0% found this document useful (0 votes)
161 views8 pagesEssential Functions of Hospital Departments
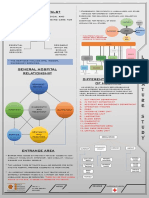
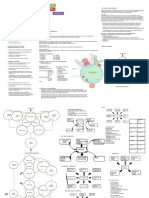
The document contains the answers to 5 questions from a mid-term examination for an MBA in Hospital and Health Management. It defines a hospital according to the WHO and lists its main functions. It discusses factors to consider when organizing an outpatient department, such as location, space requirements, and common problems. It also describes the various functional areas of an operating theater, including reception, operating rooms, and the post-anesthetic care unit. Finally, it discusses advantages and disadvantages of open wards, services provided by hospitals, and qualities of a good hospital administrator.
Uploaded by
shreya sumanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
161 views8 pagesEssential Functions of Hospital Departments
The document contains the answers to 5 questions from a mid-term examination for an MBA in Hospital and Health Management. It defines a hospital according to the WHO and lists its main functions. It discusses factors to consider when organizing an outpatient department, such as location, space requirements, and common problems. It also describes the various functional areas of an operating theater, including reception, operating rooms, and the post-anesthetic care unit. Finally, it discusses advantages and disadvantages of open wards, services provided by hospitals, and qualities of a good hospital administrator.
Uploaded by
shreya sumanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd