Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 Cancer HO Set1 (Intro) Zoom Lec
1 Cancer HO Set1 (Intro) Zoom Lec
Uploaded by
karl montano0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pages1 Cancer HO Set1 (Intro) Zoom Lec
1 Cancer HO Set1 (Intro) Zoom Lec
Uploaded by
karl montanoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
1
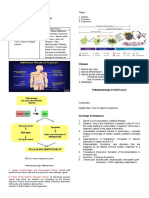
Cancer Carcinoma in Situ- Neoplasm which remains
A disease process whereby cells proliferate confined on the site of origin.
abnormally, ignoring-regulating signals in the
environment surrounding cells. Cellular Adaptive Process:
Estimated New Cancer Cases, Both Sexes in US 1. Hyperplasia
(2020) American CA Society:
1. Digestive System 2. Metaplasia
2. Genital System
3. Breast 3. Dysplasia
4. Respiratory System
5. Urinary System 4. Anaplasia
6. Skin
7. Lymphoma
8. Leukemia Contact Inhibition
9. Endocrine System - cessation of growth ones the cell comes in
10. Oral Cavity & Pharynx contact with another cell. It switches off cell
growth by blocking the synthesis of DNA, RNA &
Definition of Terms: CHON.
Aberrant Cellular Growth It is an alteration in
the normal cellular growth Types of cells according to their ability to
undergo regeneration:
Apoptosis 1. Labile
2. Stable
Cyst- A closed sac having a distinct membrane 3. Permanent or Fixed
and developing abnormally
Secondary Prevention- Early Detection of CA
Metastasis- It is the spread of cancer cells A. Health history and PE
B. Screening Methods
Neoplasm - Greek: NEO “new” Plasia “growth 1. Mammography
of tissue ; A mass of new tissue that grows
independently of its surrounding structures Pap Smear
Carcinoma - A specific form of CA or malignant Prostate exam
tumor arising from epithelial cells.
Digital rectal exam
Tumor- It is a lump, mass, or swelling or
enlargement 2. Self-care practices
Breast Self Exam
Sarcoma
Testicular exam
Oncogenes Tumor - genes that promote cell
proliferation and are capable of triggering 4. Sigmoidoscopy and
cancerous characteristics
Fecal occult blood test
Oncology - The field or study of cancer
Diagnostic Tools in Detecting Cancer
Proto-oncogenes - These are benign forms of A. Laboratory Tests
oncogenes necessary for some normal cellular 1. CBC /Differential count
functions, especially growth and development.
Differentiation – extent to w/c tissue cells
resemble normal cells Serum Electroyles
Ca – increase, bone metastasis
Progression- Na – Decrease, Bronchogenic CA
K – decrease, Liver CA
Neoplastic Progression
2. Tumor Markers or proteins associated with
specific cancer
2
1. Serum prostate- specific antigen (PSA) C. Electrosurgery
D. Cryosurgery
2. Alpha-fetoCHON (AFP) E. Chemosurgery
F. Laser Surgery
3. Cancinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) G. Stereotactic Radiosurgery
B. Cytologic Examination Other forms of Surgery:
Ex: Papanicolaou Test (PapSmear) 1. Prophylactic
2. Palliative
3. Reconstructive
Nursing Management in Cancer Surgery
C. Oncologic Imaging
1. Complete a thorough pre-operative
1. Radiographs/ X-ray
assessment .
Chest X-ray
2. Provide education and emotional
Mammograms
support.
CT Scan/MRI
3. Communicate frequently with the
2. Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
health team members .
3. Biopsy
4. Assess the patient’s responses to the
surgery and monitor possible
complications.
D. Invasive diagnostic techniques
5. Provide comfort.
Biopsy
6. Initiate as early as possible plans for
Cyst aspiration
discharge, follow-up and home care and
Cystoscopy
treatment to ensure continuity of care.
7. Patients and family are encouraged to
use community resources such as the
Philippine Cancer Society.
Management of Patient with Neoplastic
Diseases
Goals:
1. cure
2. control
3. palliation
A. SURGERY
* Diagnostic Surgery
3 methods:
a. Excisional biopsy
b. Incisional biopsy
c. Needle biopsy
* Surgery as Primary Treatment
Goal: TO remove the entire tumor or as much
as possible and any involved surrounding tissue,
including regional lymph nodes.
2 Common Procedures:
1. Local incision
2. Wide or Radical Excision
New Approaches: SURGERY AS PRIMARY
TREATMENT
A. Video
B. Salvage surgery
You might also like
- Oncology Nursing NotesDocument12 pagesOncology Nursing Notesjoyrena ochondra100% (8)
- Pathology MCQ - NeoplasiaDocument5 pagesPathology MCQ - NeoplasiaRaj Patel92% (12)
- Cellular AbrasionDocument16 pagesCellular Abrasionmolina ababonNo ratings yet
- Med Surg (Oncology)Document169 pagesMed Surg (Oncology)DardarConstantinoNo ratings yet
- 3 1 Neoplasia PDFDocument3 pages3 1 Neoplasia PDFPrabhat GuptaNo ratings yet
- NeoplasiaDocument2 pagesNeoplasiaFayon JamesNo ratings yet
- DR Evelyn Pathophysiology - Carcinogenesis MRCCC - 2013Document119 pagesDR Evelyn Pathophysiology - Carcinogenesis MRCCC - 2013Ida MuntheNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia: Benito K. Lim Hong III, M.DDocument51 pagesNeoplasia: Benito K. Lim Hong III, M.DGokul PoudelNo ratings yet
- Oncology NursingDocument19 pagesOncology NursingMarlowe DulayNo ratings yet
- SURG Surgical OncologyDocument5 pagesSURG Surgical Oncologyfatima angelica LingonNo ratings yet
- NRS Review Notes - CancerDocument20 pagesNRS Review Notes - CancerMariecar GarazaNo ratings yet
- Levels of Prevention Primary Secondary TertiaryDocument3 pagesLevels of Prevention Primary Secondary Tertiarymyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Care of Patients With CancerDocument57 pagesCare of Patients With CancerAyessa Yvonne PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Oncology NursingDocument3 pagesOncology NursingJalishia Mae DumdumaNo ratings yet
- Cancer NotesDocument7 pagesCancer NotesKyla Mae JumaritoNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument8 pagesCancerChrisMerellNo ratings yet
- Oncology: Farrahiyah IsmailDocument33 pagesOncology: Farrahiyah IsmailaisyahambaliNo ratings yet
- Tumors by SadekDocument22 pagesTumors by SadekAhmed El SayedNo ratings yet
- Unexplained Ascites, A Sign For Neuroendocrine Carcinoma: Case ReportDocument3 pagesUnexplained Ascites, A Sign For Neuroendocrine Carcinoma: Case ReportsandzatNo ratings yet
- Care For Women: With Ovarian, Cerviacl, Vulvar and Endometrial CancerDocument26 pagesCare For Women: With Ovarian, Cerviacl, Vulvar and Endometrial CancerAhmad JradeenNo ratings yet
- Cellular Aberrations Cancer, Malignant Neoplasm, Oncologic DisorderDocument5 pagesCellular Aberrations Cancer, Malignant Neoplasm, Oncologic DisorderIrish Eunice Felix100% (1)
- Neoplastic Disorders: Pathogenesis of CancerDocument37 pagesNeoplastic Disorders: Pathogenesis of CancerEn ConejosNo ratings yet
- MS CA and EN Ans KeyDocument15 pagesMS CA and EN Ans KeyAydh Dim-Mac RsclNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia IIDocument44 pagesNeoplasia IIJeevan SunaNo ratings yet
- Care of The Clients With Cancer: Prof. Hashim N. Alawi Jr. RN, MANDocument78 pagesCare of The Clients With Cancer: Prof. Hashim N. Alawi Jr. RN, MANjisooNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Client With CancerDocument63 pagesNursing Care of Client With CancermikErlhNo ratings yet
- Cervic Tumour - SummaryDocument9 pagesCervic Tumour - SummaryRUDOLF YUSON BM20110052No ratings yet
- Thyroid CancerDocument15 pagesThyroid CancerA. Lizette PabloNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cancer Notes - G7 3BSN1Document52 pagesOvarian Cancer Notes - G7 3BSN1Shyne HazyNo ratings yet
- Mixed Adenoneuroendocrine Carcinoma of The Gallbladder: Case PresentationDocument3 pagesMixed Adenoneuroendocrine Carcinoma of The Gallbladder: Case PresentationGeorgiana WltNo ratings yet
- Lecture Handouts Oncology NursingDocument12 pagesLecture Handouts Oncology NursingTiffany Luv AdriasNo ratings yet
- Nursing OncologyDocument131 pagesNursing Oncologyapi-3818438100% (5)
- Neoplasia Case Studies142654Document1 pageNeoplasia Case Studies142654Patrick Ngo'nga ChifwemaNo ratings yet
- Bedah Onkologi: Dr. Kristanto Yuli Yarso, SPB (K) OnkDocument33 pagesBedah Onkologi: Dr. Kristanto Yuli Yarso, SPB (K) OnkAdhelia Galuh PrmtsrNo ratings yet
- Nursing OncologyDocument208 pagesNursing OncologyfelxhuNo ratings yet
- CA A Cancer J Clinicians - March April 1988 - Virji - Tumor Markers in Cancer Diagnosis and PrognosisDocument23 pagesCA A Cancer J Clinicians - March April 1988 - Virji - Tumor Markers in Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosistem gastonNo ratings yet
- Oncology Nursing NotesDocument12 pagesOncology Nursing NotesBavitha BNo ratings yet
- Surgical Case Report 2022 Mesoth PerithDocument3 pagesSurgical Case Report 2022 Mesoth PerithJeanne LahogueNo ratings yet
- NATALINODocument99 pagesNATALINOShiangNo ratings yet
- An Uncommon Poorly Differentiated Small Cell Neuro-Endocrine Carcinoma of Urinary Bladder A Review With Case ReportDocument3 pagesAn Uncommon Poorly Differentiated Small Cell Neuro-Endocrine Carcinoma of Urinary Bladder A Review With Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Oncology Nursing Part 1 2Document51 pagesOncology Nursing Part 1 2fleur harrisonNo ratings yet
- PancreatoblastomaDocument16 pagesPancreatoblastomaDr Farman AliNo ratings yet
- 2.2. Surgical OncologyDocument21 pages2.2. Surgical OncologyMiguel C. DolotNo ratings yet
- Understanding CancerDocument5 pagesUnderstanding CancerEunice Villa CuñadaNo ratings yet
- 0105 - NeoplasiaDocument22 pages0105 - Neoplasiacipriano2No ratings yet
- CancerDocument4 pagesCancerPaul AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- BiomarkerDocument18 pagesBiomarkeranggaririnNo ratings yet
- Oncology Handouts PDFDocument21 pagesOncology Handouts PDFPhilip Simangan100% (1)
- Learning Material Ovarian CancerDocument5 pagesLearning Material Ovarian CancerJonathan R. YadaoNo ratings yet
- Sister Mary Joseph Nodule As Cutaneous.9Document3 pagesSister Mary Joseph Nodule As Cutaneous.9Fernando MartinezNo ratings yet
- The-Biology-Of-Cancer RUSHILDocument17 pagesThe-Biology-Of-Cancer RUSHILRushilNo ratings yet
- Nicha-Cancer PresentationDocument13 pagesNicha-Cancer Presentationapi-452284231No ratings yet
- CA A Cancer J Clinicians - March April 1988 - Virji - Tumor Markers in Cancer Diagnosis and PrognosisDocument23 pagesCA A Cancer J Clinicians - March April 1988 - Virji - Tumor Markers in Cancer Diagnosis and PrognosisIssahaku AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Cancer: Tien Gartinah, MNDocument5 pagesCancer: Tien Gartinah, MNAnonymous VoR18nTNo ratings yet
- Cancer Updated (1) (1) (1) - Compatibility ModeDocument13 pagesCancer Updated (1) (1) (1) - Compatibility Modeaisha alsuwaidiNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM - 2S11 - Molecular Basis of OncogenesisDocument17 pagesBIOCHEM - 2S11 - Molecular Basis of OncogenesisRonak Upadhyay100% (1)
- Development of Electrochemical Biosensor For Breast Cancer Detection Using Gold Nanoparticle Doped CA 15-3 Antibody and Antigen InteractionDocument7 pagesDevelopment of Electrochemical Biosensor For Breast Cancer Detection Using Gold Nanoparticle Doped CA 15-3 Antibody and Antigen InteractionwardaninurindahNo ratings yet
- Colon Cancer CellsFrom EverandColon Cancer CellsMary MoyerNo ratings yet
- Salivary Gland Cancer: From Diagnosis to Tailored TreatmentFrom EverandSalivary Gland Cancer: From Diagnosis to Tailored TreatmentLisa LicitraNo ratings yet
- Neuroendocrine Tumors: Surgical Evaluation and ManagementFrom EverandNeuroendocrine Tumors: Surgical Evaluation and ManagementJordan M. CloydNo ratings yet
- Cell Movement and Neoplasia: Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Cell Tissue and Organ Culture Study Group, Held at the Janssen Research Foundation, Beerse, Belgium, May 1979From EverandCell Movement and Neoplasia: Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Cell Tissue and Organ Culture Study Group, Held at the Janssen Research Foundation, Beerse, Belgium, May 1979M. De BrabanderRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Vital Signs Written ReportDocument7 pagesVital Signs Written Reportkarl montanoNo ratings yet
- SymptomatologyDocument2 pagesSymptomatologykarl montanoNo ratings yet
- Lydia HallDocument1 pageLydia Hallkarl montanoNo ratings yet
- Sertraline Generic Name: Sertraline Hydrochloride Brand Name: Zoloft Classification: SSRI Antidepressant Mode of ActionDocument11 pagesSertraline Generic Name: Sertraline Hydrochloride Brand Name: Zoloft Classification: SSRI Antidepressant Mode of Actionkarl montanoNo ratings yet
- EAU Guidelines On: Penile CancerDocument38 pagesEAU Guidelines On: Penile Cancerhypebeast dopeNo ratings yet
- Baneji PDFDocument6 pagesBaneji PDFSuraj YadavNo ratings yet
- Skin Tumor AgusDocument54 pagesSkin Tumor AgusHafida AuliaristaNo ratings yet
- 03 - OMF PathDocument29 pages03 - OMF Pathlabasgrazuoli0% (2)
- Prognostic Indicators in Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: Diana S. Dean, MD, and Ian D. Hay, MB, PHD, FRCPDocument11 pagesPrognostic Indicators in Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: Diana S. Dean, MD, and Ian D. Hay, MB, PHD, FRCPRum Afida RasfaNo ratings yet
- Animal Cytology (Compatibility Mode)Document13 pagesAnimal Cytology (Compatibility Mode)AdarshBijapurNo ratings yet
- PA - Dasar Neoplasma (DrBerti) PDFDocument67 pagesPA - Dasar Neoplasma (DrBerti) PDFElearning FK UnhasNo ratings yet
- (PATHOLOGY) NeoplasiaDocument137 pages(PATHOLOGY) Neoplasiaten tazapNo ratings yet
- Lung Cancer 1Document44 pagesLung Cancer 1DR.OMAR ABDALLANo ratings yet
- CA MammaeDocument30 pagesCA MammaeAlfiany SahrNo ratings yet
- Oncology Nursing-2 PDFDocument22 pagesOncology Nursing-2 PDFHebsiba PonnayyanNo ratings yet
- FMGE LRR Pathology Part 1Document62 pagesFMGE LRR Pathology Part 1Vishal KumarNo ratings yet
- Lung Cancer: By: Ivan Emmanuel BokingkitoDocument51 pagesLung Cancer: By: Ivan Emmanuel BokingkitoIvanNo ratings yet
- The Enzyme Treatment For Cancer (1909, Committee On Scientific Research of The N.Y. Skin & Cancer Hospital) - William Seaman Bainbridge (1870-1947)Document42 pagesThe Enzyme Treatment For Cancer (1909, Committee On Scientific Research of The N.Y. Skin & Cancer Hospital) - William Seaman Bainbridge (1870-1947)My-RavenNo ratings yet
- c2Document34 pagesc2markmkoNo ratings yet
- PosterDocument45 pagesPosterRoxana Alexandra BogosNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic CancerDocument30 pagesPancreatic CancerHealth Education Library for People75% (4)
- Thymic Carcinoma State of The Art ReviewDocument11 pagesThymic Carcinoma State of The Art ReviewRaul Matute MartinNo ratings yet
- Vet Pathol 2011 2011 ACVP Annual Meeting E1 E51Document52 pagesVet Pathol 2011 2011 ACVP Annual Meeting E1 E51Haroon RashidNo ratings yet
- Icam 1Document10 pagesIcam 1dusseldorf27No ratings yet
- Structure & Characterstics of Normal & Cancer CellsDocument58 pagesStructure & Characterstics of Normal & Cancer CellsVinay SahuNo ratings yet
- 12 - Husain Guidelines For Pathologic Diagnosis of Malignant MesotheliomaDocument21 pages12 - Husain Guidelines For Pathologic Diagnosis of Malignant MesotheliomaHedda Michelle Guevara NietoNo ratings yet
- Salivary Gland TumorDocument62 pagesSalivary Gland Tumordeepak kumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Cancer PrepU QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Cancer PrepU QuestionsKevin ClarkNo ratings yet
- KanMend NMCDDocument32 pagesKanMend NMCDSincerely ReynNo ratings yet
- Carcinosarcoma of The Ampulla of Vater PDFDocument2 pagesCarcinosarcoma of The Ampulla of Vater PDFAlifatul MaslachahNo ratings yet
- Bệnh tuyến nước bọt.ppt (Handout 2020)Document84 pagesBệnh tuyến nước bọt.ppt (Handout 2020)Ken DangNo ratings yet
- Textbook Ebook Glitterland 3Rd Edition Alexis Hall All Chapter PDFDocument43 pagesTextbook Ebook Glitterland 3Rd Edition Alexis Hall All Chapter PDFtroy.washburn181100% (4)
- Evaluation of A New Binary System of Grading Oral Epithelial Dysplasia For Prediction of Malignant TransformationDocument7 pagesEvaluation of A New Binary System of Grading Oral Epithelial Dysplasia For Prediction of Malignant TransformationbrboyNo ratings yet