Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BI Checklist: Troubleshoot A Positive Biological Indicator in Steam Sterilization
Uploaded by
Mohammed S.GoudaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BI Checklist: Troubleshoot A Positive Biological Indicator in Steam Sterilization
Uploaded by
Mohammed S.GoudaCopyright:
Available Formats
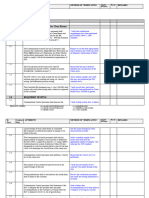
BIOLOGICAL INDICATORS
BI Checklist: Troubleshoot a Positive Biological
Indicator in Steam Sterilization
Biological indicators, or BIs, play an important role in steam sterilization validation. BIs contain microorganisms proven to resist sterilization. Using BIs in the
steam sterilization process helps validate that the conditions to kill microorganisms, such as bacterial spores, were met.
But what if a positive culture results after processing the BI in a validated steam sterilization cycle?
Use this checklist to uncover errors in operator experience, load preparation and sterilizer conditions.
STEAM STERILIZATION CYCLE(S) BIOLOGICAL INDICATORS STEAM STERILIZER EQUIPMENT MICROORGANISMS
Review Records of Cycles with Review Biological Indicator Inspect Sterilizer Functionality for Review Environmental Monitoring
Positive Results Procedures Abnormalities Data for Airborne Microorganisms
and/or Particulate Matter
Assess charts of physical Verify that the biological indicator Verify condensate traps on the jacket
parameters monitored and recorded has the correct spore count and and chamber are clean and functional Ensure environment is free of
during the cycle for irregularities D-value for the application microscopic dust and soil, which can
Ensure that the strainers on steam contain common laboratory
Compare cycle parameters to the Confirm the BI was stored in supply and condensate piping are contaminants and endospores
parameters of validated cycles to manufacturer-recommended clean
ensure adequate temperatures, conditions prior to testing Verify floors, walls, ceilings and work
exposure times or accumulated F0 Inspect the chamber strainer to surfaces are cleaned and disinfected
Validate the location of the BI in the make sure it’s clean regularly
Verify that a positive control BI was chamber, test pack or device meets
not inadvertently exchanged for an SOPs Use load probes or thermocouples to Ensure the laminar flow clean bench
exposed one by re-evaluating all BI verify temperature distribution in the work surface is cleaned with 70%
and culture media control test Ensure strict aseptic techniques sterilizer chamber is within proper isopropanol (or equivalent) and dry
results from the relevant interval were used during the culturing parameters during exposure before use
Review available chemical indicator Use negative controls to test and Ensure that the sterilizer cycle timer Review maintenance records of the
records verify the sterility of the culture media accurately meets factory HEPA filters
specifications
Identify if a spore suspension was
directly inoculated on the product or Run a Bowie-Dick and/or a leak test
Review Cycle Procedures simulated product, which can cause on prevacuum steam sterilizers to
detect inadequate air removal from
Perform Identification Testing on
clumping and affect the resistance
Review the assembly and materials of the inoculated material the chamber or air in the steam Subcultures
of the test pack or device supply
Ensure the temperature and humidity If available, perform a built-in Conduct a basic identification test to
at all locations within the incubator chamber leak test cycle and determine if the positive biological
Ensure load storage prior to the cycle
met SOPs compare the results to previous indicator culture is a BI organism
was at the temperature set by
standard operating procedures (SOPs) tests to ensure the leak rate meets
Make sure the incubator and fan
Confirm load placement within the received routine cleaning to
sterilizer met SOPs eliminate particulates which can
cause contamination
Verify the Calibration
Evaluate all routine and unscheduled
maintenance If Verify Self-Contained Biological
TM
Review the calibration documentation
Indicators (SCBI) were used, make
Review the incident log book sure the VerifyTM cap wasn’t sealed
Calibrate the sterilizer temperature
until after it was exposed to the
and pressure channels using
sterilization cycle
Discuss the relevant cycles with the National Institute of Standards and
sterilization technician Technology (NIST) traceable
Verify the sterilizer cycle parameters
measurements
if the SCBI experiences
“caramelization,” or an amber color
change, due to heat overexposure
Ensure that Utilities Meet Sterilizer
Requirements
Repeat the Biological Indicator Test
Check for water priming at the boiler,
Discontinue use of the sterilizer until faulty traps, or a faulty steam
satisfactory results are obtained condensate return system, which can
from a repeat biological indicator create excessive condensate in the
test and all applicable quality steam
assurance guidelines are met Ensure steam isn’t super-heated by
verifying the pressure and
temperature in the sterilizer jacket is
lower than in the sterilizer chamber
Verify there aren’t considerable
amounts of non-condensable gases
in the sterilizer steam supply due to
inadequate deaeration of the steam
generator feedwater
Mentor, OH | sterislifesciences.com | Phone 1-440-354-2600 | lifesciences@steris.com LSFC-BR4165.F-IT-E 09/2018
You might also like
- Comparativa Terragene y 3MDocument12 pagesComparativa Terragene y 3MBlackHorse13100% (2)
- Autoclave Validation ProcedureDocument2 pagesAutoclave Validation ProcedurePancho SanchezNo ratings yet
- How To Ensure Safety For Castable MixingDocument4 pagesHow To Ensure Safety For Castable MixingNaelNo ratings yet
- Unofficial Developer Guide To HL7v3 BasicsDocument24 pagesUnofficial Developer Guide To HL7v3 BasicsShamilNo ratings yet
- Case Study For Hepatitis BDocument24 pagesCase Study For Hepatitis BEmma Mariz Bernas Garcia67% (6)
- HACCP Case StudyDocument4 pagesHACCP Case StudyEmmanuel AfriyieNo ratings yet
- Technical Tip: Overview of A Parametric Release Cycle For Eo SterilizationDocument3 pagesTechnical Tip: Overview of A Parametric Release Cycle For Eo SterilizationRakeshNo ratings yet
- ETO Sterilization Methods GuideDocument44 pagesETO Sterilization Methods GuideCRYSTAL2100100% (1)
- 62 The Basics of Bioburden TestingDocument2 pages62 The Basics of Bioburden Testinghitham shehataNo ratings yet
- SterilizationDocument35 pagesSterilizationGeeta BhagchandaniNo ratings yet
- Moist Heat Sterilization Validation and Requalification STERISDocument4 pagesMoist Heat Sterilization Validation and Requalification STERISDany RobinNo ratings yet
- SterileprocessvalidationDocument43 pagesSterileprocessvalidationRajat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Validation of SterilizationDocument11 pagesValidation of SterilizationAndrea AmezcuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Sterilization MonitorsDocument6 pagesChapter 3 - Sterilization MonitorsFarzana HossainNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument6 pagesHACCPErena Iyra ChiocoNo ratings yet
- Sterilizing Grade Filter & Filter Validation - Mr. Ajeet Singh - 09-03-2007Document29 pagesSterilizing Grade Filter & Filter Validation - Mr. Ajeet Singh - 09-03-2007ajeets362790% (10)
- Introduction of QC in Pharma IndustryDocument28 pagesIntroduction of QC in Pharma IndustryAnggia Bia AmandaNo ratings yet
- Sterility Testing Lab Audit Checklist: Date: Client Name: Auditors: Site AddressDocument21 pagesSterility Testing Lab Audit Checklist: Date: Client Name: Auditors: Site AddressElena StoevaNo ratings yet
- TB 1005 en 00 RevbDocument8 pagesTB 1005 en 00 RevbswerNo ratings yet
- Technical Tip: Overview of An Ethylene Oxide ValidationDocument3 pagesTechnical Tip: Overview of An Ethylene Oxide ValidationRakeshNo ratings yet
- Cleaning Validation For Medical Device ManufacturingDocument12 pagesCleaning Validation For Medical Device ManufacturingDCG CandyNo ratings yet
- BB - Self AuditDocument18 pagesBB - Self AuditFe Rackle Pisco JamerNo ratings yet
- Biological Indicator ChecklistDocument2 pagesBiological Indicator ChecklistHoang100% (2)
- 55 Selection of Appropriate Internal Process Challenge Devices PCDsDocument4 pages55 Selection of Appropriate Internal Process Challenge Devices PCDsRakeshNo ratings yet
- Systems-Based Inspections For Cleaning Validation: ObjectivesDocument11 pagesSystems-Based Inspections For Cleaning Validation: ObjectivesPrashansa Shrestha100% (1)
- YANGYUAN Beverage Aseptic Filling Microbiological Validation ProtocolDocument18 pagesYANGYUAN Beverage Aseptic Filling Microbiological Validation Protocolqiaohongzedingtalk.comNo ratings yet
- Validation of Sterile Filtration ArticleDocument10 pagesValidation of Sterile Filtration Articleortizan8No ratings yet
- OPRP PlanDocument3 pagesOPRP Plan20125320No ratings yet
- Sterilization Validation QsiteDocument52 pagesSterilization Validation Qsiteskype2121No ratings yet
- Quality Guarantee: ResponsibleDocument3 pagesQuality Guarantee: Responsibleapi-638919540No ratings yet
- 1007 Inservice Chemical Indicators PDFDocument3 pages1007 Inservice Chemical Indicators PDFAbu RaihanNo ratings yet
- EO Validation Overview: 7 Steps for Ethylene Oxide Sterilization Process ValidationDocument2 pagesEO Validation Overview: 7 Steps for Ethylene Oxide Sterilization Process ValidationNur HayatiNo ratings yet
- PMPS Manufacturing Environmental Monitoring ValidationDocument4 pagesPMPS Manufacturing Environmental Monitoring ValidationBLUEPRINT Integrated Engineering ServicesNo ratings yet
- Drug Product-Based Integrity Testing Establishing A Product/filter Test Minimum ValueDocument2 pagesDrug Product-Based Integrity Testing Establishing A Product/filter Test Minimum ValueVijay Kumar NandagiriNo ratings yet
- Cleaning Validation Protocol TemplateDocument3 pagesCleaning Validation Protocol Templatemuhammad asifNo ratings yet
- Biological Indicators Training Slide Deck 1651517737Document64 pagesBiological Indicators Training Slide Deck 1651517737chdz2822No ratings yet
- 9433 - Sterlity Test Medical Devices - Web ReadyDocument4 pages9433 - Sterlity Test Medical Devices - Web ReadyZETTYNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Validation Ethylene OxideDocument4 pagesGuidelines For Validation Ethylene OxideanimeluisNo ratings yet
- European Pharmacopoeia Methods of Sterile Product PreparationDocument21 pagesEuropean Pharmacopoeia Methods of Sterile Product PreparationMostafa Afify100% (2)
- Sterilization Indicators 1Document11 pagesSterilization Indicators 1nusrath siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Edited Clean Room Checklist (ISO 14644)Document6 pagesEdited Clean Room Checklist (ISO 14644)hassan.extndNo ratings yet
- sterility-testing-sterisart-second-supplier-validation-guide-1--dataDocument4 pagessterility-testing-sterisart-second-supplier-validation-guide-1--datadinesh singhNo ratings yet
- GMP 5 Sr7Document3 pagesGMP 5 Sr7Mohamed TiemaNo ratings yet
- VAL 200 Selection and Use of Biological Indicators During Validation StudiesDocument5 pagesVAL 200 Selection and Use of Biological Indicators During Validation StudiesKranti YadavNo ratings yet
- Tzhvab210 F2JB95581Document2 pagesTzhvab210 F2JB95581Christian SFNo ratings yet
- Bubble Point Values An1505en MsDocument11 pagesBubble Point Values An1505en Msdavid andres sandi ovaresNo ratings yet
- Validation of Raw MaterialsDocument23 pagesValidation of Raw MaterialsMohamed ZakiNo ratings yet
- Depyrogenation TunnelDocument6 pagesDepyrogenation TunnelPrachi MishraNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Identification & Source Indication of ContaminantsDocument6 pagesBacterial Identification & Source Indication of Contaminantsstuffy1984No ratings yet
- BIO Purifier Product BrochureDocument2 pagesBIO Purifier Product BrochuresrisaravananNo ratings yet
- 12 Performance Qualification of EO Process Method CDocument4 pages12 Performance Qualification of EO Process Method CRakeshNo ratings yet
- Bio-X Quality Assurance GuideDocument16 pagesBio-X Quality Assurance GuideMykolaNo ratings yet
- Validation Needs for Sterile FiltrationDocument27 pagesValidation Needs for Sterile FiltrationLarissa GolucciNo ratings yet
- Usp 61 Microbiological Examination of Nonsterile Products Microbial Enumeration TestsDocument5 pagesUsp 61 Microbiological Examination of Nonsterile Products Microbial Enumeration TestsyuniarwindiNo ratings yet
- 0056-0060 (61) Microbiological Examination of Nonsterile Products - Microbial Enumeration TestsDocument5 pages0056-0060 (61) Microbiological Examination of Nonsterile Products - Microbial Enumeration TestsMerrene Bright Divino JudanNo ratings yet
- Biological Indicators-Resistance Performance Tests GoodDocument3 pagesBiological Indicators-Resistance Performance Tests Goodmingsu1156No ratings yet
- Principles of Disinfectant ValidationDocument33 pagesPrinciples of Disinfectant Validationbiladi sulton100% (1)
- HACCPDocument2 pagesHACCP20125320No ratings yet
- Autoclave Validation GuideDocument2 pagesAutoclave Validation GuideDarshilNo ratings yet
- 61 Microbiological Examination of Nonsterile Products Microbial Enumeration TestsDocument5 pages61 Microbiological Examination of Nonsterile Products Microbial Enumeration TestsChrist FarandyNo ratings yet
- The Concise Calibration & Test Equipment Management Guide: The Concise Collection, #1From EverandThe Concise Calibration & Test Equipment Management Guide: The Concise Collection, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Validation of Sterilization Equipments: Aseptic Area ValidationsDocument51 pagesValidation of Sterilization Equipments: Aseptic Area ValidationsSweekar BorkarNo ratings yet
- Building Management System (BMS) - Validation OverviewDocument6 pagesBuilding Management System (BMS) - Validation OverviewlastrajNo ratings yet
- Bao Duong May Tiet TrungDocument51 pagesBao Duong May Tiet TrungĐức CườngNo ratings yet
- F0 What It Means - How To Calculate It - How To Use Itv3 PDFDocument34 pagesF0 What It Means - How To Calculate It - How To Use Itv3 PDFJosé Manuel Pais-Chanfrau100% (1)
- Sterl IzationDocument50 pagesSterl IzationYuliatyRettaHutahaeanNo ratings yet
- General Description: Fob4 Ts Technical ManualDocument39 pagesGeneral Description: Fob4 Ts Technical ManualMohammed S.GoudaNo ratings yet
- Steamsterilizer4 DemoreportDocument45 pagesSteamsterilizer4 DemoreportsppNo ratings yet
- Sterl IzationDocument50 pagesSterl IzationYuliatyRettaHutahaeanNo ratings yet
- Moist Heat Sterilization Highlights On Equivalent Time F0Document5 pagesMoist Heat Sterilization Highlights On Equivalent Time F0Rushyanth KR100% (1)
- Steam Sterilization and The 2007 Revision of PDA Technical Report 1Document59 pagesSteam Sterilization and The 2007 Revision of PDA Technical Report 1Carlos Medina Cisterna100% (5)
- Guideline For Sterilization Process Validation: (Date:1995-11-01)Document17 pagesGuideline For Sterilization Process Validation: (Date:1995-11-01)Antonius MikaelNo ratings yet
- Conducting The ISO 14644-3 Cleanroom Recovery Test With The MET ONE 3400Document9 pagesConducting The ISO 14644-3 Cleanroom Recovery Test With The MET ONE 3400Mohammed S.GoudaNo ratings yet
- CSS Guide SteamSterilizationCycles PDFDocument31 pagesCSS Guide SteamSterilizationCycles PDFJesus PerezNo ratings yet
- Qualification of AutoclavesDocument39 pagesQualification of Autoclavesjermac17100% (1)
- Optimizing The Sterilization Process of Canned FooDocument9 pagesOptimizing The Sterilization Process of Canned FooMohammed S.GoudaNo ratings yet
- DCVMN Heat Sterilisation v3 1 PDFDocument94 pagesDCVMN Heat Sterilisation v3 1 PDFAnkush KharwalNo ratings yet
- 17 QuestionsDocument34 pages17 Questionsmuzammil21_ad100% (1)
- اللغة النوبية كيف نكتبهاDocument100 pagesاللغة النوبية كيف نكتبهاMohammed S.GoudaNo ratings yet
- Ucm 072171Document23 pagesUcm 072171Vizit31No ratings yet
- Ucm 072171Document23 pagesUcm 072171Vizit31No ratings yet
- Recovery Time For ISO Class 8 Cleanrooms: Create PDF in Your Applications With The PdfcrowdDocument4 pagesRecovery Time For ISO Class 8 Cleanrooms: Create PDF in Your Applications With The PdfcrowdMohammed S.GoudaNo ratings yet
- Sellenis S-Jet 600 Series User Manual V5Document91 pagesSellenis S-Jet 600 Series User Manual V5Mohammed S.GoudaNo ratings yet
- Qualify Facilities, HVAC and Water Systems: Jerry LaneseDocument144 pagesQualify Facilities, HVAC and Water Systems: Jerry LaneseMohammed S.GoudaNo ratings yet
- Bao Duong May Tiet TrungDocument51 pagesBao Duong May Tiet TrungĐức CườngNo ratings yet
- PIDs Best Practices PDFDocument80 pagesPIDs Best Practices PDFmawooaNo ratings yet
- Hikma Pharmaceuticals-Apis Sterile Bms System: Installation/Operation Qualification ProtocolDocument39 pagesHikma Pharmaceuticals-Apis Sterile Bms System: Installation/Operation Qualification ProtocolMohammed S.GoudaNo ratings yet
- Lyophilization Process ReportDocument42 pagesLyophilization Process ReportMohammed S.GoudaNo ratings yet
- 620dun User ManualDocument112 pages620dun User ManualMohammed S.GoudaNo ratings yet
- Microwave-Assisted Freeze-Drying of Monoclonal Antibodies: Product Quality Aspects and Storage StabilityDocument21 pagesMicrowave-Assisted Freeze-Drying of Monoclonal Antibodies: Product Quality Aspects and Storage StabilityMohammed S.GoudaNo ratings yet
- To Study The Prevalence of Anaemia in Indoor Patients of Tertiary Care CentreDocument3 pagesTo Study The Prevalence of Anaemia in Indoor Patients of Tertiary Care CentreIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Nursing TheoriesDocument4 pagesNursing TheoriesSamantha Joy VidalNo ratings yet
- Acrysil LTDDocument64 pagesAcrysil LTDreciprocationsNo ratings yet
- Ohio Drug Law Enforcement Fund 2023 AwardsDocument2 pagesOhio Drug Law Enforcement Fund 2023 AwardsWKYC.comNo ratings yet
- CCSF - Annual Salary Ordinance - 2010 - Aso 2009-2010 - 07-21-09Document219 pagesCCSF - Annual Salary Ordinance - 2010 - Aso 2009-2010 - 07-21-09prowagNo ratings yet
- Master Nauli for a Strong Core and DigestionDocument7 pagesMaster Nauli for a Strong Core and DigestionOVVCMOULINo ratings yet
- ESSAY 9 (When Grandiosity Speaks, Medical Students Are Supposed To Listen..)Document5 pagesESSAY 9 (When Grandiosity Speaks, Medical Students Are Supposed To Listen..)Kay BorzsonyNo ratings yet
- Mental Health and WellbeingDocument5 pagesMental Health and WellbeingNicole Ofili100% (1)
- Preparation of Tablet From Naagdon Plant by Wet Granulation Method For Treatment of Excessive Bleeding in PilesDocument14 pagesPreparation of Tablet From Naagdon Plant by Wet Granulation Method For Treatment of Excessive Bleeding in PilesIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Jurnal MFSDocument11 pagesJurnal MFSAfni YusnitaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Hypertension in Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument7 pagesPathophysiology of Hypertension in Chronic Kidney DiseaseRifka WidianingrumNo ratings yet
- G1a115016 - Tesa SeptiariDocument12 pagesG1a115016 - Tesa SeptiariTesa SeptiariNo ratings yet
- User Manual For The SpirometerDocument4 pagesUser Manual For The SpirometerAlex WilliamsNo ratings yet
- MCQ I JAN 2018 - With PDFDocument19 pagesMCQ I JAN 2018 - With PDFSpacetoon DaysNo ratings yet
- Partner Institutes and Focal Person List PDFDocument1 pagePartner Institutes and Focal Person List PDFHamza IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Classification Techniques For Medical Data: April 2018Document6 pagesAnalysis of Classification Techniques For Medical Data: April 2018Ahmed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Philippine HMO not liable for DSTDocument2 pagesPhilippine HMO not liable for DSTLara YuloNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Fitness Testing For Sport and ExerciseDocument6 pagesUnit 7 Fitness Testing For Sport and ExerciseClayesmorePENo ratings yet
- Pre AnestesiDocument64 pagesPre AnestesiKevin YonathanNo ratings yet
- Brown Rice-Beyond The Color Reviving A Lost Health Food - A ReviewDocument6 pagesBrown Rice-Beyond The Color Reviving A Lost Health Food - A ReviewDinesh Babu PugalenthiNo ratings yet
- Glasgow Coma Scale Canvas NCM 116 SkillsDocument6 pagesGlasgow Coma Scale Canvas NCM 116 Skillsbing bongNo ratings yet
- The Inside Story of The Papal Birth ControlDocument5 pagesThe Inside Story of The Papal Birth ControlKenneth DavisNo ratings yet
- Dr. Nirali Patel Pediatric Emergency MedicineDocument31 pagesDr. Nirali Patel Pediatric Emergency Medicinemarsan12No ratings yet
- Group F - Nursing Kardex Written OutputDocument7 pagesGroup F - Nursing Kardex Written OutputMatty JolbitadoNo ratings yet
- Dr. Bondoc Found Liable for Grave Misconduct in Delivery CaseDocument3 pagesDr. Bondoc Found Liable for Grave Misconduct in Delivery CaseSalie VillafloresNo ratings yet
- SOP For Fumigation in Microbiology Lab - Pharmaceutical GuidelinesDocument1 pageSOP For Fumigation in Microbiology Lab - Pharmaceutical GuidelinesranaNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Problem in ChildrenDocument4 pagesNutritional Problem in Childrennaufal umerNo ratings yet