Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ASD with Pleural Effusion and Ascites
Uploaded by
Hapsari Kartika DewiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ASD with Pleural Effusion and Ascites
Uploaded by
Hapsari Kartika DewiCopyright:
Available Formats
ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT WITH UNUSUAL
CLINICAL PRESENTATION: MASSIVE
PLEURAL EFFUSION AND ASCITES
Anindita Setyoningrum , Anggoro Budi Hartopo , Vita Yanti Anggraeni ,
1 1,2 1,2
Dyah Wulan Anggrahini2, Lucia Kris Dinarti 1,2
1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health and Nursing, Universitas Gadjah Mada
– Dr. Sardjito Hospital, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
2Department of Cardiology and Vascular Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health and Nursing, Universitas Gadjah Mada
– Dr. Sardjito Hospital, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Background
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is congenital heart disease which mostly found in adult patients with 10% incidence. ASD
causes left-to-right intracardiac shortcuts with right ventricular (RV) volume overload, increased pulmonary blood flow,
pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH), RV hypertrophy and right heart failure (RHF). We here report a case of ASD with
massive pleural effusion and ascites which were unusual clinical presentation.
Case Presentation
A 32 years old female presented to the emergency room with exertional dyspnea, ortopnea, paroxysmal
nocturnal dyspnea, abdominal distension and swollen legs. On physical examination, we found elevated
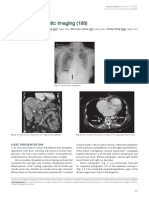
jugular venous pressure, cardiomegaly, pleural effusion, ascites and splenomegaly. Chest X-ray revealed
cardiomegaly and bilateral pleural effusion. The electrocardiogram showed right axis deviation and right
ventricle hypertrophy. No specific findings were found in investigations to unravel the cause of massive
pleural effusion and ascites. Transthoracic echocardiogram showed normal left ventricular function with
a left-to-right shunt secundum ASD and high probability pulmonary hypertension (PH). The right atrium
and ventricle were dilated with severe tricuspid regurgitation. The RV systolic pressure was 50.65
mmHg. The RV function was reduced (TAPSE was 11 mm). NTproBNP level was elevated, i.e. 19033.0
pg/mL. Intravenous diuretics and sildenafil were administered and resulted in gradual clinical Figure. Chest Radiographing Imaging of the
improvement. patient showing bilateral pleural effusion with
pneumonia
Discussion
Pleural effusion and ascites is an unusual presentation of ASD. Previous report showed ASD patient with pleural effusion and ascites
related to constrictive pericarditis. Right sided heart chamber overload and pulmonary over circulation can lead to sign and symptoms
of heart failure. Ultimately, ASD patients will suffer from RHF, with manifestation of ascites, pleural effusion and peripheral edema. The
PAH appears to be an aggravating factor. Treatment with diuretics and PAH-targeted therapy subsided pleural effusion and ascites,
supporting the underlying cause of PAH and RHF.
Conclusion
ASD with massive pleural effusion and ascites is rarely found. ASD contribute to development
of PAH and RHF, resulted in this unusual clinical presentation.
Keywords: ASD, ascites, massive pleural effusion, right ventricle dysfunction, right heart failure
You might also like
- SMJ-59-279Document5 pagesSMJ-59-279Faradiba MaricarNo ratings yet
- Abstract Book Lcu 6th 2023Document56 pagesAbstract Book Lcu 6th 2023Graham Allen ShowNo ratings yet
- RHC in PapvdDocument8 pagesRHC in PapvdkhairachungNo ratings yet
- A Case of Profound Hypothyroidism Presenting With Hypertensive Emergency and Large Amount of Pericardial EffusionDocument7 pagesA Case of Profound Hypothyroidism Presenting With Hypertensive Emergency and Large Amount of Pericardial EffusionShannya PuaNo ratings yet
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus Stenting For Palliation of Severe Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in ChildhoodDocument5 pagesPatent Ductus Arteriosus Stenting For Palliation of Severe Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in ChildhoodEffendi TanNo ratings yet
- EBSTEIN'S ANOMALY Dhini - Maju 17 Juli 2014Document29 pagesEBSTEIN'S ANOMALY Dhini - Maju 17 Juli 2014Azizi PranokoNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure in A ChildDocument8 pagesHeart Failure in A ChildChici FarlinaNo ratings yet
- Hipertensioni Arterial Sekondar AutosavedDocument80 pagesHipertensioni Arterial Sekondar AutosavedFlo FlaNo ratings yet
- Poster Presentation CCRA Malang 2014Document3 pagesPoster Presentation CCRA Malang 2014alfarobi yogiNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument12 pagesJurnalFKWNo ratings yet
- Best Management in Isolated Right Ventricular Hypoplasia With Septal Defects in AdultsDocument7 pagesBest Management in Isolated Right Ventricular Hypoplasia With Septal Defects in AdultsReinaldi octaNo ratings yet
- Aortic Dissection Misdiagnosed As A Hypertensive Crisis: A Case ReportDocument5 pagesAortic Dissection Misdiagnosed As A Hypertensive Crisis: A Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Lutembacher's Syndrome at KolonodaleDocument7 pagesLutembacher's Syndrome at KolonodaleWayan GunawanNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kasus-Acute Embolic Stroke As The Sole Presentation of Infective Endocarditis in Mitral Valve ProlapseDocument2 pagesLaporan Kasus-Acute Embolic Stroke As The Sole Presentation of Infective Endocarditis in Mitral Valve ProlapseSari Novianty SilitongaNo ratings yet
- Case Report - An Uncommon Association of Ebstein's Anomaly and Rheumatic Mitral StenosisDocument4 pagesCase Report - An Uncommon Association of Ebstein's Anomaly and Rheumatic Mitral StenosisRJMNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular DisordersDocument62 pagesCardio Vascular DisordersUday Kumar100% (1)
- Abstrak INAECHODocument21 pagesAbstrak INAECHOAgung Angga KesumaNo ratings yet
- Piis0167527314008699 PDFDocument4 pagesPiis0167527314008699 PDFwenyinriantoNo ratings yet
- Jurnal InfeksiDocument6 pagesJurnal InfeksiDevita BerlianaNo ratings yet
- 23 59 1 PBDocument6 pages23 59 1 PBrazgriz1412No ratings yet
- Acute Limb Ischemia Masquerading As Stroke: A Case ReportDocument7 pagesAcute Limb Ischemia Masquerading As Stroke: A Case ReporttsaniyaNo ratings yet
- Posters / International Journal of Cardiology 155S1 (2012) S129-S227Document1 pagePosters / International Journal of Cardiology 155S1 (2012) S129-S227Wati MehraNo ratings yet
- 08IMMN15Document18 pages08IMMN15methuselahchintalaNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Heart Disease With Complication of Atrial FibrillationDocument3 pagesRheumatic Heart Disease With Complication of Atrial FibrillationsamudraandiNo ratings yet
- Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome With Intact Atrial Septum - Case ReportDocument6 pagesHypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome With Intact Atrial Septum - Case ReportKarthic V.ManiNo ratings yet
- Asd + SaDocument4 pagesAsd + SaFitria YusriNo ratings yet
- Journal Case Report CDM-2-147Document3 pagesJournal Case Report CDM-2-147pierhot_11No ratings yet
- 45 1057Document5 pages45 1057Gabriela PinticanNo ratings yet
- Obesity in Patient with VSD and Pulmonary HypertensionDocument8 pagesObesity in Patient with VSD and Pulmonary HypertensionDr AnitaHsParewasiNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument12 pagesTetralogy of Fallotneetuthakur100% (4)
- Acute Myocarditis As A Complication of Acute Rheumatic Fever With Right Ventricle Thrombus in ChildrenDocument5 pagesAcute Myocarditis As A Complication of Acute Rheumatic Fever With Right Ventricle Thrombus in ChildrenFikrialmunawar FikrialmunawarNo ratings yet
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- EHB 2015 Paper 157Document4 pagesEHB 2015 Paper 157Cringuta ParaschivNo ratings yet
- Anaesthetic Management of A Patient With Ebsteins Anomaly Posted For Cerebral Abscess DrainageDocument5 pagesAnaesthetic Management of A Patient With Ebsteins Anomaly Posted For Cerebral Abscess DrainageIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Anterolateral Papillary Muscle Rupture As A Result of Single-Vessel Coronary Artery Disease Without Myocardial InfarctionDocument3 pagesAnterolateral Papillary Muscle Rupture As A Result of Single-Vessel Coronary Artery Disease Without Myocardial InfarctionDonatas AustysNo ratings yet
- Vol08 1 87-88strDocument2 pagesVol08 1 87-88strAry-Adhi PutrantoNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgery-2Document10 pagesMedical Surgery-2Wanjiku NderituNo ratings yet
- 556 M Deatials PDFDocument3 pages556 M Deatials PDFTinton PristiantoNo ratings yet
- Case Reports AbstractsDocument7 pagesCase Reports AbstractsNovie AstiniNo ratings yet
- Hypoplastic Right Heart Syndrome, Absent Pulmonary Valve, and Non-Compacted Left Ventricle in An AdultDocument4 pagesHypoplastic Right Heart Syndrome, Absent Pulmonary Valve, and Non-Compacted Left Ventricle in An AdultReinaldi octaNo ratings yet
- CardioNET 2022 Book of AbstractDocument16 pagesCardioNET 2022 Book of AbstractSTOCARE DATENo ratings yet
- Cha Pte R 1 1 Con Ge Nit Al Heart DiseasesDocument70 pagesCha Pte R 1 1 Con Ge Nit Al Heart DiseasessanjivdasNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Treatment of Adult Congenital Heart Disease Patients with ASDDocument17 pagesPerioperative Treatment of Adult Congenital Heart Disease Patients with ASDPutri SatrianyNo ratings yet
- Double-Outlet Left Ventricle and Vascular MalformationsDocument3 pagesDouble-Outlet Left Ventricle and Vascular MalformationsRaul UrietaNo ratings yet
- Preskas Hypoxic Spell Patofisiologi Dan ManajemenDocument22 pagesPreskas Hypoxic Spell Patofisiologi Dan Manajemensurya marthiasNo ratings yet
- Role of Echocardiography As Supporting Diagnostic Modality in Localized Stanford Type A Aortic DissectionDocument11 pagesRole of Echocardiography As Supporting Diagnostic Modality in Localized Stanford Type A Aortic DissectionNurcahyaKuswardhanaNo ratings yet
- Recurrent Pleural Effusion from Unknown CauseDocument3 pagesRecurrent Pleural Effusion from Unknown CauseJaya Semara PutraNo ratings yet
- CHD by GetasewDocument35 pagesCHD by Getasewshimeles teferaNo ratings yet
- General Anesthesia Technique in Tetralogy of Fallot Patient Undergo Tooth Extraction SurgeryDocument4 pagesGeneral Anesthesia Technique in Tetralogy of Fallot Patient Undergo Tooth Extraction SurgeryHarleen QuinzeelNo ratings yet
- Anatomopathological Session: A 20 Year-Old Man With Heart Failure Due To Restrictive CardiomyopathyDocument8 pagesAnatomopathological Session: A 20 Year-Old Man With Heart Failure Due To Restrictive CardiomyopathyGuilherme AméricoNo ratings yet
- MK Final PaperworkDocument15 pagesMK Final Paperworkapi-727427971No ratings yet
- Lecture 17a VHDDocument70 pagesLecture 17a VHDKishan ArrumugamNo ratings yet
- Case 5: Tutor GuideDocument18 pagesCase 5: Tutor GuidelubnaNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Scientific Research: General MedicineDocument4 pagesInternational Journal of Scientific Research: General MedicineTriple ANo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j CCL 2020 04 008Document12 pages10 1016@j CCL 2020 04 008Linda Silvana SariNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Diseases: TopicsDocument19 pagesCongenital Heart Diseases: TopicsMaheen SyedNo ratings yet
- medicina-58-00892Document8 pagesmedicina-58-00892Faradiba MaricarNo ratings yet
- Eisenmenger SyndromeDocument41 pagesEisenmenger SyndromeJennifer DixonNo ratings yet
- Hal 1-10Document3 pagesHal 1-10Hapsari Kartika DewiNo ratings yet
- First periodDocument11 pagesFirst periodHapsari Kartika DewiNo ratings yet
- Present AnDocument3 pagesPresent AnHapsari Kartika DewiNo ratings yet
- Naspub ArticleDocument7 pagesNaspub ArticleHapsari Kartika DewiNo ratings yet
- CDC HAI Prevention: Outbreaks, Costs, ResistanceDocument35 pagesCDC HAI Prevention: Outbreaks, Costs, ResistanceHapsari Kartika DewiNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Gastroenterology Fellowship Program HandbookDocument37 pagesPediatric Gastroenterology Fellowship Program HandbookAna-Mihaela BalanuțaNo ratings yet
- Piis0891524517301311 PDFDocument9 pagesPiis0891524517301311 PDFRegita Westri AprilaNo ratings yet
- Perdarahan Saluran CernaDocument46 pagesPerdarahan Saluran CernaHapsari Kartika DewiNo ratings yet
- HapsariKartikaDewi AKREDITASFKTPDocument1 pageHapsariKartikaDewi AKREDITASFKTPHapsari Kartika DewiNo ratings yet
- Tetanus: Maria Banica & Sophie NamDocument19 pagesTetanus: Maria Banica & Sophie NamSuwantin Indra SariNo ratings yet
- New Pe 2 Module DraftDocument29 pagesNew Pe 2 Module DraftSteffanie Michelle SabinoNo ratings yet
- K - 12 Heart As A Pump (Fisiologi)Document36 pagesK - 12 Heart As A Pump (Fisiologi)missirenaNo ratings yet
- FOUR CHAMBERS OF THE HEARTDocument7 pagesFOUR CHAMBERS OF THE HEARTJohn TecsonNo ratings yet
- Ms - CardiovascularDocument70 pagesMs - CardiovascularMark OngNo ratings yet
- B SC - Operation Theater TechnologyDocument61 pagesB SC - Operation Theater Technologyhamsalekha KarnaticNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE - LIGHT AND COLOURSDocument56 pagesSCIENCE - LIGHT AND COLOURSSoh Mei LingNo ratings yet
- Piri Pharm Tables Pharmacology Therapeutics SpringDocument110 pagesPiri Pharm Tables Pharmacology Therapeutics SpringNormala Macabuntal SaripadaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesNursing Care PlanGem Ma100% (7)
- แนวข้อสอบภาษาต่างประเทศ - ภาษาอังกฤษ อ่านง่ายและเข้าใจ xDocument30 pagesแนวข้อสอบภาษาต่างประเทศ - ภาษาอังกฤษ อ่านง่ายและเข้าใจ xโจโค โบะNo ratings yet
- Acs - Esc 2023 - BsquangDocument18 pagesAcs - Esc 2023 - BsquangHuy PhạmNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Update: Continuing Education ColumnDocument9 pagesCardiopulmonary Resuscitation Update: Continuing Education Columnkang soon cheolNo ratings yet
- BNB ListDocument73 pagesBNB ListbenNo ratings yet
- Mitral StenosisDocument17 pagesMitral StenosisMuhammad Alauddin Sarwar100% (8)
- Chapter 8 Transport in Mammals - Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesChapter 8 Transport in Mammals - Lecture Notesapi-3728508100% (2)
- Guidelines and Procedures of Phyisical Fitness TestDocument2 pagesGuidelines and Procedures of Phyisical Fitness TestMaurinne Angeline GuloyNo ratings yet
- CAD - Ischemic Heart Disease: AtherosclerosisDocument5 pagesCAD - Ischemic Heart Disease: Atherosclerosisbri ngNo ratings yet
- PONR - Comprehensive Nursing Health History and Physical ExaminationDocument21 pagesPONR - Comprehensive Nursing Health History and Physical ExaminationDRJC100% (1)
- Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial FlutterDocument4 pagesAtrial Fibrillation and Atrial FlutterROHITNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Blood - Body BitsDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Blood - Body BitsJohnny Miller60% (5)
- Post-CABG Care Plan and Assessment GuideDocument31 pagesPost-CABG Care Plan and Assessment GuideYeria Rayanti100% (1)
- Q 1Document33 pagesQ 1m1.nourianNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan HF FinalDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan HF FinalCristina L. JaysonNo ratings yet
- Physiology 102Document5 pagesPhysiology 102Javed AkhlaqNo ratings yet
- Science Class 8 Respiration and CirculationDocument9 pagesScience Class 8 Respiration and Circulationamnakazmi100% (1)
- Dyspnea, Orthopnea, and Paroxysmal Nocturnal DyspneaDocument4 pagesDyspnea, Orthopnea, and Paroxysmal Nocturnal DyspneaBukhari SiregarNo ratings yet
- BioK QQ 6.2 QPDocument2 pagesBioK QQ 6.2 QPesteban1013264503No ratings yet
- Benefits of Sports and Exercise for StudentsDocument55 pagesBenefits of Sports and Exercise for StudentsArpit PatelNo ratings yet
- MCQs on Chest Injuries and Thoracic SurgeryDocument35 pagesMCQs on Chest Injuries and Thoracic SurgeryFan Eli100% (15)
- Biology Class 9 Kerala Notes Part 1 (English Medium) by OdakkalDocument13 pagesBiology Class 9 Kerala Notes Part 1 (English Medium) by Odakkalmariyu palakkot tms100% (5)
- Daftar Pustaka KSMDocument4 pagesDaftar Pustaka KSMFajar YuniftiadiNo ratings yet