Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 2b, Line and Letters
Uploaded by
Muhammad Nadeem KhanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Week 2b, Line and Letters
Uploaded by
Muhammad Nadeem KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
CE-112L: Engineering Drawing for Civil Engineers (Lab)
Fall 2018
WEEK 2 (part 2)
Types of Lines and Lettering
Set squares can be used in combination to draw different angles as shown below.
Types of lines:
Have a look at figure given below, it shows different types of lines.
Prepared by: Engr Arsalan Khan
Course Instructor: Engr. Hamna Shakeel Page I of V
CE-112L: Engineering Drawing for Civil Engineers (Lab)
Fall 2018
a. Visible/Solid lines
These are heavy, thick black lines, approximately 0.020” (0.5mm) thick. These are uniform in color and density, are used
to define visible edges and surface boundaries of an object.
b. Hidden lines
These are medium sized, dashed lines, approximately 0.015” thick (0.4mm). The dashes shall be four times as long as
the intermittent space (2mm long space -> 8mm long line). These lines are a little lighter as compared to the visible
lines. These are used to define those edges of an object which are not directly visible (hidden edges).
c. Leader lines
These are thin lines, 0.010” (0.25mm) thick, and used to give dimension or to connect an explanatory note to an object.
It can have an arrowhead or a dot, starting from the object and ending at the note.
d. Center lines
These are long-space-short lines, i.e. composed of alternate long and short dashes. The long line may have any
convenient length, but the short lines are 1/8 of the long line and the intermittent spaces must be 1/16 of the long line.
These are used to locate the center of an object.
e. Phantom lines
These are thin lines in a pattern as long line-space-short line-space-short line. Their approximate thickness is 0.010”
(0.25mm). These lines are used to show the outline of the adjacent part of the object, which is relative to, but not the
actual part of the drawing.
Cutting Plane Lines are similar to phantom lines, there objective is different. These are used where the objects are cut in
order to see the internal details of it.
f. Continuation/Break lines
These are thin lines, approximately 0.010” (0.25mm) thick, with short zigzags within them, and are drawn to show long
breaks or continuation in the drawing.
Now look at the following drawing and figure out the different types of lines used in it.
Prepared by: Engr Arsalan Khan
Course Instructor: Engr. Hamna Shakeel Page II of V
CE-112L: Engineering Drawing for Civil Engineers (Lab)
Fall 2018
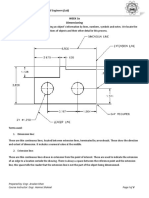
Lettering:
How will your
technical drawing
look if you write in it
like this????......
Prepared by: Engr Arsalan Khan
Course Instructor: Engr. Hamna Shakeel Page III of V
CE-112L: Engineering Drawing for Civil Engineers (Lab)
Fall 2018
Technical lettering is the process of forming letters, numerals, and other characters in technical drawing. Lettering is
writing the titles, giving dimensions or writing a note or other important particulars on the drawing.
Lettering should be done properly in clear, legible and uniform style. It should be simple so that it could be done
freehand and speedily. Guide lines should be used for lettering. They are light layout lines, spaced apart according to
the characters’ height, and serve to help keep freehand lettering at a uniform height.
Generally, the main titles are written in 8mm size, the sub-titles in 7mm size, while notes and dimension figures are
written in 5mm size.
Remember: lettering is to be done at the end when all the drawing is complete with 2H pencil.
Your perfection in
technical drawing is
counted…
:)
Prepared by: Engr Arsalan Khan
Course Instructor: Engr. Hamna Shakeel Page IV of V
CE-112L: Engineering Drawing for Civil Engineers (Lab)
Fall 2018
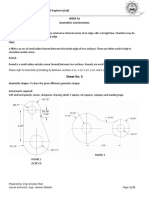
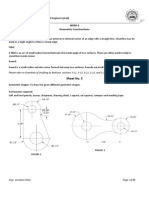
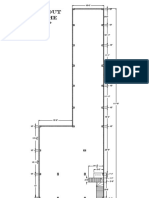
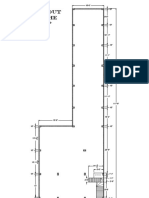
Sheet No. 2
Lines & Lettering: To draw the given shapes as a practice exercise for different types of lines
Instruments required:
Soft and hard pencils, eraser, sharpener, drawing sheet, t square, set squares, masking tape and compass.
Final output:
Prepared by: Engr Arsalan Khan
Course Instructor: Engr. Hamna Shakeel Page V of V
You might also like
- Technical Drawing BookDocument94 pagesTechnical Drawing BookYulius Feryanlie100% (8)
- Engineering Drawing Practical ManualDocument95 pagesEngineering Drawing Practical ManualMohamad Nadzri YahayaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Module 1Document9 pagesEngineering Drawing Module 1Aldrin Villanueva100% (2)
- Engineering Drawing - Introduction - EBCDocument94 pagesEngineering Drawing - Introduction - EBCrupa225chandu_327248No ratings yet
- 60372-Engineering Drawing 1Document133 pages60372-Engineering Drawing 1Pallavi Deotale100% (1)
- 416E, 422E and 428E Backhoe Loader Hydraulic System: Fluid Power SymbolsDocument2 pages416E, 422E and 428E Backhoe Loader Hydraulic System: Fluid Power SymbolsJorge Mendoza100% (2)
- Engineering DrawingDocument55 pagesEngineering DrawingMd NaimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Lines & LeteringDocument55 pagesLecture 1 - Lines & Leteringmmarybenson11No ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Book 2022-2023 1st TermDocument232 pagesEngineering Drawing Book 2022-2023 1st TermEl-Farouk Omar100% (2)
- Engineering Drawing ModuleDocument8 pagesEngineering Drawing ModuleAldrin Villanueva100% (3)
- Case Digests in Statutory Construction Philippine Law StudentDocument58 pagesCase Digests in Statutory Construction Philippine Law StudentJoshua Emmanuel100% (5)
- 1 58503 283 2 2Document65 pages1 58503 283 2 2marcelo_adcampNo ratings yet
- Alphabet of LinesDocument12 pagesAlphabet of LinesAl Sah Him100% (1)
- DLL SubstanceDocument3 pagesDLL SubstanceReign Honrado100% (1)
- Basic Engineering DrawingDocument38 pagesBasic Engineering DrawingVignesh SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Building Construction and DrawingFrom EverandBuilding Construction and DrawingRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- IC Workshop Materials 09 - Construction Drawing PracticesDocument43 pagesIC Workshop Materials 09 - Construction Drawing PracticesooiNo ratings yet
- Lec-1 Engineering DrawingDocument63 pagesLec-1 Engineering Drawingmuhammad awaisNo ratings yet
- Introduction Engineering GraphicsDocument47 pagesIntroduction Engineering GraphicsCHRISTIAN FRANCIS NAYRENo ratings yet
- Science8 Q4 SLM4Document16 pagesScience8 Q4 SLM4Joel VillegasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Architectural Drafting: DraftsmanDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Architectural Drafting: DraftsmanLeonie ClavecillasNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing - Lettering and Lines PresentationDocument67 pagesEngineering Drawing - Lettering and Lines PresentationSrini KumarNo ratings yet
- W3 LecturesDocument5 pagesW3 Lectures8356shaheerNo ratings yet
- CPE414 Engineering DrawingDocument24 pagesCPE414 Engineering Drawinganita mazlanNo ratings yet
- Week 4a, Geometric ConstructionDocument4 pagesWeek 4a, Geometric ConstructionMuhammad Nadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Week 3A Dimensioning: CE-112L: Engineering Drawing For Civil Engineers (Lab) Fall 2018Document5 pagesWeek 3A Dimensioning: CE-112L: Engineering Drawing For Civil Engineers (Lab) Fall 2018Muhammad Nadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Week 2a, Instruments and Their UsesDocument7 pagesWeek 2a, Instruments and Their UsesMuhammad Nadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- W1 Module 1-Drawing Instruments and AccessoriesDocument9 pagesW1 Module 1-Drawing Instruments and AccessorieschienikolaoNo ratings yet
- Basic Drawing and Plane Geometry - STD VerDocument89 pagesBasic Drawing and Plane Geometry - STD VerkaronaNo ratings yet
- Lesson No. 1: Types of DrawingDocument17 pagesLesson No. 1: Types of DrawingJames Philip RelleveNo ratings yet
- Engg Drawing Viva QuestionsDocument8 pagesEngg Drawing Viva Questionsmahdzia0% (1)
- Tup Engineering Lettering Assign 1Document9 pagesTup Engineering Lettering Assign 1Carlo Jhan LolongNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 Introduction Engineering GraphicsDocument57 pagesLecture 01 Introduction Engineering GraphicsMuhammad Naseem Ishaq /ME Lab Engineer100% (1)
- W6 LectureDocument4 pagesW6 LectureYounas BilalNo ratings yet
- National Textile UniversityDocument20 pagesNational Textile UniversitysarmadranaNo ratings yet
- Engieering Drawing NotesDocument10 pagesEngieering Drawing NotesAvijit PaulNo ratings yet
- Lines, Angles, Letters, Dimensioning and Rectiliner FiguresDocument71 pagesLines, Angles, Letters, Dimensioning and Rectiliner FiguresShahir KingNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing - BookDocument150 pagesEngineering Drawing - Bookgurumahesh gNo ratings yet
- Learners Activity SheetDocument2 pagesLearners Activity SheetMichael John SegarinoNo ratings yet
- Info Sheet 1 - TechDrawingDocument8 pagesInfo Sheet 1 - TechDrawingGizaw TadesseNo ratings yet
- TD1 IntroductionDocument11 pagesTD1 Introductionmosesochieng337100% (1)
- Module 4 Draw 113Document28 pagesModule 4 Draw 113Hanah ArzNo ratings yet
- M MM M M M MM M!"M #M $M$$ M % &'M (M) M M M M#M$MDocument25 pagesM MM M M M MM M!"M #M $M$$ M % &'M (M) M M M M#M$MSaood KhanNo ratings yet
- TO Engineering Drawing: Marks Awarded: /7 + /3 /10Document13 pagesTO Engineering Drawing: Marks Awarded: /7 + /3 /10Aamir AliNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing 1Document49 pagesEngineering Drawing 1Thorne Adam Danor100% (1)
- Types of Lines in Engineering DrawingDocument6 pagesTypes of Lines in Engineering DrawingmerouaneinconuNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 (Inroduction & Lettering)Document9 pagesExperiment No. 1 (Inroduction & Lettering)Jatin GargNo ratings yet
- Sheet No. 1 (Lettering Dimensioning & Lines)Document8 pagesSheet No. 1 (Lettering Dimensioning & Lines)bhavyaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Book 2022 2023 1st Term 2 1 80Document80 pagesEngineering Drawing Book 2022 2023 1st Term 2 1 80Epimaque NkurunzizaNo ratings yet
- Intro To ArchldraftingDocument9 pagesIntro To Archldraftingbernie_uy100% (3)
- Drawing TD BasicssDocument56 pagesDrawing TD BasicssAluNo ratings yet
- Title BlockDocument2 pagesTitle BlockSuktara-Drubatara TaritNo ratings yet
- Lettering and Dimensioning PracticesDocument37 pagesLettering and Dimensioning PracticesAKIRA HarashiNo ratings yet
- "Civil Engineering" - Drawing CE-105: Prepared By: Samreen ShabbirDocument39 pages"Civil Engineering" - Drawing CE-105: Prepared By: Samreen Shabbirsamreen shabbirNo ratings yet
- EGCD Unit-1Document86 pagesEGCD Unit-1Bhuma Naga PavanNo ratings yet
- Caed PDF Notes I SemDocument161 pagesCaed PDF Notes I SemjovanNo ratings yet
- Technical DrawingDocument43 pagesTechnical Drawinghabtemariam mollaNo ratings yet
- Template Drawings and SketchingDocument15 pagesTemplate Drawings and Sketchingjerym21001No ratings yet
- Assignment On Different Line Styles Used On Engineering DrawingsDocument6 pagesAssignment On Different Line Styles Used On Engineering DrawingsSouban JavedNo ratings yet
- Ed E1 PDFDocument35 pagesEd E1 PDFBikash ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Lab No: 02: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesLab No: 02: ObjectiveMuhammad Nadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Week 4b, Geometric Construction (Polygons)Document4 pagesWeek 4b, Geometric Construction (Polygons)Muhammad Nadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Week 6 1 Angle and 3 Angle Projections: ST RDDocument4 pagesWeek 6 1 Angle and 3 Angle Projections: ST RDMuhammad Nadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Week 3B Scales: CE-112L: Engineering Drawing For Civil Engineers (Lab) F 2018Document3 pagesWeek 3B Scales: CE-112L: Engineering Drawing For Civil Engineers (Lab) F 2018Muhammad Nadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Week 2a, Instruments and Their UsesDocument7 pagesWeek 2a, Instruments and Their UsesMuhammad Nadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Layout of The ShopDocument1 pageLayout of The ShopMuhammad Nadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Layout of The ShopDocument1 pageLayout of The ShopMuhammad Nadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- VanBaars2017 Article NumericalCheckOfTheMeyerhofBeaDocument13 pagesVanBaars2017 Article NumericalCheckOfTheMeyerhofBeaMuhammad Nadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- 2 ND PartDocument101 pages2 ND Partvishnu m vNo ratings yet
- At The Pool TSM RedDocument4 pagesAt The Pool TSM RedSarah StevensNo ratings yet
- MFRD Assignment 2 Duc CuteDocument13 pagesMFRD Assignment 2 Duc CuteanfkrNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad (Assignment#2)Document12 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad (Assignment#2)ahsanNo ratings yet
- 22kV Heat Shrink MV Transition Cable Joints For 3C PILC To 3 Single Core XLPE Cables Nexans GTM3.1Document2 pages22kV Heat Shrink MV Transition Cable Joints For 3C PILC To 3 Single Core XLPE Cables Nexans GTM3.1desai_sachin07No ratings yet
- 12V 150ah (10hr) : Shenzhen Center Power Tech - Co.LtdDocument2 pages12V 150ah (10hr) : Shenzhen Center Power Tech - Co.Ltddarwin darioNo ratings yet
- CTG 4080 Gypsum Board Systems Manual EngDocument52 pagesCTG 4080 Gypsum Board Systems Manual EngElmer Soroan BarrerasNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Error and MistakeDocument2 pagesDifference Between Error and MistakeRamzi OmaneNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination and Restraint of CatDocument6 pagesPhysical Examination and Restraint of CatDominique Joy Gayares RasoNo ratings yet
- Labour Complaint FormDocument2 pagesLabour Complaint Formmozhi selvamNo ratings yet
- Two Flavor OscillationDocument36 pagesTwo Flavor OscillationSheheryarZaheerNo ratings yet
- A Collection of Quotes From: Patrick LencioniDocument38 pagesA Collection of Quotes From: Patrick LencioniIchsan RizallusaniNo ratings yet
- BED-2912-0000922351 Backend Development Vijay Vishvkarma: Phase I - Qualifier Round 1Document1 pageBED-2912-0000922351 Backend Development Vijay Vishvkarma: Phase I - Qualifier Round 1vijayNo ratings yet
- 65 Tips To Help You Find A Job Quicker: Mark PearceDocument20 pages65 Tips To Help You Find A Job Quicker: Mark PearceMubeen GhawteNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Stage 6 Year 12 Assessment Task and Marking Guidelines Titration Prac ExamDocument6 pagesChemistry Stage 6 Year 12 Assessment Task and Marking Guidelines Titration Prac ExamD Ray0% (1)
- Stormbrixx - Fisa TehnicaDocument108 pagesStormbrixx - Fisa Tehnicamureseanu_deliaNo ratings yet
- Audiolingual Method (Alm) : Elt MethodologyDocument11 pagesAudiolingual Method (Alm) : Elt Methodologyrm53No ratings yet
- Andy Bushak InterviewDocument7 pagesAndy Bushak InterviewLucky ChopraNo ratings yet
- 10 Smart Tips To Confidently Answer J-1 Visa Interview Questions - Global Internships 4Document1 page10 Smart Tips To Confidently Answer J-1 Visa Interview Questions - Global Internships 4Mariana San MartinNo ratings yet
- Task 1 Identify Typical Sources of Harmonics in A Power SystemDocument12 pagesTask 1 Identify Typical Sources of Harmonics in A Power SystemSean Galvin100% (1)
- Managing The Finance FunctionDocument12 pagesManaging The Finance FunctionDumplings DumborNo ratings yet
- Linear Search in JavaDocument2 pagesLinear Search in JavaWipuli Lochana DisanayakeNo ratings yet
- Gamification Toward A Definition PDFDocument4 pagesGamification Toward A Definition PDFFrancis Joe RodriguezNo ratings yet
- marketing strategy of fastrackDocument85 pagesmarketing strategy of fastrackAnam FatimaNo ratings yet
- Servo - Cookbook - MbedDocument6 pagesServo - Cookbook - MbedCảnh ManuNo ratings yet
- E-07e-AUF Magnetic Fields in CoilsDocument7 pagesE-07e-AUF Magnetic Fields in CoilsV. GrigorasNo ratings yet