Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kami Export - Rogdrena (2023) Troupe - Role-Of-Homologous-Structures
Uploaded by
Stacy TroupeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kami Export - Rogdrena (2023) Troupe - Role-Of-Homologous-Structures
Uploaded by
Stacy TroupeCopyright:
Available Formats
Tree of life: Anatomy, evolution, and the role of
homologous structures
By Heather Scoville, ThoughtCo., adapted by Newsela staff on 09.12.19
Word Count 725
Level 1130L
Image 1. A humpback whale jumps in the water. Whales have flippers, which contain homologous structures to human legs and arms. Photo
by: AlbertoLoyo/Getty Images
If you've ever noticed that a human hand and a monkey's paw look similar, then you already know
something about homologous structures. A homologous structure is an organ or body part in one
species that closely resembles an organ or body part in another species. Recognizing homologous
structures can help scientists compare different species. These structures are also helpful for
classifying and organizing the many different kinds of organisms on the planet.
Scientists say these similarities are evidence that life on Earth shares a common ancient ancestor,
and that many or all other species evolved from this common ancestor over time. Evidence of this
common ancestry can be seen in the structure and development of homologous structures, even if
the functions of these structures are different.
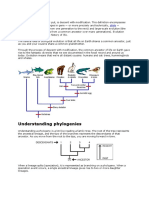
Examples Of Organisms
When organisms are closely related, their homologous structures tend to be quite similar. Many
mammals, for example, have similar limb structures. The flipper of a whale, the wing of a bat, and
This article is available at 5 reading levels at https://newsela.com.
the leg of a cat are all very similar to the human arm.
Each of these limb structures has a large upper "arm" bone, and in humans, this bone is known as
the humerus. The lower part of the limb is made of two bones, with a larger bone on one side (the
radius in humans) and a smaller bone on the other side (the ulna). These species also have a
collection of smaller bones in the "wrist" area, and these wrist bones are called carpal bones in
humans. The carpal bones lead into the "fingers" or phalanges.
Even though the limb bone structures may be very
similar in different species, the functions of these
structures vary widely. Limbs in vertebrates can be
used for flying, swimming or walking. Humans use
their arms for various tasks. These different functions
evolved through natural selection over millions of
years.
Homology And Evolution
Carolus Linnaeus was a Swedish botanist. In the
1700s, he created a system of taxonomy. In biology,
taxonomy is the science of naming and categorizing organisms. At that time, Linnaeus classified
species based on their looks, but as time passed and technology advanced, homologous structures
became more important in classifying species on the phylogenetic tree of life. This is an
evolutionary tree that shows relationships among different species.
Linnaeus' taxonomy system placed species into broad categories. The major categories, from
general to specific, are kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species. As technology
evolved, it allowed scientists to study life at the genetic level. Using genetic information, scientists
updated the categories to include the category of domains, and this is now the broadest category in
the taxonomic hierarchy. Organisms are grouped by domain according to structural differences in
ribosomal RNA, a protein found in cells.
Scientific Advances
Changes in technology have impacted the way that scientists categorize species. For example,
whales were once classified as fish because they live in water and have flippers. After it was
discovered that those flippers were homologous to human legs and arms, whales were moved to a
part of the tree more closely related to humans. Further genetic research has demonstrated that
whales may be more closely related to hippos.
Bats were originally thought to be closely related to birds and insects. Everything with wings was
put into the same branch of the phylogenetic tree. After more research and the discovery of
homologous structures, it became apparent that not all wings are the same. Even though all wings
are designed to help organisms get airborne, wings can be very different in their structures. While
the bat wing resembles the human arm in structure, the bird wing is very different, as is the insect
wing. Scientists realized that bats are more closely related to humans than to birds or insects. They
then placed bats on a corresponding branch of the tree of life.
Today, homologous structures are widely accepted as evidence of evolution. It wasn't until the
latter half of the 20th century that researchers were able to analyze and compare DNA between
This article is available at 5 reading levels at https://newsela.com.
species. Only then could researchers confirm the evolutionary relatedness of species with
homologous structures.
This article is available at 5 reading levels at https://newsela.com.
Quiz
1 Which option would Carolus Linnaeus MOST likely agree with? Which line from the article supports your answer?
(A) Bats and birds should be grouped together in the same category of organism. "At that time, Linnaeus
classified species based on their looks, but as time passed and technology advanced, homologous
structures became more important in classifying species on the phylogenetic tree of life."
(B) Whales and fish are in the same category because they share several homologous structures. "For
example, whales were once classified as fish because they live in water and have flippers."
(C) In order to correctly classify different species of organisms scientists must analyze their DNA. "It wasn't
until the latter half of the 20th century that researchers were able to analyze and compare DNA between
species."
(D) Most animals descended from a common set of organisms. "Evidence of this common ancestry can be
seen in the structure and development of homologous structures, even if the functions of these
structures are different."
2 According to the article, homologous structures are structurally similar but can be used to accomplish different goals.
Which paragraph BEST supports the idea outlined above?
(A) If you've ever noticed that a human hand and a monkey's paw look similar, then you already know
something about homologous structures. A homologous structure is an organ or body part in one
species that closely resembles an organ or body part in another species. Recognizing homologous
structures can help scientists compare different species. These structures are also helpful for classifying
and organizing the many different kinds of organisms on the planet.
(B) Even though the limb bone structures may be very similar in different species, the functions of these
structures vary widely. Limbs in vertebrates can be used for flying, swimming or walking. Humans use
their arms for various tasks. These different functions evolved through natural selection over millions of
years.
(C) Changes in technology have impacted the way that scientists categorize species. For example, whales
were once classified as fish because they live in water and have flippers. After it was discovered that
those flippers were homologous to human legs and arms, whales were moved to a part of the tree more
closely related to humans. Further genetic research has demonstrated that whales may be more closely
related to hippos.
(D) Bats were originally thought to be closely related to birds and insects. Everything with wings was put
into the same branch of the phylogenetic tree. After more research and the discovery of homologous
structures, it became apparent that not all wings are the same. Even though all wings are designed to
help organisms get airborne, wings can be very different in their structures. While the bat wing
resembles the human arm in structure, the bird wing is very different, as is the insect wing. Scientists
realized that bats are more closely related to humans than to birds or insects. They then placed bats on
a corresponding branch of the tree of life.
3 Read the selection from the section "Homology And Evolution."
Linnaeus' taxonomy system placed species into broad categories. The major categories, from
general to specific, are kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species.
The author uses the word "family" to mean?
(A) a parent-child relationship
(B) a collection of homologous structures
(C) a type of genetic material
(D) a group of different species
This article is available at 5 reading levels at https://newsela.com.
4 Read the following paragraph from the section “Homology And Evolution.”
Carolus Linnaeus was a Swedish botanist. In the 1700s, he created a system of taxonomy. In
biology, taxonomy is the science of naming and categorizing organisms. At that time, Linnaeus
classified species based on their looks, but as time passed and technology advanced,
homologous structures became more important in classifying species on the phylogenetic tree of
life. This is an evolutionary tree that shows relationships among different species.
Which of the following words from the paragraph provides context clues to the meaning of the word "taxonomy"?
(A) botanist
(B) biology
(C) categorizing
(D) structures
This article is available at 5 reading levels at https://newsela.com.
You might also like
- Evidences of Evolution - 210520 - 115553Document7 pagesEvidences of Evolution - 210520 - 115553Christine FayeNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument24 pagesBIOLOGYKyla Lizette MorilloNo ratings yet
- Understanding Phylogenies: The DefinitionDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Phylogenies: The DefinitionShikure ChanNo ratings yet
- CH5 - Lesson 16 The Process of Evolution PDFDocument5 pagesCH5 - Lesson 16 The Process of Evolution PDFgwynethNo ratings yet
- Comparative Anatomy, Embryology & Vestigial StructuresDocument11 pagesComparative Anatomy, Embryology & Vestigial StructuresDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Evolution For EvidenceDocument20 pagesEvolution For Evidenceivanjade627No ratings yet
- Biology II For Health Studies Majors: Written Assignment Unit: 01 Topic: Evidence of EvolutionDocument7 pagesBiology II For Health Studies Majors: Written Assignment Unit: 01 Topic: Evidence of EvolutionAhmed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Position Paper About Evolution 1Document3 pagesPosition Paper About Evolution 1Johnryl AraosNo ratings yet
- Phyl Ogen y of Phylum ChordataDocument10 pagesPhyl Ogen y of Phylum Chordatamirandajealyn28No ratings yet
- Bukti Evolusi, HomologiDocument11 pagesBukti Evolusi, HomologiAndi Citra PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Analogous StructuresDocument4 pagesAnalogous StructuresRense Jun PunsalanNo ratings yet
- Evidences of EvolutionDocument14 pagesEvidences of Evolutionmoonshyne100% (1)
- Cassification of Living ThingsDocument11 pagesCassification of Living ThingsFidia Diah AyuniNo ratings yet
- Evidences of Evolution ReviewerDocument4 pagesEvidences of Evolution ReviewerJax LetcherNo ratings yet
- Evolution Project 2Document5 pagesEvolution Project 2api-300733245No ratings yet
- Evidences of EvolutionDocument9 pagesEvidences of EvolutionNobisuke NobiNo ratings yet
- Evidences of EvolutionDocument5 pagesEvidences of EvolutionJax LetcherNo ratings yet
- A Drawing by Edward TysonDocument2 pagesA Drawing by Edward TysonCezaraTeodorescuNo ratings yet
- Science Notes Jagran JoshDocument191 pagesScience Notes Jagran Joshनितीन लाठकरNo ratings yet
- CBR Bahasa Inggis NurtriDocument4 pagesCBR Bahasa Inggis NurtriNurtri PasaribuNo ratings yet
- Iodiversity and VolutionDocument36 pagesIodiversity and VolutionMayden Grace Tumagan GayatgayNo ratings yet
- Evolutionary EvidenceDocument14 pagesEvolutionary EvidenceRomie GalloNo ratings yet
- The Theory of EvolutionDocument9 pagesThe Theory of EvolutionElana SokalNo ratings yet
- Darwin's Theory EssayDocument6 pagesDarwin's Theory EssayLogkeetha SarckunadasanNo ratings yet
- Handout For Week 4Document4 pagesHandout For Week 4Cheena Francesca LucianoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Relevance, Mechanisms, Evidence/Bases, and Theories of EvolutionDocument5 pagesWeek 1 - Relevance, Mechanisms, Evidence/Bases, and Theories of EvolutionDharyn Khai100% (2)
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT)Document13 pagesSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT)GraceEstoleCaloNo ratings yet
- Theory of Descent With ModificationDocument3 pagesTheory of Descent With ModificationAmitAgarwalNo ratings yet
- General ScienceDocument30 pagesGeneral SciencepapayaoffcNo ratings yet
- BIO - 10 - 45 - V2 - DM - Evidence of EvolutionDocument5 pagesBIO - 10 - 45 - V2 - DM - Evidence of EvolutionAlbina YulmukhametovaNo ratings yet
- EvolutionDocument4 pagesEvolutionChaudhry AzeemNo ratings yet
- DNA Supports Distinct Kinds: ExplanationDocument4 pagesDNA Supports Distinct Kinds: ExplanationMary Ann Leona SelgaNo ratings yet
- Group 4 ReportingDocument23 pagesGroup 4 ReportingNanami MumuzunoNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 A.1 Comparative Anatomy of The Domestic: ChickenDocument5 pagesActivity 3 A.1 Comparative Anatomy of The Domestic: ChickenArhlieJaneEvangelista0% (1)
- Science LayoutDocument2 pagesScience LayoutGillian OpolentisimaNo ratings yet
- Sample Academic Reading Sentence CompletionDocument3 pagesSample Academic Reading Sentence CompletioncovenantNo ratings yet
- Origin of Life On Earth. Getty/Oliver BurstonDocument15 pagesOrigin of Life On Earth. Getty/Oliver BurstonRaquel Elardo AlotaNo ratings yet
- General ScienceDocument32 pagesGeneral ScienceHaruka NanaseNo ratings yet
- 9-10 Cassification of Living ThingsDocument9 pages9-10 Cassification of Living ThingsDesi Aziya FitriNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Outline Allan Romero: I. Observations Provide Evidence For TheoriesDocument3 pages1.3 Outline Allan Romero: I. Observations Provide Evidence For TheoriesAllan RomeroNo ratings yet
- Classification of Living ThingsDocument3 pagesClassification of Living ThingsBolu AdediranNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9.1 Evolution and Its EvidenceDocument24 pagesLesson 9.1 Evolution and Its EvidenceJohn Cesar CastilloNo ratings yet
- Evolutionary TheoryDocument14 pagesEvolutionary Theoryapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Evidence For Evolution Factsheet v2Document5 pagesEvidence For Evolution Factsheet v2api-364379734No ratings yet
- Fossils and The Origin and Diversification of BirdsDocument1 pageFossils and The Origin and Diversification of BirdsNabashis MisraNo ratings yet
- Human Evolution and Ecology: Who Are We and Where Are We?Document12 pagesHuman Evolution and Ecology: Who Are We and Where Are We?rakhmatov UlanNo ratings yet
- Caminalcule Evolution LabDocument12 pagesCaminalcule Evolution LabJimeno100% (1)
- Front Page BiologyDocument5 pagesFront Page BiologyLucianne HerreraNo ratings yet
- Biological EvolutionDocument54 pagesBiological EvolutionMa. Krizia Tiny ParconNo ratings yet
- EVOLUTIONDocument15 pagesEVOLUTIONKiama GitahiNo ratings yet
- Evidences of Evolution Module 6-7Document47 pagesEvidences of Evolution Module 6-7GLAIZA CALVARIONo ratings yet
- IB Biology 5.1 OutlineDocument4 pagesIB Biology 5.1 OutlineAndres SaraviaNo ratings yet
- B 10 VRV 5164Document56 pagesB 10 VRV 5164Reaper-sanNo ratings yet
- Taxonomic Nomenclature2Document18 pagesTaxonomic Nomenclature2zendamariesabinayNo ratings yet
- Explain Darwin's Observations and InferencesDocument13 pagesExplain Darwin's Observations and InferencesLe Phuong LyNo ratings yet
- Week - Two - Ento - Docx Filename - UTF-8''Week Two EntoDocument5 pagesWeek - Two - Ento - Docx Filename - UTF-8''Week Two EntoKaydina GirNo ratings yet
- Evidence For Evolution: Key PointsDocument25 pagesEvidence For Evolution: Key PointsJennena Marie VeranoNo ratings yet
- B 10 VRV 5164Document55 pagesB 10 VRV 5164api-283593849No ratings yet
- Natural SelectionDocument81 pagesNatural Selectionpatricia piliNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF Campbell Biology 11th Edition by Lisa A Urry PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Campbell Biology 11th Edition by Lisa A Urry PDFinga.morley147100% (40)
- CladisticDocument27 pagesCladisticKylie MorganNo ratings yet
- PhylogeneticsDocument49 pagesPhylogeneticschristyNo ratings yet
- Reloj MolecularDocument8 pagesReloj MolecularfryddaproblesNo ratings yet
- Revision Geonoma Phytotaxa 2011Document271 pagesRevision Geonoma Phytotaxa 2011DaniPhytomaniacNo ratings yet
- 6.2 MEGA WorkshopDocument3 pages6.2 MEGA Workshopprogress dubeNo ratings yet
- EarthAndLifeScience (SHS) Q2 Mod29 TheProcessOfEvolution V1Document18 pagesEarthAndLifeScience (SHS) Q2 Mod29 TheProcessOfEvolution V1Emer Perez100% (7)
- Great English - Grammar Rules, Reference Lists and General Knowledge - Isabel UysDocument10 pagesGreat English - Grammar Rules, Reference Lists and General Knowledge - Isabel UysyoussefNo ratings yet
- Molecular Markers, Natural History and EvolutionDocument522 pagesMolecular Markers, Natural History and Evolutionorecabar50% (2)
- Wiley 1978 Evolutionary Species ConceptDocument11 pagesWiley 1978 Evolutionary Species ConceptTaylor UrieNo ratings yet
- Palaeontologia Electronica: Principles of Paleontology (Third Edition)Document3 pagesPalaeontologia Electronica: Principles of Paleontology (Third Edition)asad nadeemNo ratings yet
- Legume ClassificationDocument34 pagesLegume Classificationnicro1No ratings yet
- Fernandez Et Al, 2018-Phylogenomics, Diversification Dynamics, and Comparative Transcriptomics Across The SpiderDocument15 pagesFernandez Et Al, 2018-Phylogenomics, Diversification Dynamics, and Comparative Transcriptomics Across The Spiderfosudavid.jfNo ratings yet
- Constructing-a-PhylogenyDocument5 pagesConstructing-a-PhylogenyLuana Lima FreitasNo ratings yet
- Phylogenetic TreeDocument3 pagesPhylogenetic Treeapi-321706148No ratings yet
- General Biology 2: Investigative Files: Into The Depths of EvolutionDocument29 pagesGeneral Biology 2: Investigative Files: Into The Depths of EvolutionAndevie Balili IguanaNo ratings yet
- Cladistics PDFDocument4 pagesCladistics PDFmanoj_rkl_07100% (1)
- HIBBETT Et Al. - 2007 - A Higher-Level Phylogenetic Classification of The FungiDocument39 pagesHIBBETT Et Al. - 2007 - A Higher-Level Phylogenetic Classification of The FungiBianca SilvaNo ratings yet
- Lizards AnolesDocument528 pagesLizards AnolesDiego Juen100% (1)
- Current Perspectives On The Evolution of Birds PDFDocument8 pagesCurrent Perspectives On The Evolution of Birds PDFExcelNo ratings yet
- Cladogram DLPDocument3 pagesCladogram DLPNIDELYN PRETENo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Evolution and DiversityDocument11 pagesLab 2 Evolution and DiversityginaNo ratings yet
- The Origin and Early Evolution of EukaryotesDocument12 pagesThe Origin and Early Evolution of EukaryotesTomas PinedaNo ratings yet
- Evidence For Evolution: Key PointsDocument25 pagesEvidence For Evolution: Key PointsJennena Marie VeranoNo ratings yet
- download/computer Science PDFDocument20 pagesdownload/computer Science PDFSayan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 PhylogenyDocument36 pagesGen Bio 2 PhylogenyConrado Juisan CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Morphological Analysis Figure 1. Rooted Consensus Tree Obtained From Morphological Data of VerongidaDocument17 pagesMorphological Analysis Figure 1. Rooted Consensus Tree Obtained From Morphological Data of VerongidaBug AphidNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 8Document7 pagesLab Report 8Jhon Patrick DelmonteNo ratings yet
- Evolution 4Th Edition by Futuyma Douglas Full ChapterDocument41 pagesEvolution 4Th Edition by Futuyma Douglas Full Chapterrosa.green630100% (23)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseFrom EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (52)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (598)
- The Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (633)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainFrom EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (111)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (217)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (517)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- Minds Make Societies: How Cognition Explains the World Humans CreateFrom EverandMinds Make Societies: How Cognition Explains the World Humans CreateRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (24)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsFrom EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2083)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Lymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthFrom EverandLymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightFrom EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Remnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsFrom EverandRemnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)