPMC - Microbiology Case StudyRomie SolacitoNo ratings yet
- BIOL 2900 Learning OutcomesDocument11 pagesBIOL 2900 Learning OutcomesTalk To MeNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Summary 13 - 14 Part 1Document13 pagesMicrobiology Summary 13 - 14 Part 1Jessica MalinNo ratings yet
- Rational Antibiotic Usage and Antibiotic Policy - Dr. FirmansyahDocument76 pagesRational Antibiotic Usage and Antibiotic Policy - Dr. Firmansyahjay neefNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Notes: By: Khurram AbbasDocument48 pagesPharmacology Notes: By: Khurram AbbasAsma AnjumNo ratings yet
- Aztreonam: Finals 08 By: MmikidsüDocument2 pagesAztreonam: Finals 08 By: MmikidsüVince CabahugNo ratings yet
- AEFIDocument35 pagesAEFIMisha ModiNo ratings yet
- Transes PharmacodynamicsDocument36 pagesTranses PharmacodynamicsGwyneth Koleen Lopez100% (1)
- Lista e Librave MjekesoreDocument4 pagesLista e Librave MjekesoreEmily OwenNo ratings yet
- Dirty Medicine - FortuneDocument2 pagesDirty Medicine - FortuneHarshaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic CoverageDocument1 pageAntibiotic CoverageYNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument2 pagesAntibioticsShalini PanchalNo ratings yet
- H 2 o 2Document3 pagesH 2 o 2Muzammal hoque mollahNo ratings yet
- antimicrobial agents تجميعيDocument5 pagesantimicrobial agents تجميعيahmedmahmoudfelefil93No ratings yet
- Annex A of FA 2020-422 Updated As of 7april2020 PDFDocument19 pagesAnnex A of FA 2020-422 Updated As of 7april2020 PDFSerjoe N. RosalNo ratings yet
- Glossary I (Part 1) - Lactams: Class and Subclass Designations and Generic NameDocument5 pagesGlossary I (Part 1) - Lactams: Class and Subclass Designations and Generic NameDIEGO FERNANDO URIBE JARAMILLONo ratings yet
- Pt. Sarta Tiga Medika: Solution For Your HealtDocument5 pagesPt. Sarta Tiga Medika: Solution For Your HealtAde HanityaNo ratings yet
- HW 03 On IUPAC NamingDocument1 pageHW 03 On IUPAC NamingEMERALDARCANISTNo ratings yet
- Visual Critical Care Antibiotic Guide 2019-2Document1 pageVisual Critical Care Antibiotic Guide 2019-2Adna NelsonNo ratings yet
- BHP ALL UNIT NewDocument48 pagesBHP ALL UNIT NewDinda Nurafni HapsahNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycosides SARDocument10 pagesAminoglycosides SARPrince Pavan100% (1)
- List Obat GenerikDocument1 pageList Obat GenerikFate DreamworkNo ratings yet
- Antibiotika AminoglikosidaDocument12 pagesAntibiotika AminoglikosidaEVY INDRIYANINo ratings yet
- Classification of AntibioticsDocument5 pagesClassification of AntibioticsdenaNo ratings yet
- SS-Laktamski Antibiotici: Peroralni Parenteralni Penicilaza Rezistentni PeniciliniDocument5 pagesSS-Laktamski Antibiotici: Peroralni Parenteralni Penicilaza Rezistentni PeniciliniMali PrstNo ratings yet
- List of Sanitizer Testing LabDocument2 pagesList of Sanitizer Testing LabAbhijeet kumbharNo ratings yet
- Modul-4 - Logistik TBDocument29 pagesModul-4 - Logistik TBlusyNo ratings yet
- Esbl GNBDocument4 pagesEsbl GNBPutri Nilam SariNo ratings yet
- List of AntibioticsDocument11 pagesList of AntibioticsD. BarNo ratings yet
- Conformat - FogCleanerDocument12 pagesConformat - FogCleanerduna tarimaNo ratings yet
- Romania Biocide FormulationsDocument167 pagesRomania Biocide FormulationstomellefsenNo ratings yet
- Alsoft A - Saraya Co PDFDocument2 pagesAlsoft A - Saraya Co PDFVixiMerahNo ratings yet
- Table: Selected Antibacterial Antibiotics Antibiotics THAT . Mechanism of Action Names of Drugs Notes and ProblemsDocument4 pagesTable: Selected Antibacterial Antibiotics Antibiotics THAT . Mechanism of Action Names of Drugs Notes and ProblemsTJNo ratings yet
- Annex A: List of Notified Hand Sanitizers and Rubbing Alcohol ProductsDocument22 pagesAnnex A: List of Notified Hand Sanitizers and Rubbing Alcohol ProductsGigiPasayloonNo ratings yet
- Mohamad Hamad Formulating Antiseptic Disinfectant ItemsDocument12 pagesMohamad Hamad Formulating Antiseptic Disinfectant ItemsMohamad Hamad50% (4)
- Laporan Sisa Stock (Harga Jual) : Pt. Haris Dua Empat SejahteraDocument25 pagesLaporan Sisa Stock (Harga Jual) : Pt. Haris Dua Empat SejahteraIntaan NurainiiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ronald Irwanto Natadidjaja, SPPD - Kpti, Finasim: PendidikanDocument28 pagesDr. Ronald Irwanto Natadidjaja, SPPD - Kpti, Finasim: PendidikanayuNo ratings yet
- Drug Import-LinezolidDocument13 pagesDrug Import-LinezolidShantanu MannaNo ratings yet
- ANTIBIOTICDocument5 pagesANTIBIOTICThe KhuwaarsNo ratings yet
- Anta Assignment SAMPLEDocument3 pagesAnta Assignment SAMPLEMSKCNo ratings yet