Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wave Mechanics Top Expected MCQs
Uploaded by
PriyabrataTarai0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views4 pagesScience
Original Title
Wave mechanics Top expected MCQs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentScience
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views4 pagesWave Mechanics Top Expected MCQs
Uploaded by
PriyabrataTaraiScience
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Zs,
We eee ee
A particle possesses a kinetic energy E and mass m, then its de Broglie wavelength is
h
A) Tink © niImE
»
5.
© ae @ 3
Pam 1
OV: © Tame
An electron is accelerated through a potential difference of V volts. The de Broglie +
wavelength of the electron is
12.27 12.27
® I i
© 1227 WF (@ 1227
. Read the statements (A and B) and choose the answer:
(A) The de Broglie wavelength of a moving particle is inversely proportional to its
momentum
(B) Only a charged particle in motion is associated with matter waves
(@) A and B are correct
(®) A and B are wrong
(2) A is wrong and B is correct CAREER WAVE ~
Ad) Ais correct and B is wrong
4,
If the momentum of a particle is doubled then its de Broglie wavelength
halves (®) doubles
(0) quadruples (@ remains the same
The masses of neutron and electron are m, and m, respectively. If they have the same de
Broglie wavelength, then their velocities should be in the ratio
me
(a) 1:1 A) in,
me
¥
6. An c-particle has a mass 4 m, and a proton m,. If they possess the same kinetic energy,
then the ratio of the de Broglie wavelengths is
(1:4 () 4:1
() 2:1 eta) 1:2
7. The characteristics of wave function y are
(@ Real function, finite and discontinuous
8) Complex, single valued, finite and continuous function
() Complex, infinite and discontinuous function
(@ Complex single valued and infinite
8. The wave function for the motion of a particle in a potential well of width a is given as
__ (nme
Vy, = B sin(— J, then B is
1 1
7 ® f
: 7 Yi
af @ He
‘oni . CAREER WAVE
9. When the wave function is normalized then necccess Gua aoa
@ vy=l ® wytd,=1
a 2
0 Jvvta=1 0) Juwrd,=1
4 fe
10. Increasing the potential difference between anode and filament in Davisson-Germer
experiment
(@) causes an increase in the wavelength of the electron-waves
(b) causes a decrease in the wave velocity
Ay causes a decrease in the wavelength of the electron-waves
(@ causes a decrease in the momentum of the electron
11. For a particle of mass m confined to a cubical box of side L, the allowed values of energy
E are given as
242 242
h mh
@ ~*,n=1,2,3 py En =1,2,3
mL? ome
we n?h?
© n= 1,2,3
mn Qu"
12. An electron is confined to a potential box of infinite height and width 10 A. The probability
of finding the particle in a small interval Av at the centre of the box for the energy state
immediately above the ground state is
_Aa) zero () 05
(9 09 ' @1.:
13. If a charged particle of mass m is accelerated through a potential difference of V volts,
the de Broglie wavelength is proportional to
1
@ v2 ) Vv
1
4) Vv? @v
14, The deBroglie hypothesis is associated with —_
(a) wave nature of o-particles only (®) wave nature of radiations
(c) wave nature of electrons only wave nature of all material particles
15. Which of the following phenomena cannét be expressed by wave nature of light?
(a) Interference (0) Diffraction
(0) Polarization _(d) Photoelectric effect
16. Matter waves |
(a) are longitudinal _(b) show diffraction
(0) are electromagnetic (@ always travel with speed of light
17. Of the following moving with the same velocity, the one which has largest wavelengy,
is
(@) a photon 6), an electron
(0) an o-particle (@ a neutron
18. The uncertainty principle holds for of
(a) macroscopic particles only
48) microscopic particles only _ CAREER WAVE
(9) macroscopic and microscopic particles both : ——
(d) neither macroscopic nor microscopic particles
19. The uncertainty principle can not hold for the following pairs
(a) energy and time (0) position and momentum
(Q) angular momentum and angle __{d) linear momentum and angle
20. Matter waves were first experimentally observed by
(@) Frank-Hertz 48 Davisson and Germer
(0) Ster-Gerlach (@) de-Broglie.
21. If the momentum of a particle is increased to four times, then the deBroglie wavelength
will become
(@) half (b) four times
(twice 4d) one-fourth
22. The Schrodinger time-independent wave equation for free particle is
a 2
“a mm Yt E-vy=0 ® ivy +(v-By=0
1? 2 9
© am” ¥ +Ey=0 @ Evy -Ey=0
23, Schrédinger time dependent wave equation for free particle is
ne ay . oy n ey , ay
© “oma ~ nS A) mae =~ zp
Qma?y — i oy may a
© Ge ogt Bar Pag a
24, An o-particle and a proton have the same kinetic energy. The ratio of their wavelength
is (m,, = 4mp)
@ 1:2
() 2:1
Mo) 1:4 ue
@4
aera ae
25. In Davisson-Germer experiment, nickel crystal acts as
(@) perfect absorber (b) perfect reflector
(©) two dimensional grating ~{d) three dimensional diffra ating
26. Momentum of a photon of energy hv is wy
@ Ww ( hve
ey hv/c (d) has no momentunC AREER WAVE
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Multiply by 1: Material Number Material DescriptionDocument5 pagesMultiply by 1: Material Number Material DescriptionPriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- ScreenshotDocument1 pageScreenshotPriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
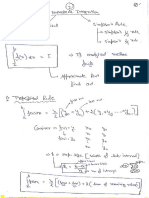
- Trapezoidal and Simpson RulesDocument8 pagesTrapezoidal and Simpson RulesPriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- ATC-Physics Lec-9.3 MODERN PHYSICS Bohr's Model #ATC#AO #Photonics #.Mp4Document100 pagesATC-Physics Lec-9.3 MODERN PHYSICS Bohr's Model #ATC#AO #Photonics #.Mp4PriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- ScreenshotDocument1 pageScreenshotPriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- Vebeiy : Tegdnfenahm of EnemyDocument14 pagesVebeiy : Tegdnfenahm of EnemyPriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- Sound dpp-3 (Mix)Document2 pagesSound dpp-3 (Mix)PriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- Test-1 ElectrostaticsDocument4 pagesTest-1 ElectrostaticsPriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- SWOT Template For PowerPointDocument1 pageSWOT Template For PowerPointPriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Practice Set.Document36 pagesCurrent Electricity Practice Set.PriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- dpp-6 2Document3 pagesdpp-6 2PriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- E - . Ooul: CA) S T T e ChargeDocument2 pagesE - . Ooul: CA) S T T e ChargePriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- P - Symbol Last - Close Last - Volume TYPE PositionDocument2 pagesP - Symbol Last - Close Last - Volume TYPE PositionPriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus & Weightage of Questions For On-Line Examination ADVERTISEMENT No: 05/2020 Manager (Fire Services)Document9 pagesSyllabus & Weightage of Questions For On-Line Examination ADVERTISEMENT No: 05/2020 Manager (Fire Services)Satya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations Top Questions NotesDocument19 pagesDifferential Equations Top Questions NotesPriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- Scan ThermoplusoneDocument18 pagesScan ThermoplusonePriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument100 pagesSoundPriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonics Most Important MCQsDocument2 pagesUltrasonics Most Important MCQsPriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- Lec-7 4Document100 pagesLec-7 4PriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- Superconductivity 1mark Top Expected MCQsDocument3 pagesSuperconductivity 1mark Top Expected MCQsPriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- Lec-7 5Document100 pagesLec-7 5PriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- Lec-7.6Document100 pagesLec-7.6PriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- Lec-7.3 - SOUNDDocument100 pagesLec-7.3 - SOUNDPriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- Dpp-6 (Lec 5.7)Document3 pagesDpp-6 (Lec 5.7)PriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- dpp-6 2Document3 pagesdpp-6 2PriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- Unit-6 - Physics - Wave Optics (Practice and Solution)Document53 pagesUnit-6 - Physics - Wave Optics (Practice and Solution)PriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- Tab DelimitedDocument561 pagesTab DelimitedPriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- Elearning Courses - EdX and SNTI (Tata Steel)Document17 pagesElearning Courses - EdX and SNTI (Tata Steel)PriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet
- 359 JD Creating A Winning Marketing MixDocument4 pages359 JD Creating A Winning Marketing MixPriyabrataTaraiNo ratings yet