Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Of Demand Ue Solute Val Ab The Se U: ,) E (Lasticity of Demand Ee C Pri E
Of Demand Ue Solute Val Ab The Se U: ,) E (Lasticity of Demand Ee C Pri E
Uploaded by
asim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageThis document defines and explains different types of elasticity, including price elasticity of demand, cross elasticity of demand, income elasticity of demand, and elasticity of supply. Price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price. Total revenue is negatively related to price changes for elastic demands but positively related for inelastic demands. Income elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in income. Elasticity of supply measures the responsiveness of quantity supplied to a change in price.
Original Description:
Original Title
Elasticity summary
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document defines and explains different types of elasticity, including price elasticity of demand, cross elasticity of demand, income elasticity of demand, and elasticity of supply. Price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price. Total revenue is negatively related to price changes for elastic demands but positively related for inelastic demands. Income elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in income. Elasticity of supply measures the responsiveness of quantity supplied to a change in price.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageOf Demand Ue Solute Val Ab The Se U: ,) E (Lasticity of Demand Ee C Pri E
Of Demand Ue Solute Val Ab The Se U: ,) E (Lasticity of Demand Ee C Pri E
Uploaded by
asimThis document defines and explains different types of elasticity, including price elasticity of demand, cross elasticity of demand, income elasticity of demand, and elasticity of supply. Price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price. Total revenue is negatively related to price changes for elastic demands but positively related for inelastic demands. Income elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in income. Elasticity of supply measures the responsiveness of quantity supplied to a change in price.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
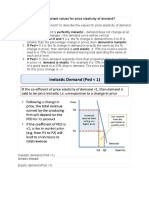
ELASTICITY
Price Elasticity of Demand (Ed),
%∆𝑄𝑑/ 𝑄𝑑 𝐴𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒
Use the absolute value of demand ,│Ed│= %∆𝑃/ 𝑃 𝐴𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒
;
when P = price, Q = quantity demanded, Average= initial Q or P + new Q or P/2
If Ed > 1, Elastic demand
If Ed < 1, Inelastic demand
If Ed = 1, Unitary Elastic demand
If Ed = 0, Perfectly Inelastic demand
If Ed = ∞, Perfectly Elastic demand
Total Revenue (TR) and Elasticity, TR= P*Q
If the demand is Elastic: while the price increase; TR decreases
while the price decreases; TR increases
Negative relationship, (Luxury goods)
If the demand is Inelastic: while the price increase; TR increases
while the price decreases; TR decreases
Direct relationship, (Necessities goods)
%∆𝑸𝒅
Cross Elasticity of Demand* Don't use absolute value = %∆ 𝑷𝒓𝒊𝒄𝒆 𝒐𝒇 𝒔𝒖𝒃𝒔𝒕𝒊𝒕𝒖𝒕𝒆 𝑶𝑹 𝒄𝒐𝒎𝒑𝒍𝒆𝒎𝒆𝒏𝒕
IF cross Ed > 1 (Positive); the good is a substitute
IF cross Ed < 1 (Negative); the good is a complement
%∆𝑸𝒅
Income Elasticity of Demand= %∆ 𝑰𝒏𝒄𝒐𝒎𝒆
If EI > 1 (Positive), Income Elastic demand (Normal good; Luxury goods)
If it's 0 < EI < 1, Income Inelastic demand (Normal good; Necessities goods)
If EI < 0 (negative), Income Inelastic demand (Inferior good)
%∆𝑸𝒔
Elasticity of Supply= %∆𝑷
If Es = 1, Unitary Elastic supply
If Es = 0, Perfectly Inelastic supply. e.g., Monetary supply.
If Es = ∞, Perfectly Elastic supply
You might also like
- Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument18 pagesElasticity of Demand and SupplyMochimNo ratings yet
- Elasticity - II BBA, BCIS ModifiedDocument36 pagesElasticity - II BBA, BCIS ModifiedSubrat PantaNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand For BBADocument82 pagesElasticity of Demand For BBAinfinity warzNo ratings yet
- Elasticity: Prof. (DR.) Vandana BhavsarDocument27 pagesElasticity: Prof. (DR.) Vandana BhavsarAkhil JosephNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Supply Notes Mid Point - ECO415Document2 pagesElasticity of Supply Notes Mid Point - ECO415Syed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand: Dr. Utpal ChattopadhyayDocument22 pagesElasticity of Demand: Dr. Utpal ChattopadhyaydivyamadhavanNo ratings yet
- Price Elasticity of DemandDocument6 pagesPrice Elasticity of DemandIfteakher Ibne HossainNo ratings yet
- Elascity SongDocument3 pagesElascity SongJason ChenNo ratings yet
- ECON Quiz 2 Reviewer From AdrianDocument20 pagesECON Quiz 2 Reviewer From AdrianAika AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Type of Elasticity Absolute Value ExplanationDocument3 pagesType of Elasticity Absolute Value ExplanationAk CerenNo ratings yet
- Notes On Price Elasticity of DemandDocument5 pagesNotes On Price Elasticity of DemandSilent GirlNo ratings yet
- L8ECO113 Elasticity of DemandDocument25 pagesL8ECO113 Elasticity of DemandVineet KumarNo ratings yet
- 8 TopicsinConsumerBehaviour PDFDocument20 pages8 TopicsinConsumerBehaviour PDFAnshu JainNo ratings yet
- Topic3 ElasticittDocument30 pagesTopic3 ElasticittMạnh Nguyễn VănNo ratings yet
- Economics Formula SheetsDocument8 pagesEconomics Formula SheetsSteph GomezNo ratings yet
- Econ Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesEcon Cheat SheetLarryNo ratings yet
- Elasticity and Its Applications - 5 - 6 - 920220823223838Document26 pagesElasticity and Its Applications - 5 - 6 - 920220823223838Aditi SinhaNo ratings yet
- Ch5 Price Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument1 pageCh5 Price Elasticity of Demand and Supply董振鸿No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document11 pagesChapter 3Sue EdahNo ratings yet
- Eco 162 (Chapter 3)Document24 pagesEco 162 (Chapter 3)yasmeenNo ratings yet
- 106 Managerial EconomicsDocument9 pages106 Managerial EconomicspratsondasNo ratings yet
- Elasticity EconomicsDocument25 pagesElasticity EconomicsMaryjoy Sadiwa AlmeroNo ratings yet
- ch-5 Elasticity & Its Application CompletedDocument20 pagesch-5 Elasticity & Its Application CompletedShubham DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Module 3 GST 104Document25 pagesModule 3 GST 104Somod BadmusNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand ECODocument45 pagesElasticity of Demand ECOYash TRIPATHINo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument22 pagesElasticity of DemandRajveer SinghNo ratings yet
- 8.3.6 - Elasticity of DemandDocument3 pages8.3.6 - Elasticity of DemandJunior PyareNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4-Elasticity and Its TypesDocument33 pagesLecture 4-Elasticity and Its Typeszahra naheedNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument16 pagesElasticity of DemandHumayun95% (20)
- Elasticity Concept: Ie 323-3: Principles of EconomicsDocument33 pagesElasticity Concept: Ie 323-3: Principles of EconomicsKaren Kaye BulanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 2023 MPH WUDocument43 pagesLecture 3 2023 MPH WULawal titilayoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 ElasticityDocument22 pagesChapter 7 ElasticityRayan AlkabsiNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument19 pagesElasticityMeherun nisaNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument34 pagesElasticity of DemandRajeshsharmapurangNo ratings yet
- Price Elasticity of DemandDocument15 pagesPrice Elasticity of DemandGoransh KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Ecn - 601 Exam 1 Study GuideDocument16 pagesEcn - 601 Exam 1 Study GuidekalkajiNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5. ElasticityDocument2 pagesChapter-5. Elasticityairahcali123No ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand - PPTDocument39 pagesElasticity of Demand - PPTShikha SinghNo ratings yet
- IOA Personal NotesDocument9 pagesIOA Personal NotesmadsNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of MicroeconomicsDocument6 pagesSyllabus of Microeconomicsmint20051018No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document5 pagesTutorial 33456123No ratings yet
- Elasticity of Supply 2 1Document11 pagesElasticity of Supply 2 1Nguyễn Như NgọcNo ratings yet
- The Elasticity of DemandDocument7 pagesThe Elasticity of DemandAraoluwamide BolarinwaNo ratings yet
- Elasticities of DemandDocument13 pagesElasticities of DemandMeharunnessa AkifaNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument26 pagesElasticitysajannt1538No ratings yet
- Slutsky Equation As An ElasticityDocument5 pagesSlutsky Equation As An ElasticityGerald HartmanNo ratings yet
- G10 Market EquilibriumDocument18 pagesG10 Market EquilibriumAprilia RumahorboNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Elasticity of DemandDocument22 pagesChapter 5 Elasticity of DemandAvi JhaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 6 NotesDocument6 pagesCh. 6 NotesEmily LauNo ratings yet
- PreferncesDocument4 pagesPreferncesAndres BarreraNo ratings yet
- Concepts of ElasticitiesDocument24 pagesConcepts of ElasticitiesRonald VillamartinNo ratings yet
- MBF GE Econ PPT Ch05Document16 pagesMBF GE Econ PPT Ch05Mustapha AmpatuanNo ratings yet
- Naveena SamaDocument19 pagesNaveena SamaSägñîk KàtårïNo ratings yet
- Elasticity and Its ApplicationsDocument22 pagesElasticity and Its ApplicationsChaseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ElasticityDocument24 pagesChapter 3 Elasticityalymsrh810No ratings yet
- AME - Session 3Document63 pagesAME - Session 3Dev MittalNo ratings yet
- Income and Cross Price Elasticity of DemandDocument5 pagesIncome and Cross Price Elasticity of DemandReemaz SuhailNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Cultural Differences in International BusinessDocument21 pagesThe Importance of Cultural Differences in International BusinessasimNo ratings yet
- The Role of Express Delivery Services in Cross Border E-Commerce in Africa: Case of The Cemac Sub RegionDocument77 pagesThe Role of Express Delivery Services in Cross Border E-Commerce in Africa: Case of The Cemac Sub RegionasimNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management: Strategy, Planning, and Operation: Seventh Edition, Global EditionDocument52 pagesSupply Chain Management: Strategy, Planning, and Operation: Seventh Edition, Global EditionasimNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management: Strategy, Planning, and Operation: Seventh Edition, Global EditionDocument39 pagesSupply Chain Management: Strategy, Planning, and Operation: Seventh Edition, Global Editionasim100% (1)
- Supply Chain Management: Strategy, Planning, and Operation: Seventh Edition, Global EditionDocument34 pagesSupply Chain Management: Strategy, Planning, and Operation: Seventh Edition, Global EditionasimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Stock ValuationDocument21 pagesChapter 7 - Stock ValuationasimNo ratings yet
- Eq Chapter 6,7,8,9 EqDocument6 pagesEq Chapter 6,7,8,9 EqasimNo ratings yet
- Final Chapter 8 - Risk and ReturnDocument60 pagesFinal Chapter 8 - Risk and ReturnasimNo ratings yet
- Exam Chap 13Document60 pagesExam Chap 13asimNo ratings yet
- Governance Value Analysis and Marketing Strategy: Journal of Marketing January 1999Document55 pagesGovernance Value Analysis and Marketing Strategy: Journal of Marketing January 1999asimNo ratings yet
- Final Version RevisedDocument25 pagesFinal Version RevisedasimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Short - Run Costs and Output DecisionsDocument74 pagesChapter 8 Short - Run Costs and Output DecisionsasimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Stock ValuationDocument36 pagesChapter 7 - Stock ValuationasimNo ratings yet