Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Availability Zones Are Physically Separate Datacentres Within An Azure Region
Uploaded by
MustaqueOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Availability Zones Are Physically Separate Datacentres Within An Azure Region
Uploaded by
MustaqueCopyright:
Available Formats
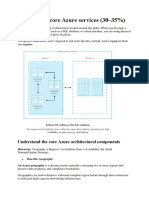
Availability Zones are physically separate datacentres within an Azure region.
Each Availability Zone is made up of one or more datacentres equipped with
independent power, cooling, and networking. It is set up to be an isolation
boundary. If one zone goes down, the other continues working.
Availability Zones are connected through high-speed, private fibre-optic networks.
Not every region has support for Availability Zones.
Availability Zones are primarily for VMs, managed disks, load balancers, and SQL
databases.
Azure services that support Availability Zones fall into two categories:
Zonal services – you pin the resource to a specific zone (for example, virtual
machines, managed disks, IP addresses)
Zone-redundant services – platform replicates automatically across zones (for
example, zone-redundant storage, SQL Database).
Each Azure region is always paired with another region within the same geography (such as
US, Europe, or Asia) at least 300 miles away. This approach allows for the replication of
resources (such as virtual machine storage) across a geography that helps reduce the
likelihood of interruptions due to events such as natural disasters, civil unrest, power
outages, or physical network outages affecting both regions at once.
Data continues to reside within the same geography as its pair (except for
Brazil South) for tax and law enforcement jurisdiction purposes.
There are also some global Azure services that do not require you to select a region, such
as
1. Microsoft Azure Active Directory,
2. Microsoft Azure Traffic Manager, and
3. Azure DNS.
There are three key characteristics of SLAs for Azure products and services:
1. Performance Targets
2. Uptime and Connectivity Guarantees
3. Service credits
8|Page
You might also like
- AZ900 2 - Azure ServicesDocument29 pagesAZ900 2 - Azure ServicesNed MaverickNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Azure FundamentalsDocument39 pagesMicrosoft Azure Fundamentalspdvprasad_obieeNo ratings yet
- Az 900 Part1Document49 pagesAz 900 Part1gauri shankarNo ratings yet
- Understand Datacenters and Regions in AzureDocument3 pagesUnderstand Datacenters and Regions in AzureBondriedNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Azure Fundamentals Exam Cram: Second EditionFrom EverandMicrosoft Azure Fundamentals Exam Cram: Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cloud ComputingDocument2 pagesCloud Computingashish ojhaNo ratings yet
- Az 900 VnetDocument28 pagesAz 900 VnetmaheshNo ratings yet
- Cloud InfrastructureDocument2 pagesCloud InfrastructureTechnical GulabiNo ratings yet
- Describe Cloud Concepts (15 - 20%) : Describe The Benefits and Considerations of Using Cloud ServicesDocument12 pagesDescribe Cloud Concepts (15 - 20%) : Describe The Benefits and Considerations of Using Cloud ServicesNaresh KatamNo ratings yet
- Azure Fundamentals TrainingDocument65 pagesAzure Fundamentals TrainingPaulina ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Practical No. 1: Aim: Study About Distributed Database System. TheoryDocument22 pagesPractical No. 1: Aim: Study About Distributed Database System. TheoryPrathmesh ChopadeNo ratings yet
- AZ-900T00 Microsoft Azure Fundamentals-02Document43 pagesAZ-900T00 Microsoft Azure Fundamentals-02Ironman75% (4)
- Az 900Document24 pagesAz 900AMitNo ratings yet
- Azure FundamentalDocument117 pagesAzure Fundamentalivanjanitra10aNo ratings yet
- Az Storage NotesDocument13 pagesAz Storage NotesmaheshNo ratings yet
- Basics of AWSDocument25 pagesBasics of AWSjaganjNo ratings yet
- Azure AZ 900Document163 pagesAzure AZ 900ΑΝΑΣΤΑΣΙΑ ΜΑΓΓΙΝΑNo ratings yet
- AZ-900T0xModule 02core Azure ServicesDocument43 pagesAZ-900T0xModule 02core Azure ServicesAnshul AakotkarNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Cloud ServiceDocument8 pagesModule 1: Cloud ServiceSunnie LuNo ratings yet
- AWS Module 3 - AWS Global InfrastructureDocument36 pagesAWS Module 3 - AWS Global InfrastructuredsadasdasdasNo ratings yet
- Advanced Database Management SystemDocument6 pagesAdvanced Database Management SystemTanushree ShenviNo ratings yet
- Azure Foundations Cheat SheetsDocument19 pagesAzure Foundations Cheat Sheetsxapehox36292% (12)
- Active DirectoryDocument9 pagesActive DirectorygetjijocjohnNo ratings yet
- CC VivaDocument13 pagesCC VivaJainil ShahNo ratings yet
- 2 Cloud HostingDocument2 pages2 Cloud HostingSantanuNo ratings yet
- Enusmicrosoftazurevirtualtrainingdayfundamentals 1637594071438Document160 pagesEnusmicrosoftazurevirtualtrainingdayfundamentals 1637594071438Inked IntutionsNo ratings yet
- AWS Global InfrastructureDocument6 pagesAWS Global InfrastructureAshu TuliNo ratings yet
- UCS531-Cloud ComputingDocument52 pagesUCS531-Cloud ComputingShivam AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Active Directory Is A Directory Service Used To Store Information About The Network ResourcesDocument5 pagesActive Directory Is A Directory Service Used To Store Information About The Network ResourcesRaghunath KSNo ratings yet
- Az 900Document139 pagesAz 900Sanjay ChinnuNo ratings yet
- Azure Unleashed: Harnessing Microsoft's Cloud Platform for Innovation and GrowthFrom EverandAzure Unleashed: Harnessing Microsoft's Cloud Platform for Innovation and GrowthNo ratings yet
- Aws InfrastructureDocument13 pagesAws InfrastructurelabgibNo ratings yet
- Study Notes 1Document12 pagesStudy Notes 1Kajal ShelarNo ratings yet
- Understanding CloudDocument8 pagesUnderstanding CloudsendilNo ratings yet
- Cloud Practitioner Part1Document15 pagesCloud Practitioner Part1Ali ZoubairNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Certified Azure Fundamentals AZ-900 Quick Reference SheetDocument45 pagesMicrosoft Certified Azure Fundamentals AZ-900 Quick Reference SheetalbertotecaNo ratings yet
- Azure Fundamentals Unit 2Document25 pagesAzure Fundamentals Unit 2Parthraj VasoyaNo ratings yet
- Solution cs66 Week 01 Assignment 01Document2 pagesSolution cs66 Week 01 Assignment 01karolee2No ratings yet
- AZ-900 MicrosoftAzureFundamentalsDocument80 pagesAZ-900 MicrosoftAzureFundamentalsWilliamette Core80% (5)
- Cloud Computing - 2Document150 pagesCloud Computing - 2Frank HackNo ratings yet
- The VPC Offers The Function of The PrivateDocument3 pagesThe VPC Offers The Function of The PrivatedaliasobhiNo ratings yet
- AZURE AZ 500 STUDY GUIDE-2: Microsoft Certified Associate Azure Security Engineer: Exam-AZ 500From EverandAZURE AZ 500 STUDY GUIDE-2: Microsoft Certified Associate Azure Security Engineer: Exam-AZ 500No ratings yet
- What Is SAN Zoning?: Hard Zoning Soft ZoningDocument10 pagesWhat Is SAN Zoning?: Hard Zoning Soft ZoningPabbathi Prabhakar0% (1)
- Expresscluster X Wan Edition: Nec Corporation of AmericaDocument4 pagesExpresscluster X Wan Edition: Nec Corporation of Americavedamaker2751No ratings yet
- Mission-Critical Databases in The Cloud. Oracle Rac On Amazon Ec2 Enabled by Skycluster®Document13 pagesMission-Critical Databases in The Cloud. Oracle Rac On Amazon Ec2 Enabled by Skycluster®Daniel Bernal YhamaNo ratings yet
- Relational Cloud: A Database-as-a-Service For The CloudDocument6 pagesRelational Cloud: A Database-as-a-Service For The Cloudarteepu4No ratings yet
- Azure FundamentalsDocument5 pagesAzure FundamentalsRamziNo ratings yet
- Relational Cloud: A Database-as-a-Service For The CloudDocument7 pagesRelational Cloud: A Database-as-a-Service For The Cloudarteepu4No ratings yet
- Describe Azure Architecture and ServicesDocument74 pagesDescribe Azure Architecture and ServicesBommireddy RambabuNo ratings yet
- Instance: A Bare Metal or Virtual Machine (VM) Host Running in The Cloud. Oracle CloudDocument64 pagesInstance: A Bare Metal or Virtual Machine (VM) Host Running in The Cloud. Oracle CloudSm SaimumNo ratings yet
- AWS Solution Architect Module IDocument17 pagesAWS Solution Architect Module ISarbajit PatraNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Azure Fundamentals - 02 - Core Azure ServicesDocument20 pagesMicrosoft Azure Fundamentals - 02 - Core Azure ServicesSherif HassanNo ratings yet
- SnowflakeDocument3 pagesSnowflakeimanonNo ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery For Azure Applications - Microsoft DocsDocument23 pagesDisaster Recovery For Azure Applications - Microsoft DocsSpl FriendsNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems Cloud Computing Implementations - ChallengesDocument4 pagesEmbedded Systems Cloud Computing Implementations - ChallengesFossilShale Embedded TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- AWS Course - 5-5Document1 pageAWS Course - 5-5aashrafib31No ratings yet
- System Design & ArchitectureDocument4 pagesSystem Design & Architecturemiguel ángel pelosNo ratings yet
- En WBNR Ebook Srdem58911slidesDocument164 pagesEn WBNR Ebook Srdem58911slidesradhia saidaneNo ratings yet
- Snowflake:: Data Warehouse For CloudDocument2 pagesSnowflake:: Data Warehouse For CloudLakshmi VaidyanathanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document14 pagesUnit 1DevilNo ratings yet
- Encryption at Rest Encryption in Transit: Azure SQL Database Always Enforces Encryption (SSL/TLS) For All ConnectionsDocument1 pageEncryption at Rest Encryption in Transit: Azure SQL Database Always Enforces Encryption (SSL/TLS) For All ConnectionsMustaqueNo ratings yet
- Cloud Deployment ModelsDocument1 pageCloud Deployment ModelsMustaqueNo ratings yet
- English - FinalDocument2 pagesEnglish - FinalMustaqueNo ratings yet
- English - Final2303Document2 pagesEnglish - Final2303MustaqueNo ratings yet
- Grow Roses From CuttingsDocument11 pagesGrow Roses From CuttingsMustaqueNo ratings yet
- Indian Rupee SymbolDocument9 pagesIndian Rupee SymbolMustaqueNo ratings yet