Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2015 Physics Paper 2
2015 Physics Paper 2
Uploaded by
superpooh-10 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views11 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views11 pages2015 Physics Paper 2
2015 Physics Paper 2
Uploaded by
superpooh-1Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
iC
2015-DSE
PHY
PAPER 2
Please stick the barcode label here.
HONG KONG EXAMINATIONS AND ASSESSMENT AUTHORITY
anda Number
PHYSICS PAPER 2
Question-Answer Book
11.45 am ~ 12.45 pm (1 hour)
This paper must be answered in English
INSTRUCTIONS
(1). After the announcement of the start of the examination, you
should first write your Candidate Number in the space
provided on Page 1 and stick barcode labels in the spaces
provided on Pages 1, 3, 5, 7 and 9.
(2) This paper consists of FOUR sections, Sections A, B, C
and D. Each section contains eight multiple-choice
questions and one structured question which carries
10 marks. Attempt ALL questions in any TWO sections.
(3) Write your answers to the structured questions in the
ANSWER BOOK provided. For multiple-choice questions,
blacken the appropriate circle with an HB pencil, You
should mark only ONE answer for each question. If you
mark more than one answer, you will receive NO MARKS
for that question,
(4) Graph paper and supplementary answer sheets will be
provided on request. Write your candidate number, mark
the question number box and stick a barcode label on each
sheet, and fasten them with string INSIDE the Answer
Book.
(5) The Question-Answer Book and Answer Book will be
collected SEPARATELY at the end of the examination.
(6) The diagrams in this paper are NOT necessarily drawn to
scale.
(7). The last two pages of this Question-Answer Book contain a
list of data, formulae and relationships which you may find
useful
(8) No extra time will be given to candidates for sticking on the
‘barcode labels or filing in the question number boxes after
the ‘Time is up’ announcement,
OFBTRRMKE — PRATT
Hong Kong Examinations and Assessment Authority
All Rights Reserved 2015,
*A15 0
E2mMc x
2015-DSE-PHY 2-1 1
Section A : Astronomy and Space Science
Qu: Multiple-choice questions
1.1 A satellite is orbiting the Earth at a distance h from the Earth’s surface. What is the gain in gravitational
potential energy ofthe satellite in the orbit with respect tothe Earth's surface ?
‘m= mass of the satellite
R= radius of the Earth
‘g = acceleration due to gravity on the Earth’s surface
sgl) Mec i
Rei) ee © O
sm)
(22
$
mmf
1.2. Where isthe best location on Earth to build an observatory s0 as to observe most of the celestial sphere ?
A. latitude 90°N leer ee ete)
B. latitude 90° S
Cate 0 o. Oe. ©
D. Its the same for any latitude
1.3. The Barth receives solar radiation of power Pp per unit area. Estimate the power of solar radiation received
per unit area on Pluto which is 40 AU from the Sun,
eo, os ce
: 0. 0. Gg@
a
“lee
me)
14 Which of the following observations by Galileo contradict with the geocentric model of the universe ?
(1) the discovery of satellites of Jupiter
(2) the retrograde motion of Mars
@) the changing phase of Venus
A. (and Q) only A B c D
B. (1) and@) only
c. (2) and (3) only. ° ° ° °
D. (1), (2) and (3)
2015-DSE-PHY 2-2 2
Please stick the barcode label here.
1.3 When the Earth lines up with the Sun and Mars as shown, how does Mars appear to move across the night sky
as viewed from Earth ?
‘A. Mars moves from west to east against the background stars.
B, Mars moves from east to west against the background stars.
C. Mars does not move against the background stars.
D. The movement of Mars cannot be determined because the east and west directions are not known.
be co
OO 0 ©
1.6 Which constellations and in what sequence can be seen to pass the Earth's meridian at night in January ?
Sagittarius
Capricom 5 tae
Capricorn, Sagittarius, Scorpio
Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn
‘Taurus, Gemini, Cancer
Cancer, Gemini, Taurus
2015.DSE-PHY 2-3 3 (commen >
pope
Please stick the barcode label here.
absolute magnitude [ apparent magnitude
sarX 28 aT |
star ¥ Sa 32
According to the information given above, which of the following about stars and Y is/are correct ?
(1) Luminosity of tars greater than that of star Y. Qu: Structured question
) Atelescope collects more energy per unit area per unit time from star Xthan from sta ¥
Figure 1.1 shows a distant binary star system viewed by an observer on Earth whois also on the orbital plane ofthe
A. Only (1) is correct. is Bi ¢ Dy two stars. ‘The system consists of stars 1 and 2 with masses m, and m; respectively orbiting in uniform circular
alee Ono. .0 O Imation about their centre of mase O under thelr mutual gravitational foes, “They move withthe same perlod in
D.
ayer as 2) Ae cor {wo orbits of radii rand r; with orbital speeds v, and v; respectively.
Both (1) and (2) are incorrect.
‘observing along
18. The respective absorption spectra of hydrogen from Galaxy XX, in the laboratory, and Galaxy ¥ are shown the lin of sight
below Figure 1.1 =
violet red observer on Earth
ee
Galaxy X positive direction
laboratory By finding the radial velocity 1, of the two stars inferred from the Doppler shift (\.) of the hydrogen-alpha
line (H,) observed on Earth, astronomers are able to deduce the masses of the stars. Assume that the centre of mass
Of the binary system is stationary with respect to the observer. Figure 1.2 shows the radial velocity curves for the
Galaxy ¥ two stars. The direction moving away from the observer is taken to be positive velocity.
200 4
Which of the following descriptions about the motions of Galaxy X and Galaxy Y and their velocities vy and vy 150
relative to the Earth is correct?
~ 100
Gataxy X velocities Galaxy ¥ 5
A. moving away from Earth yale ler ‘moving towards Earth & 50
B, moving away from Earth Tox for moving towards Earth ce
C. moving towards Earth lox li< lor roving away from Earth ee sooo
D. moving towards Earth Toe! > lov ‘moving away from Earth 2
zB -30
een fc. D 2
=100 |
Oe) © O
=150]
200]
(a) (i) What does it mean by radial velocity v, of a star observed on Earth ? (1 mark)
(ii) Identify which point, 4, B, C or D, marked on the radial velocity curve corresponds to the orbital
position of star | (in solid line) at the instant shown in Figure 1.1 (1 mark)
(b) Find, from Figure 1.2, the orbital speed v, of star 1 and calculate its orbital radius r Using a similar method,
= or otherwise, find the orbital radius r, of star 2 (4 marks)
=
(©) By considering the circular motion of star 1, calculate the mass m, of star 2. (marks)
(@) A spectrometer can only measure change of wavelength larger than 0.5 nm. Explain whether this instrument
is suitable to measure the Doppler shift A of the hydrogen-alpha line (4g = 656,28 nm) of the two stars,
(2 marks)
2015-DSE-PHY 2-4 4 2015-DSE-PHY 2-5 5 Goontothenetpage >
Section B : Atomic World
Q2: Muttiple-choice questions
2.1 A beam of «particles with the same initial kinetic energy
are scattered by a heavy nucleus N. In the figure, if P is @
possible path for one of the a-particles, which of the paths,
Q, Rand S, isfare possible for these a-particles ?
sis phd ent doses gs Be
B. Rand S only
. OF On 0 0
D. ‘Sonly
22. Which othe following provides experimental evidence for discrete energy levels in atoms ?
(Oye ewlcrin oft sedis clachrge tbo
(2) theapectum of tungsten filament lamp
GE) precio op eater yori acing in val
_ Oe Bye ee ot
Peat ©2070. Oo
C. ()and Q) only
D. —_@)and G) only
2.3 Ina photoelectric experiment, monochromatic light of frequency fis incident upon a metal surface and the
stopping potential for the photoelectrons emitted is V,. If the frequency fis changed, how would V, vary
with f?
Se ie Boi By
°
cency. Ree
0 0 f
emer” 3
Oro, OO!
24 A spy aircraft is cruising at a height of 10 km above the Earth’s surface. It is equipped with a camera having
‘an objective lens of aperture 10 cm. Estimate the minimum separation of two small objects on the Earth’s
surface to be distinguished by this camera, Assume that both objects emit light of wavelength 500 nm.
A. 005m Ae ee ce
Be 0061m
c0.10m Oo 0 90 9
D. 022m
rois-psePny2-6 6
26
27
28
Please stick the barcode label here.
incident
monochromatic light
+
Ls
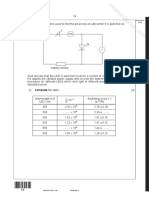
‘A photocell is connected to a d.c. source as shown. Monochromatic light is incident on cathode C of the
Photocell so that photoelectrons are emitted. ‘The maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons reaching anode
‘A depends on
(1) the kind of metal making the cathode surface.
2) the voltage of the d.c. source.
) the intensity of the monochromatic light used.
A. only ec
B. (3) only,
C @)and @)only OF O 0 2
D. —@)andG) only
Aurora Borealis (Northern lights) are often observed in skies at high latitudes, When energetic electrons from.
‘outer space collide with the oxygen atoms in the upper atmosphere, the oxygen atoms are excited. The
subsequent emission of light is usually green light of wavelength 558 nm. ‘The minimum speed of these
energetic electrons is of order of magnitude
A. 10? ms". A B c D
B, 10'ms
an ©) 6 ©)
D. 10° ms“.
‘Which ofthe following can increase the resolving power of a transmission electron microscope (TEM) ?
(1) increasing the anode voltage in the electron gun
2) decreasing the aperture of the magnetic objective lens
G) increasing the separation between the magnetic projection lens and the fluorescent screen
A (only oS
BL Q)only
© ()and G) only Oo Oo o0o 0
D. — @)and G) only
Zine oxide (ZnO) is used in some suntan lotion. Which of the following statements is/are correct ?
(1) Nano-sized ZnO can block ultra-violet radiation while bulk-sized ZnO cannot.
(2) Nano-sized ZnO is more effective in reflecting visible light than bulk-sized ZnO.
(3) Suntan lotion with nano-sized ZnO appears transparent when applied to the skin.
A (1) only A B Cc D
B. G)only
C. ()and @) only OO 0 ©
D. — @)and @) only
2015-DSE-PHY 2-7 7 coaraTee »
Please stick the barcode label here.
Q
structured question
‘The energy levels , of an electron in a hydrogen atom from the Bohr model can take the form below:
= 236
E, eV where n= 1,2,3,
Section C : Energy and Use of Energy
(@) Bohr’s idea was sometimes criticized by some physicists as semi-classical and semi-quantum. Point out ONE oe
classical aspect in the Bohr model i (mark) Q.3: Multiple-choice questions
(©) ome ena pit of view, the ysl meaning ofeydoge atom begin is eomad at, 11 Atami edn te ceting of room 8 ob source. Teun on be ord ner
the lamp is 600 lux. Assuming that the lamp emits light uniformly in all directions, what is the illuminance on
the floor around point X as indicated in the diagram ? Neglect any reflections of the walls and the ceiling
(©) Ifthe minimum energy required to ionize a hydrogen atom in the ground state is E, express the min
‘momentum p of a photon for ionizing such a hydrogen atom in terms of E and another physical constant.
(@ marks)
lamp
5.0m
(@ Hydrogen atoms in the ground state are bombarded by electrons each with kinetic energy 12.9 eV. 25m
(Show that these hydrogen atoms can be excited at most to the third excited state (ie. n=4). (2 marks)
x 00 hx
Gi) Fora hydrogen atom excited tothe third excited state (n= 4), what i the de Broglie wavelength ofthe
ofbsing ern into en: the ebay he eleton na yop atom om the ce A Bc oD
Bohr model is equal 00.053 (unit: nm), where n= 1,23, (2 marks) x
a ao CG 150ux eo) (2 Ce)
D. 300hux
(iii) Copy the energy level diagram below to your answer book and draw arrow(s) to illustrate all
possible transitions leading to emission of photons by these excited hydrogen atoms. (2 marks)
3.2 The schematic diagram below shows a solar cell under sunlight. Incident light photons reach the cell's
Jjunetion of p-type and n-type semiconductor layers. Which of the following sequences correctly explains how
+ Sa electrical energy can be supplied to the load ?
3
Ne :
~ Sirk
2 = toad
‘hydrogen atoms celectron
junction Hons
(1) The electric field developed within the junction draws free electrons and holes to the n-type and p-type
layers respectively.
(2) Free electrons flow to the p-type layer through the load and rejoin the holes there.
G) Incident light photons knock out electrons from atoms in the junction such that free electrons result,
leaving the holes behind,
()>Q2)>G) A B Cc D
M>@)>@
B27 7 |
B+
pop>
3.3 A satellite is powered by a solar panel of an area of 100 m? and having a conversion efficiency of 15%,
Sunlight falls fom a direction 30° to the normal of the panel. The solar constant is 1370 Wm, Estimate the
electrical power output of this solar panel
10.3 kW
Ve)
178kW
20.6 kW OO 2 2
58.2kW
2015-DSE-PHY 2-8 8 2015-DSE-PHY 2-9 9 Saar >
pep
3.4 Acoal-fired power plant generates and transmits electrical energy to consumers a long distance away. When a
3.6
‘consumer connects an incandescent lamp to the mains supply, the following data illustrates what happens per
1000 J of energy in coal converted to electrical energy which is then supplied to the lamp.
Loss during generation process in the power plant 6005
Loss during transmission before reaching the lamp 1005
Heat generated by the lamp 2501
Visible light generated by the lamp 50)
‘What is the end-use energy efficieney ofthis incandescent lamp ?
AD 5% As Pvp BY 4) Gre mp,
B 125%
C. 167% Orr OK @ ex @
D. 30%
‘The following graph shows the percentage of absorption of different electromagnetic radiations when passing
through two types of glasses X and ¥. One of them is to be chosen for windows of buildings in Hong Kong.
With the consideration of energy efficiency of buildings, which statement is correct ?
percentage of
absorption
glass ¥
glass.X
wavelength / nm
Ces ew,
400 visible light 700
‘A. Xshould be chosen as it is better than Y in reducing the need of air conditioning and the amount of
lighting.
B. _Y-should be chosen as it is better than X'in reducing the need of airconditioning and the amount of
lighting
©, _X should be chosen as it can greatly reduce the need of airconditioning although it needs a bit more
amount of lighting than Y.
D. _F’should be chosen as it can greatly reduce the need of air conditioning although it needs a bit more
amount of lighting than X.
A dimmene: ck? D.
Opn Qe On QO)
The diagram shows a wall composed of two layers X and Y of equal thicknesses. pst
‘The thermal conductivity of the material of is higher than that of Y. The two sides
of the wall are maintained at different temperatures 7; and 7: Which of the 7,
following statements isare correct ? iy
(1) The thermal transmittance of layer ¥ is higher than that of layer ¥.
2). The energy flowing through layer X per second is greater than that through layer ¥, XY
3). The temperature drop across layer ¥ is smaller than that across layer ¥.
A. (only AOR. C.D
B. Q)only
C (and @) only Oo Ow 9
D. — @)and G) only
2015-DSE-PHY 2-10 10
2015-DSE-PHY 2-11 11
‘A power plant is always running at its maximum output power of 1800 MW. However, as the demand of
electricity utuates greatly within a day, a hydroelectric storage system is therefore designed to increase the
‘output in the high demand period. During the 14 hours of low demand period in a day, the average demand is
only 600 MW and the excess output is used to pump water from the lower reservoir to the upper one. When
the demand is higher than 1800 MW, the water returns to the lower reservoir through a turbine to generate
electricity.
‘upper reservoir
300m
pump / turbine
lower reservoir
Assume that the hydroelectric storage system is 100% efficient, find the minimum capacity (in kg of water) of
the upper reservoir required. (g=9.81 ms)
A 103 x10! kg ee cb
Bo 147 10% kg
Cc. 206% 10 kg OO 2 0
D. 3.08% 10% kg
‘What is the function of the moderator in a nuclear fission reactor ?
A. It slows down neutrons and this helps increase the rate of nuclear fission.
B. _Itslows down neutrons and this helps reduce the rate of nuclear fission.
C. Tt absorbs neutrons and this helps reduce the rate of nuclear fission,
D. It generates neutrons for nuclear fission.
oc
©; 0,20; ©
Goontothenedpage >
Q43: Structured question
Figure 3.1 shows the Energy Efficiency Label of an air-conditioner X.
ENERGY LABEL
“Annual Energy Consumption (in kW h)
Figure 3. (ooting based on 1200 hous operation
2525. Ee
6.80 Rare AULT,
nice) Cooling Capacity GW)
| aa
| emcee @ Emsp
(a) This air-conditioner i installed in a room of floor area of 20.0 m? and height of 3.0 m.
Given: density of air= 1.2 kgm, specific heat capacity of air= 1000 J kg! °C
(i Estimate the time required to cool the room from 33°C to 25°C. Assume that the density and specific
heat capacity of air remain constant throughout (@ marks)
(i) Suggest a reason why the actual time for cooling from 33°C to 25°C is longer than the result found
in @. (1 mark)
(b) (@ Find the average electrical power input (in kW) of air-conditioner X during operation. (mark)
cooling capacity
‘lecrical power input
having a value greater than 1 violates the principle of conservation of energy because the amount of
hheat removed by the air-conditioner is greater than the electrical power input. Discuss the student's
comment. G marks)
(i) Find the value of for this air-conditioner. A student comments that this ratio
2015-DSE-PHY 2-12 12
(©) X isa cool-only air-conditioner as it can only cool air. Nowadays, ‘reverse-cycle air-conditioners’ (RCAC)
that can either cool or warm air are available in the market and they have the same major components of
Figure 3.2 shows a simplified schematic diagram of an RCAC with four components 4, 8, C and D, in which
is the expansion valve and C is the compressor.
expansion
valve 4
Figure 3.2 D B
outdoor indoor
compresso™t
(If the RCAC operates in a mode to warm air during winter time, give the direction of the flow of
reffigerant stating from compressor C using the leters 4, B, C and D. State in which component, A, B
or D, the refrigerant has the highest temperature (@ marks)
(ii) Suggest ONE modification that can convert a cool-only air-conditioner into an RCAC. (mark)
2015-DSE-PHY 2-13 13
Goontothened page >
Section D : Medical Physics
Q44: Multiple-choice questions
4.1 Peter suffers from a certain eye defect and needs to wear spectacles. The diagram shows the spectacle lens
for correcting this defect. Which statements are correct ?
spectacle lens
close to the eye
parallel rays from a point z
ofa distant object
Diagram NOT drawn to seale :
(1). Peter is suffering from short sightedness.
@) Point Xis the near point of his unaided eye.
G)_IFXis 0.8 m from the spectacle lens, the power of the lens should be 1.25 D.
(Q) and @) only ee cD.
(1) and G) only
Q) and (3) only O70, 2 ©
(), @)and 3)
comp
4.2. Which of the following are disadvantages of a fibre optic endoscope ?
(1). Anesthesia is sometimes required.
(2). Itcan only be used for viewing the inner surface of an organ with cavity.
(3) Itmay cause internal bleeding.
A. (1)andQ) only
B.(1)andG) only
C.— @)and G) only
D. (1), @)and@)
Re ae Soh ip
© 2..0 .0
43° The following diagram shows an ultrasound scanner with an array of crystals. A pair of electrodes is
connected across each crystal. Which ofthe following statements is/are correct ?
| cys
electrodes fF
=
ski
(1). The gel is used to reduce the attenuation of ultrasound when passing the gap between the scanner and
the skin.
2) When a crystal receives ultrasound, an electrical signal is generated between the electrodes by
piezoelectric effect.
(3). This scanner is designed for taking B-scan images.
A. only ee cD
B. Q)only
© (and () only OO 60 >
D. — @)and @) only
(2015-DSE-PHY 2-14 14
44° Ultrasound scanning is NOT suitable for the lungs because air in the lungs
‘A. has a high attenuation coefficient and can absorb almost Ae cD
all the ultrasound.
B, has a low atenuation coeficient and ean absorb alms =O O O O
all the ultrasound.
C. has high acoustic impedance compared to soft tissue and
can reflect almost all the ultrasound.
D. has low acoustic impedance compared to soft tissue and
can reflect almost all the ultrasound.
4s ae
:— at 1 >>
ae 2
H Bu
‘The diagram shows an X-ray beam passing through a metal block of linear attenuation coefficient sz Its
imensty i reduced from 110 4. Ifthe metal block is replaced by another one of the same thickness but
hhaving a linear attenuation coefficient of 3,4, what would the intensity of the emergent X-ray beam be ?
oe AB CD
: © 6 0 Oo
Bae
8
i moe
9
1
D6
4.6 The image of a computed tomography (CT) scan is of size 32 em x 32 em and the size of each pixel of the
image is 0.391 mm’, Which matrix size below corresponds to the resolution of this CT scan image ?
128128 Abc
256256
$12 x 512 ° ° ° °
Tod 1028
pap>
4.7 A doctor decides to conduct radionuclide imaging of a patient’s kidneys. Which of the following is the main
reason for choosing radionuclide imaging rather than other imaging methods ?
A. Diagnosis of the kidneys* function can be made.
B, Fine details of the kidneys’ structure can be seen,
C. The image produced has the highest resolution compared
to the other methods,
D. Diagnosis will give highly specific information of the
kind of kidney disease.
A B cD
© 0 0 0
4.8 The following radioactive sources are all non-toxic and readily absorbed by a certain organ. Which one is the
most suitable to be used as a tracer for radionuclide imaging ofthat organ ?
A a y-source of half-life 16 hours A B c D
B. a y-source of halflife 8 months
c. a B-source of half-life 20 seconds ° oO ° °
Dz a #source of half-life 12 hours
aois.psc-ny 2-15 15 Goontotenednage >
Q44: Structured question
Figure 4.1 shows the structure of human ear.
Figure 4.1
(@) (Match the letters 4, B, Cand D in Figure 4.1 with the pars of the ear, namely, eardrum, oval window,
‘semi-circular canals and cochlea, State the function of C. (2 marks)
(ii) The ratio of area of A to that of D is 20. Ifthe ear amplifies the pressure of a sound signal by 25 times
totally after passing D, find the gain of pressure contributed by the lever action of the ossicles. (1 mark)
(b) Figure 4.2 shows an equal loudness curve of people with normal hearing.
sound intensity level / dB
Figure 4.2 40
2050 100 200 S00 Ik 2k Sk 10k 20k frequency /He
(8 State the loudness, in phons, represented by this curve. State the physical significance of the curve
being higher up at both ends (2 marks)
2015-DSE-PHY 2-16 16
Gil) A worker has suffered from hearing loss due to prolonged exposure to a noisy environment and the loss
is most severe for sounds around kHz frequencies. If the worker is tested for the threshold of hearing,
which of the equal loudness curves, 4, B and C, in Figure 4.3 best represents his response? Explain
‘your choice. (marks)
sound intensity level /4B.
Figure 4.3
threshold of hearing
‘of people with
normal hearing
2k Sk 10K 20k frequency /H2
(© Anengineer working near an operating engine is exposed to noise of sound intensity 80 Wm, After putting
‘on earmuffs, the sound intensity of the noise heard is reduced to 2.5 x 10" W m*. Estimate the decrease in
sound intensity level of the noise, in dB, heard after wearing the earmuffs. marks)
END OF PAPER
Sources of materials used in this paper will be acknowledged in the Examination Report and Question Papers
published by the Hong Kong Examinations and Assessment Authority ata later stage.
2015-DSE-PHY 2-17 17
Answers written on this page will not be marked.
2015-DSE-PHY 2-18,
Do not write on this page.
18
List of data, formulae and relationships
Data
‘molar gas constant
Avogadro constant
acceleration due to gravity
‘universal gravitational constant
speed of light in vacuum
charge of electron
electron rest mass
permitivity of free space
permeability offre space
atomic mass unit
astronomical unit
light year
parsee
Stefan constant
Planck constant
Rectilinear motion
For uniformly accelerated motion
Pe e+2as
R=8313 mol! Kt
a= 6:02 x 10” mot"!
g = 9.81 ms” (close to the Earth)
G= 6.67 107" WN mr kg?
€=3.00% 10° ms"
= 1.60x 10°C
sme= 911X107 kg,
= 8.85 x 10 CN m?
y= 4nx 107 Hm!
= 1.661 x 107 kg (1 wis equivalent to 931 MeV)
AU=1,50 x 10"'m
ly=9.46 x 10! m
pe = 3.09 x 10! m=3.26 ly = 206265 AU
= 5.67 x 10° Wm? K4
b= 6.63 x 103s
Mathematics
Equation ofa straight line y= mx-+e
Are length ae:
‘Surface area of cylinder = Qnrh + 2nr*
‘Volume of cylinder = wh
‘Surface area of sphere = 4m?
Volume of sphere = Su?
For small angles, sin @~= tan 0~ 0(in radians)
‘Astronomy and Space Science
Energy and Use of Energy
econ gravitational potential energy iMluminance
oe ee MET) sae of energy transfer by conduction
ar] » faa) . d
ee oppler effect
fale da thermal transmitance U-value
maximum power by wind turbine
‘Kiomis World ~~] Medical Physies
Einstein's photoelectric equation oth Rayleigh eiterion (resolving power)
1
ev power = power of lens
t
cre tesmatinorndogn stom |= 90g. ety eve (6)
oh open Z=pe acoustic impedance
ee erat = Za- 2d. pens rection coetTicent
oe Rayleigh criterion (resolving power) fo Ga tay
[=1e" transmitted intensity through a medium
2015-DSE-PHY 2-19
19
Al, E=meaT
AQ. E=1Am
A3,
Av _ ap
ar Ar
BI
B2, moment =F x d
BS. p= mgh
C2,
C3,
2015-DSE-PHY 2-20,
‘energy transfer during heating
‘and cooling.
‘energy transfer during change
of state
equation of state for an ideal gas
kinetic theory equation
‘molecular kinetic energy
force
moment ofa force
xavitational potential energy
kinetic energy
mechanical power
centripetal acceleration
Newton’s law of gravitation
fringe width in
double-sit interference
diffraction grating equation
‘equation fora single lens
DL F
© Gregr?
pa. e-—2,
aren
D3. Vv 2
rege
ba.
bs
D6.
pn
ps, 4-441
DIO. F=BOvsin 6
BL
yo tL
DI. v=o
pis, p= Het
2ar
pis, p= oT
DIS,
Di6
El, N= Ne"
In2
B=
ter
20
Coulomb's law
electric field strength due to
point charge
electric potential due to
‘point charge
clectic field between parallel plates
(numerically)
‘Beneral curent flow equation
resistance and resistivity
resistors in series
resistors in parallel
power in acireuit
force on a moving charge in a
‘magnetic field
force on a current-carrying
conductor ina magnetic field
Hall voltage
magnetic field due to long
straight wire
‘magnetic field inside a long
solenoid
induced ems
ratio of secondary voltage to
primary voltage ina transformer
law of radioactive decay
halflife and decay constant
activity and the number of
undecayed nuclei
‘mass-energy relationship
You might also like
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- 4ph1 1p Que 20190523 (Q7 Refraction, TIR)Document5 pages4ph1 1p Que 20190523 (Q7 Refraction, TIR)superpooh-1No ratings yet
- 4ph1 - 1p - Que - 20190523 (Q5 Hooke's Law and Elastic Limit)Document2 pages4ph1 - 1p - Que - 20190523 (Q5 Hooke's Law and Elastic Limit)superpooh-1No ratings yet
- Designated Hotel List v6 enDocument11 pagesDesignated Hotel List v6 ensuperpooh-1No ratings yet
- Physics: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE (9-1)Document36 pagesPhysics: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE (9-1)superpooh-1100% (2)
- 4ph1 - 1p - Que - 20190523 (Q10 Series Circuit)Document2 pages4ph1 - 1p - Que - 20190523 (Q10 Series Circuit)superpooh-1No ratings yet
- Sylphy Brochure 202104Document11 pagesSylphy Brochure 202104superpooh-1No ratings yet
- @gmail - Co: 17 The Diagram Shows A Simplified Version of The Apparatus Used in An Experiment To DetermineDocument3 pages@gmail - Co: 17 The Diagram Shows A Simplified Version of The Apparatus Used in An Experiment To Determinesuperpooh-1No ratings yet
- Pages From s19-8421-03 (Q7 Quantum)Document4 pagesPages From s19-8421-03 (Q7 Quantum)superpooh-1No ratings yet
- 2016 DSE PHY Paper 1A StepsDocument9 pages2016 DSE PHY Paper 1A Stepssuperpooh-1No ratings yet
- @gmail: Answer All QuestionsDocument3 pages@gmail: Answer All Questionssuperpooh-1No ratings yet
- 4PH0 - 1P - Que - 20170112 (Q5 I-V Graph, Circuit)Document3 pages4PH0 - 1P - Que - 20170112 (Q5 I-V Graph, Circuit)superpooh-1No ratings yet
- Pages From s19-8421-03 (Q2 Wave)Document3 pagesPages From s19-8421-03 (Q2 Wave)superpooh-1No ratings yet
- Physics Paper 1: (Sample Mock Paper) Section B: Question-Answer Book BDocument16 pagesPhysics Paper 1: (Sample Mock Paper) Section B: Question-Answer Book Bsuperpooh-1No ratings yet
- Suggested Answers and Marking Schemes: Physics Sample Mock Paper For HkdseeDocument9 pagesSuggested Answers and Marking Schemes: Physics Sample Mock Paper For Hkdseesuperpooh-1No ratings yet
- Hong Kong Examinations and Assessment Authority: Pp-Dse-Phy 1-1 MsDocument17 pagesHong Kong Examinations and Assessment Authority: Pp-Dse-Phy 1-1 Mssuperpooh-1No ratings yet
- 2015 MC AnsDocument13 pages2015 MC Anssuperpooh-1No ratings yet
- Phy - HKDSE2013 - Mock - 1A - EEDocument17 pagesPhy - HKDSE2013 - Mock - 1A - EEsuperpooh-1No ratings yet
- 2015 DSE Phy 2-MS (E)Document8 pages2015 DSE Phy 2-MS (E)superpooh-1No ratings yet
- Hong Kong Examinations and Assessment Authority: Pp-Dse-Cs (Phy) - 1 MsDocument8 pagesHong Kong Examinations and Assessment Authority: Pp-Dse-Cs (Phy) - 1 Mssuperpooh-1No ratings yet
- N12 PhotoelectricDocument1 pageN12 Photoelectricsuperpooh-1No ratings yet
- Physics Paper 1 DR Ken ChanDocument19 pagesPhysics Paper 1 DR Ken Chansuperpooh-1No ratings yet
- Allow Answer in J If (B) (I) Expressed in Joule (ECF), Otherwise Award (1 Max)Document1 pageAllow Answer in J If (B) (I) Expressed in Joule (ECF), Otherwise Award (1 Max)superpooh-1No ratings yet
- 2015 May 20 Q9 (Edexcel 4PH0 FBI)Document2 pages2015 May 20 Q9 (Edexcel 4PH0 FBI)superpooh-1No ratings yet
- Energy Stores and TransfersDocument4 pagesEnergy Stores and Transferssuperpooh-1No ratings yet
- Physics Answer Key DR Ken ChanDocument7 pagesPhysics Answer Key DR Ken Chansuperpooh-1No ratings yet