Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conditional Sentences - Rules - 4º - 2021
Conditional Sentences - Rules - 4º - 2021
Uploaded by
Miriam ChiovettaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Conditional Sentences - Rules - 4º - 2021
Conditional Sentences - Rules - 4º - 2021
Uploaded by
Miriam ChiovettaCopyright:
Available Formats
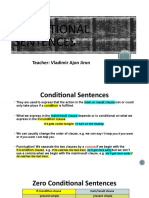
CONDITIONAL SENTENCES
ZERO CONDITIONAL
FORM
IF-CLAUSE MAIN CLAUSE
PRESENT SIMPLE PRESENT SIMPLE
If I have a big lunch, it makes me sleepy
If you mix yellow and blue, you get green
USE
We use this structure to talk about habits and general truths.
FIRST CONDITIONAL
FORM
IF-CLAUSE MAIN CLAUSE
PRESENT SIMPLE WILL + INFINITIVE
If I study, I will pass the test
If he asks me, I’ll help him
USE
We use this structure when there is a possibility that the situation in the if-clause
will happen in the future.
- In this structure we can also use a modal verb, for example, can, may,
instead of “will” in the main clause:
If we have enough time, we can visit Robert.
- We can also use the imperative in the main clause:
If you see Mary, give her a message for me, please.
*We can use “UNLESS” to mean ‘if...not’
I won’t go to the party unless you go = I won’t go to the party if you don’t go
SECOND CONDITIONAL
FORM
IF-CLAUSE MAIN CLAUSE
PAST SIMPLE WOULD + INFINITIVE
If I had a lot of money, I’d travel round the world
If he got up earlier, he wouldn’t be late for work
USE
We use this structure to talk about hypothetical present or future situations.
*We often use “WERE” instead of “was” after “if”:
If the weather were nice, I would go to the beach.
*We often use “IF I WERE YOU” to give advice:
If I were you, I’d save some money.
THIRD CONDITIONAL
FORM
IF-CLAUSE MAIN CLAUSE
PAST PERFECT WOULD + HAVE+PAST PARTICIPLE
If the weather had been nice yesterday, I would have gone to the beach
(but the weather was not nice)
If I had studied hard, I would have passed the exam.
(but I didn’t study hard)
USE
We use this structure to talk about unreal past situations. They are impossible
conditions because they refer to the past and you can change the past.
You might also like
- Relative Clauses Formal and InformalDocument2 pagesRelative Clauses Formal and InformalMiriam Chiovetta60% (5)
- Conditional SentencesDocument8 pagesConditional SentencesplaoNo ratings yet
- CONDITIONALSDocument3 pagesCONDITIONALSalexander celyNo ratings yet
- How Do You Response On The Following Conditions?Document50 pagesHow Do You Response On The Following Conditions?Evita Louise OquendoNo ratings yet
- Met. It Is Probable That A Determinated Result Might Happen. in Other WordsDocument7 pagesMet. It Is Probable That A Determinated Result Might Happen. in Other WordsDaniela EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Contitionals 0-1-2-3-MIXEDDocument21 pagesContitionals 0-1-2-3-MIXEDJavierfvc 13No ratings yet
- Advanced Conditionals ExplainedDocument10 pagesAdvanced Conditionals ExplainedZitheeq UmarNo ratings yet
- L6 Gram ConditionalsDocument5 pagesL6 Gram ConditionalslenkastarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Conditionals ExplainedDocument11 pagesAdvanced Conditionals ExplainedGeorge PetreNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument1 pageConditionalscat FNo ratings yet
- If I See Andrew at The MeetingDocument3 pagesIf I See Andrew at The MeetingRirin SetiYaniNo ratings yet
- (Lecture - 7) Conditional SentencesDocument21 pages(Lecture - 7) Conditional SentencesN. W. FlannelNo ratings yet
- P6 Contional IfDocument22 pagesP6 Contional IfVolcom OfficialNo ratings yet
- Conditionals PDFDocument10 pagesConditionals PDFMARNo ratings yet
- Zero Conditional First Conditional Second ConditionalDocument6 pagesZero Conditional First Conditional Second ConditionalDayana Bobadilla SaonaNo ratings yet
- Modul 11Document6 pagesModul 11Anisya Nada L.H.No ratings yet
- 1 and 2 ConditionalDocument4 pages1 and 2 ConditionalAnita P.No ratings yet
- 03-Zero and First ConditionalDocument2 pages03-Zero and First ConditionalKlistel AntezanaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals Course ExplanationsDocument17 pagesConditionals Course ExplanationsEmily MillsNo ratings yet
- Grammar SummaryDocument48 pagesGrammar SummaryBelén EscuderoNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument23 pagesConditionalsCarmen BugnarNo ratings yet
- b2.1 - Unit 7 - GrammarDocument7 pagesb2.1 - Unit 7 - Grammarcristina.lopez.castro96No ratings yet
- Professor: Kevin A. Brand FonsecaDocument26 pagesProfessor: Kevin A. Brand FonsecaKevin Armando Brand FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesConditional SentencesAle GarpeNo ratings yet
- SECOND Conditional: Team OneDocument13 pagesSECOND Conditional: Team OneVanessa PoulainNo ratings yet
- Zero Conditional: 2. FirstDocument4 pagesZero Conditional: 2. FirstWindy KadeNo ratings yet
- GR ConmixedDocument20 pagesGR ConmixedJason WNo ratings yet
- Conditionals 2023Document5 pagesConditionals 2023Salma BazziNo ratings yet
- Conditionals DildoraDocument17 pagesConditionals DildoraDildoraNo ratings yet
- Thidrd ConditionalDocument5 pagesThidrd Conditionallinh dophuongNo ratings yet
- Conditionals ExplanationDocument4 pagesConditionals Explanationmanuel pereiraNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument1 pageConditionalsEzequiel MartínezNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument2 pagesConditionalsyolandagarciamorenoNo ratings yet
- СONDITIONALS AND WISHESDocument9 pagesСONDITIONALS AND WISHESНастя ШепелеваNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument16 pagesConditionalsNazlıcan ŞEKERNo ratings yet
- Eng 2 Live Session 9Document8 pagesEng 2 Live Session 9carlos reynaNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences: Zero, First, Second and Third ConditionalDocument6 pagesConditional Sentences: Zero, First, Second and Third ConditionalAmjad EshteiNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument22 pagesConditionalshappyindriyono2402100% (1)
- ConditionalsDocument3 pagesConditionalsVera AtanasovaNo ratings yet
- MODALSDocument4 pagesMODALSMarnel DincolNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH ConditionalsDocument8 pagesENGLISH ConditionalsaymarmarchettiNo ratings yet
- CONDITIONALSDocument23 pagesCONDITIONALSherz eliNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences ISEMDocument21 pagesConditional Sentences ISEMAngélica Lizeth Cervantes GonzálezNo ratings yet
- 1st and Second Cond. GrammarDocument2 pages1st and Second Cond. Grammarmelek.acikgozNo ratings yet
- Advanced Grammar PDFDocument6 pagesAdvanced Grammar PDFAnahí Quinteros M.No ratings yet
- Conditionals 0, 1, 2 and 3Document13 pagesConditionals 0, 1, 2 and 3jaime herazoNo ratings yet
- Type 1 Conditional Sentences Are Used To Talk About Real and Possible SituationsDocument10 pagesType 1 Conditional Sentences Are Used To Talk About Real and Possible SituationsSadia AminNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Conditionals Time ClausesDocument17 pagesUnit 4 Conditionals Time Clausesdafne díaz peñuelaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals: Conditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseDocument12 pagesConditionals: Conditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseSamu PrietoNo ratings yet
- The Zero Conditional: If Clause (Condition) Main Clause (Result)Document6 pagesThe Zero Conditional: If Clause (Condition) Main Clause (Result)Daniel JimenezNo ratings yet
- English 9 Quarter 1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesEnglish 9 Quarter 1 ReviewerEugenio Muella100% (1)
- FB Lesson 47Document12 pagesFB Lesson 47Aisyah AzanishNo ratings yet
- Conditionals: Knowing How To State Ifs When It ComesDocument17 pagesConditionals: Knowing How To State Ifs When It ComesPammy AlivenNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences: Teacher: Vladimir Ajon JironDocument6 pagesConditional Sentences: Teacher: Vladimir Ajon JironVladimir AjonNo ratings yet
- EXAMDocument46 pagesEXAMАліна ЧірковаNo ratings yet
- The Conditionals TheoryDocument3 pagesThe Conditionals TheorycdygtjutdNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument2 pagesConditionalscrisrolo253832No ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence by Group 9Document21 pagesConditional Sentence by Group 9Nur AzizahNo ratings yet
- Conditionals B2 (Full Version)Document3 pagesConditionals B2 (Full Version)Gigi GuastellaNo ratings yet
- The Passive BachDocument2 pagesThe Passive BachMiriam ChiovettaNo ratings yet
- Extra Listening Practice - 02 (APPS)Document1 pageExtra Listening Practice - 02 (APPS)Miriam ChiovettaNo ratings yet
- Phrases For Review and ReportDocument3 pagesPhrases For Review and ReportMiriam ChiovettaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document2 pagesUnit 3Miriam ChiovettaNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice: 1 Choose The Correct AnswerDocument2 pagesPassive Voice: 1 Choose The Correct AnswerMiriam ChiovettaNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Common Time Expressions: Complete The Sentences With The Correct Form or The Verbs in The BoxDocument1 pagePresent Simple Common Time Expressions: Complete The Sentences With The Correct Form or The Verbs in The BoxMiriam ChiovettaNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronouns Subject Object Possessive 19980Document2 pagesPersonal Pronouns Subject Object Possessive 19980Miriam ChiovettaNo ratings yet