Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SCIENTIFIC TEXT - Morales Torres Santiago Yael - 653A
Uploaded by
Morales SantiagoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SCIENTIFIC TEXT - Morales Torres Santiago Yael - 653A
Uploaded by
Morales SantiagoCopyright:
Available Formats
Morales Torres Santiago Yael - 653A
Overview of the Global prevalence of Adolescent alcohol effects Cognitive and Adolescent alcohol
adolescent brain adolescent alcohol use on the human brain Functional neural functioning effects in animals
neuroimaging studies following alcohol
have identified
potential effects of
remittance
Alcohol-induced deficits are
The brain undergoes significant Alcohol is the most
arguably more impactful for alcohol use on
neurodevelopment during frequently used
adolescents than adults, given that adolescent brain
substance, as it is One functional Adolescent alcohol
adolescence, with maturation educational attainment, learning, activation during
Neuro-psychological consequences of alcohol use
generally the easiest neuroimaging study use in male rodents
continuing until around age 25. and ongoing neural development tasks of working
for adolescents to
Functional brain consequences
are the most critical developmental memory, inhibitory reported that, after has also been
access Globally, one month of associated with
tasks of adolescence control, and reward
Brain gray matter, which includes mostly 22% of males and abstinence, poorer inhibition,
sensitivity
nerve cell bodies and dendrites, tends to 5% of females binge adolescents who reflecting heightened
decrease during normal adolescent drink during Alcohol use behaviors at ages 12 previously drank impulsivity and risk
brain development via removal of weak adolescence. to 14 predict lower educational Binge drinking may heavily no longer taking in adulthood
synaptic connections and changes in the achievement in later years affect the emotional exhibited alterations
extracellular matrix. component of reward in reward activation
Globally, 22% of processing and to alcohol cues,
males and 5% of Adolescent binge drinking was
decision making, as highlighting the
White matter volume and white matter females binge drink associated with an overall cognitive
damage to the potential for
integrity increase over this period with during adolescence. deficit and specific impairments in Similar to human
posterior cerebellum adolescents to
continued myelination of axons, allowing When focusing on decision-making and inhibition studies, moderate
has been associated benefit from early
for more efficient communication country-specific alcohol use and
with cognitive and intervention and
between brain regions. adolescent binge binge drinking in
Some cognitive domains show emotional deficits recover from the
drinking, rates are male and female
dose-dependent relationships short-term effects of
reported as 36% of rodents predicts
Neurotransmitter systems, which where greater alcohol use is alcohol
males and 12% of Neuropsychological alterations in learning
transmit chemical signals across associated with poorer cognitive
females in Europe; studies demonstrate and memory during
synapses, also undergo significant functioning
30% of males and a possible dose- Long-term cessation adolescence
change in adolescence
Neurobiological consequences
6% of females in the dependent response of binge drinking (two
Structural brain consequences
Americas and of alcohol use on to four years) was
Binge and heavy drinking appears
Inhibitory control is generally lower in Western Pacific executive functioning associated with
to affect the normal
adolescence than adulthood, reflecting Regions; and ability improvements in
developmental trajectories of gray
greater excitatory synapses approximately 17– and white matter maturation immediate recall that
21% of adolescent during adolescence, particularly in coincided with control
Heavy drinkers may
males and 3–4% of the frontal and temporal lobes, performance of not
Neurotoxin exposure, particularly alcohol require more
adolescent females and interconnecting networks, drinking and
use, during adolescence can affect executive cognitive
binge drink in Africa which suggests alcohol use is improvements in
healthy brain development (cognitive, control to perform at
and South East associated with accelerated brain long-term memory
emotional, and social functioning). the same level as
Asia. aging and working memory
non-users.
Leesa, B., Meredithb, L.R., Kirklandc, A.E., Bryantd, B.E. & Squeglia, L.M. (2020). “Effect of alcohol use on the adolescent brain and behavior”. University of Sydney, University of California, American
University & Medical University of South Carolina. Retrieved on December 8th, 2020, of https://www-sciencedirect-com.pbidi.unam.mx:2443/science/article/pii/S0091305719306021?via%3Dihub
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
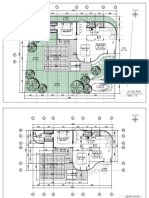
- 2023.01.25 Plan Pecatu Villa - FinishDocument3 pages2023.01.25 Plan Pecatu Villa - FinishTika AgungNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle ManagementDocument35 pagesProduct Life Cycle ManagementRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- International StandardDocument8 pagesInternational Standardnazrul islamNo ratings yet
- Wednesday 12 June 2019: ChemistryDocument32 pagesWednesday 12 June 2019: ChemistryMohammad KhanNo ratings yet
- January 2005 6677 Mechanics M1: Mark SchemeDocument7 pagesJanuary 2005 6677 Mechanics M1: Mark SchemeWael TareqNo ratings yet
- Metal Roof Roll Forming MachineDocument6 pagesMetal Roof Roll Forming MachineDarío Fernando LemaNo ratings yet
- Acer Iconia Tab W500 Pegatron EAB00 SchematicsDocument60 pagesAcer Iconia Tab W500 Pegatron EAB00 SchematicsIIIkwarkaNo ratings yet
- MSC in Subsea Engineering - Flexible Pipe Analysis Lecture JP 2023Document67 pagesMSC in Subsea Engineering - Flexible Pipe Analysis Lecture JP 2023Fakey LaazNo ratings yet
- Geographic Information Systems and Science-GoodchildDocument8 pagesGeographic Information Systems and Science-GoodchildChoc OlateNo ratings yet
- Recognizing and Classifying Daily Human Activities: Group-22Document23 pagesRecognizing and Classifying Daily Human Activities: Group-22Divyam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mesoamerica: Where Civilizations Flourished, and Crashed, RepeatedlyDocument8 pagesMesoamerica: Where Civilizations Flourished, and Crashed, RepeatedlyEnvyAmarr •No ratings yet
- TransportationDocument4 pagesTransportationShrinidhi Priyankaa 1912985630No ratings yet
- ShimadzuDocument66 pagesShimadzueka_setyowati0No ratings yet
- Syllabus: Survey Training Institute, H-8/2 IslamabadDocument7 pagesSyllabus: Survey Training Institute, H-8/2 Islamabadsajid khanNo ratings yet
- Hasnain A KhanDocument2 pagesHasnain A KhanFatima ButtNo ratings yet
- Magic Frequencies: Excerpted From The Mixing Engineer's HandbookDocument5 pagesMagic Frequencies: Excerpted From The Mixing Engineer's HandbookmehmetkurtulusNo ratings yet
- J-20 Stealth Fighter Design Balances Speed and Agility - Defense Content From Aviation WeekDocument9 pagesJ-20 Stealth Fighter Design Balances Speed and Agility - Defense Content From Aviation WeekMahesNo ratings yet
- Updated DOTr Directory As of 29 October 2021Document9 pagesUpdated DOTr Directory As of 29 October 2021Twinkle MiguelNo ratings yet
- Bastidas Et Al, 2010Document8 pagesBastidas Et Al, 2010Panji Satria N.No ratings yet
- 974-0753 Onan RDJC RDJF Diesel Engine Service Manual (09-1984)Document64 pages974-0753 Onan RDJC RDJF Diesel Engine Service Manual (09-1984)Leo BurnsNo ratings yet
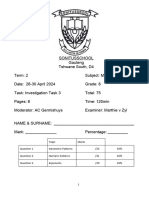
- Investigation Gr. 8Document6 pagesInvestigation Gr. 8Marthie van zylNo ratings yet
- Farm Size Factor Productivity and Returns To ScaleDocument8 pagesFarm Size Factor Productivity and Returns To ScaleAkshay YadavNo ratings yet
- 4K Resolution: The Future of ResolutionsDocument15 pages4K Resolution: The Future of ResolutionsRavi JoshiNo ratings yet
- Seajet 118 Ultra-Build Epoxy PrimerDocument2 pagesSeajet 118 Ultra-Build Epoxy PrimerRai Hasnain Ahmad DahaNo ratings yet
- QuizBowl QuestionsDocument84 pagesQuizBowl QuestionsJowel MercadoNo ratings yet
- H250 H250 H250 H250: Variable Area Flowmeter With 3W2 Angular Position TransmitterDocument40 pagesH250 H250 H250 H250: Variable Area Flowmeter With 3W2 Angular Position TransmitterJustine MarashanyeNo ratings yet
- 1 Aerodynamics Lecture - Viscous FlowDocument70 pages1 Aerodynamics Lecture - Viscous Flowccoyure100% (2)
- Valores de Laboratorio Harriet LaneDocument14 pagesValores de Laboratorio Harriet LaneRonald MoralesNo ratings yet
- Zombieworld PlaytestDocument30 pagesZombieworld PlaytestWellameGranaNo ratings yet
- Berkeley To San JoseDocument88 pagesBerkeley To San JoseTimothy HightowerNo ratings yet