Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A4 Girls UKWHO 0-4Q
Uploaded by
mihaelamicu2001204Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A4 Girls UKWHO 0-4Q
Uploaded by
mihaelamicu2001204Copyright:
Available Formats
14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 50 52 12 13 14 15 16 17 19 20 21 22 23 25 26 27 28 29 31 32 33 34 35 37 38 39 40 Adult Height
Preterm 50cm
GIRLS 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
50cm
552cm 11/2
2
21/2 3 GIRLS 124cm Prediction
ft/in cm
Data Recording
Birth Measurement
49
0 –1 year Age in weeks/ months
49 50
99.6th
98th
Age in months/ years 1– 4 years 120
5.11 180
Recording Date
Weight
99.6th 91st 5.10
Birth 48 48 Head Circumference
98th 48 75th 116
head
Head Circumference 47 47 50th
● Measure length until age 2; measure
5.9
99.6th 175 Length/Height
39 91st 99.6
th
25th height after age 2. 5.8 Location
46 46 46 112 98th
38 75th 9th
● A child’s height is usually slightly less 98th Health worker name
45 45 than their length. 5.7 170
d
50th 2nd 91st
37 44 91st 108 Measurement 2
a
44 44 0.4th 5.6
Recording Date
25th
e
75th
36 75th Weight
43 43 104 5.5 165
9th 42
h t
50th
50th Head Circumference
35
h
42 2nd 42 5.4
th
.6
100 Length/Height
g
25th
99
40cm 25th
0.4th
i
34 41 41
Head Circumference (cm)
5.3 160 Location
th
e
th 9th
98
.6 9th Health worker name
40 99 40cm 96cm 96 5.2
h
33
st
th 2nd
91
98 2nd Measurement 3
32
39 5.1 155
s t Recording Date
th
91 92 92
75
0.4th
38 h 82cm 0.4th 5.0
t Weight
31 75
th
th
50
99.6th
37 t h 99.6 80 88 88 Head Circumference
h
50 4.11 150
t
30 98th
th
th 98th Length/Height
25
25
36
g
78
84cm Plot child’s
91st h
91st .6t Location
len
29 9t
h 84 99
35 height centile on
9th
75th 76 th Health worker name
2n
d 75th 9 8
the pink lines
28
d
50th t
34 th 74 91s
2n
4 50th
80 30kg above; the black Measurement 4
0.
h
25th 5 th
numbers show
th
t
27 7 Recording Date
33 25th 72
0.4
h
9th 50t 29 average female
g
76 t h
Weight
26 2nd 32 9th 70 25 adult height for
n
Gestation in weeks this centile; Head Circumference
0.4th 2nd 9th
31cm 68 72 28 80% of children
le
2nd
Length/Height
32 34 36 38 40 42 0.4th
66cm 66 0.4
th will be within Location
68 27 ±6 cm of this
Plotting preterm infants Health worker name
64 64 value.
Use the low birthweight Measurement 5
chart for infants less than 32 62 62 64 26
Recording Date
weeks gestation and any th
other infants requiring 60 .6 60 Weight
99 25
detailed assessment. th 60cm
58 98 58cm
Head Circumference
Use this section for infants st
91 Length/Height
of less than 37 weeks 56 5th 24kg 24
gestation. As with term 99.6th 7 h Location
th .6t
infants there may be some 98th 50 99
54 th 14kg Health worker name
weight loss in the early days. 91st 25 23 23
From 42 weeks, plot on the 75th 52 9t
h 13.5 Measurement 6
0–1 year chart with d Recording Date
gestational correction. 50th 2n 22 22
50 4t
h 13
25th 0. Weight
th
Gestational age 48 th 12.5 98 Head Circumference
9th 99.6 21 21
(7 weeks preterm)
2nd Length/Height
46 12
Actual age 0.4th
20 20 Location
44cm 11.5
Gestational correction 98th Health worker name
t
Plot actual age then draw a 11kg 11 91s
19 19 Measurement 7
line back the number of
weeks the infant was preterm 10.5 Some degree of weight 91st
10.5 Recording Date
and mark the spot with an loss is common after birth. 18 18 Weight
arrow; this is the gestationally 10 10 h
Calculating the percentage 75t Head Circumference
corrected centile. 75th
9.5 weight loss is a useful way 9.5 17 17
Length/Height
to identify babies who
t
Birth Weight 9 9 Location
need assessment.
h
5.5 50th 16 16
50th Health worker name
g
8.5 8.5
i t
25th Measurement 8
e
8 8 15 15
h
5 Recording Date
25th
g
7.5 9th 7.5
w
Weight
i
14 14
4.5
e
7 2nd 7 Head Circumference
h 9th
.6t
99 13 Length/Height
6.5 6.5 13
w
0.4th
h
.6t
4 Location
99
6 6 h 2nd
12 98t 12 Health worker name
st 8th
5.5
9
3.5 5.5 Measurement 9
t 0.4th
91s
91
11 Recording Date
Weight (kg)
5 5 11
th
75 Weight
6th
99.6th
3 4.5 th 4.5 75t
h
9t 25 50 75 91 98t 99.
50
© DH Copyright 2009
98th
10 10 Head Circumference
h
91st t h
4 25 4 50t
h Length/Height
2.5 75th
th th th st
h 9
3.5 9t 3.5 9 Location
50th
n d 25th
2 h
25th 4t Health worker name
2 3 0. 3 9th 8
9th 8 Measurement 10
2nd 2.5 2.5 2nd Recording Date
UK - WHO Chart 2009
1.5 0.4th 7 0.4t
h 7
h
d
2 2 Weight
2n Head Circumference
h 1.5
.4t 1.5 6 6
1 0 Age in months/ years Length/Height
1 Age in weeks/ months 1
Gestation in weeks Location
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 5kg 1
1 /2 2 2 /2 1
3 3 /2 5kg 1
0.5kg 0.5kg Health worker name
32 34 36 38 40 42 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 50 52 12 13 14 15 16 17 19 20 21 22 23 25 26 27 28 29 31 32 33 34 35 37 38 39 40 41 43 44 45 46 47 48
Data Recording (continued)
GIRLS UK–WHO Interpreting the chart
Measurement 11 Predicting adult height
Please place sticker (if available) otherwise write in space provided.
Recording Date Assessing weight loss after birth Parents like to know how tall their child will be as an adult. The
Weight Most babies lose some weight after birth but 80% will have child’s most recent height centile (aged 2– 4 years) gives a good
Name: ________________________________________ idea of this for healthy children. Plot this centile on the adult
Head Circumference regained this by 2 weeks of age. Fewer than 5% of babies lose
Length/Height
Location
Growth Chart 0– 4 years NHS / CHI No: more than 10% of their weight at any stage; only 1 in 50 are
10% or more lighter than birth weight at 2 weeks.
height predictor to the right of the height chart to find the
average adult height for children on this centile. Four out of five
Health worker name
children will have adult heights that are within 6cm above or
Royal College of Hospital No: Percentage weight loss can be calculated as follows: below this value.
Measurement 12 Paediatrics and
Recording Date Child Health Weight loss = current weight − birth weight
Weight
Date of Birth: Percentage weight loss = Weight loss ✕ 100% Weight–height to BMI conversion chart
Birth weight BMI indicates how heavy a child is relative to his or her height
Head Circumference
and is the simplest measure of thinness and fatness from the age
Length/Height Who should use this chart? When to measure length or height For example, a child born at 3.500kg who drops to 3.150kg at of 2, when height can be measured fairly accurately. This chart4
Location Length or height should be measured whenever there are 5 days has lost 350g or 10%; in a baby born at 3.000kg, a provides an approximate BMI centile, accurate to a quarter of a
Anyone who measures a child, plots or interprets charts
Health worker name any worries about a child’s weight gain, growth or general 300g loss is 10%. centile space. For greater accuracy, calculate BMI and plot
should be suitably trained, or be supervised by someone
Measurement 13 health. directly on a BMI centile chart.
qualified to do so. For further information and training
Recording Date Careful clinical assessment and evaluation of feeding technique
materials see www.growthcharts.rcpch.ac.uk weight in kg
Weight Plotting measurements is indicated when weight loss exceeds 10% or recovery of birth BMI =
Head Circumference For babies born at term (37 weeks or later), plot each weight is slow. BMI = (height in m)2
Length/Height
A growth chart for all children measurement on the relevant chart by drawing a small dot
The UK–WHO growth chart combines World Health 99.6
Location where a vertical line through the child’s age crosses a What do the centiles mean? 98
Organization (WHO) standards with UK preterm and birth
horizontal line through the measured value. The lettering on These charts indicate a child’s size compared with children of the 91
BMI Centile
Health worker name
data. The chart from 2 weeks to 4 years of age is based on 99.6 e)
Measurement 14 the WHO growth standard, derived from measurements of
the charts (‘weight’, ‘length’ etc.) sits on the 50th centile, same age and maturity who have shown optimum growth. The
(Obes 75
98 t
providing orientation for ease of plotting. chart also shows how quickly a child is growing. The centile lines igh 50
we eight
Recording Date healthy, non-deprived, breastfed children of mothers who did
on the chart show the expected range of weights and heights (or 91 er 25
Weight Centile
v w
y O Over
Weight not smoke.1 The chart for birth measurements (32–42 weeks 9
Head Circumference gestation) is based on British children measured around Plot birth weight (and, if measured, length and head lengths); each describes the number of children expected to be 75 Ver 2
Length/Height 1990.2 The charts depict a healthy pattern of growth that is circumference) at age 0 on the 0–1 year chart. The coloured below that line (e.g. 50% below 50th, 91% below the 91st). 50 0.4
Location desirable for all children, whether breast fed or formula fed, arrows at age 0 represent UK birth weight data and show Children come in all shapes and sizes, but 99 out of 100 children
25
Health worker name and of whatever ethnic origin.3 the child’s birth centile. who are growing optimally will be between the two outer lines
(0.4th and 99.6th centiles); half will lie between the 25th and 9
Measurement 15
Weighing and measuring Weight gain in the early days varies a lot from baby to baby, 75th centile lines. 2
Recording Date
Weight Weight: use only class III clinical electronic scales in so there are no lines on the chart between 0 and 2 weeks. 0.4
metric setting. For children up to 2 years, remove all However, by 2 weeks of age most babies will be on a centile Being very small or very big can sometimes be associated with
Head Circumference
clothes and nappy; children older than 2 years should close to their birth centile. underlying illness. There is no single threshold below which a
Length/Height
wear minimal clothing only. Always remove shoes. child’s weight or height is definitely abnormal, but only 4 per 0.4 2 9 25 50 75 91 98 99.6
Location
For preterm infants a separate low birth weight chart is 1000 children who are growing optimally are below the 0.4th Height Centile
Health worker name Length: (before 2 years
available for infants of less than 32 weeks gestation and any centile, so these children should be assessed at some point to
Measurement 16 of age): proper exclude any problems. Those above the 99.6th centile for
Recording Date
other infant requiring detailed assessment. For healthy Date:
equipment is essential height are almost always healthy. Also calculate BMI if weight
infants born from 32 weeks and before 37 weeks, plot all
Weight (length board or mat). and height centiles appear very different.
Head Circumference Measurers should be measurements in the preterm section (to the left of the main Age:
Length/Height trained. The child’s shoes 0 –1 year chart) until 42 weeks gestation, then plot on the
0 –1 year chart using gestational correction, as shown below. What is a normal rate of weight gain and growth? BMI Centile:
Location and nappy should be removed. Babies do not all grow at the same rate, so a baby’s weight often
Health worker name does not follow a particular centile line, especially in the first
Height: (from 2 years): use a rigid The preterm section can also be used to assess the relative Instructions for use
Measurement 17 rule with T piece, or stadiometer; the year. Weight is most likely to track within one centile space (the 1. Read off the weight and height centiles from the growth
size of infants at the margin of ‘term’ (e.g. 37 weeks
Recording Date child’s shoes should be removed. gap between two centile lines, see diagram). In infancy, acute
gestation), but these measurements should also be plotted chart.
Weight illness can lead to sudden weight loss and a weight centile fall
Head circumference: use a at age 0 on the 0 –1 year chart. 2. Plot the weight centile (left axis) against the height centile
Head Circumference but on recovery the child’s weight usually returns to its normal
narrow plastic or paper tape to (bottom axis) on the chart above.
Length/Height centile within 2–3 weeks. However, a sustained drop through
measure where the head Gestational correction 3. If between centiles, read across in this position.
Location two or more weight centile spaces is unusual (fewer than 2% of
circumference is greatest. Any Plot measurements at the child’s actual age and then draw a
Health worker name infants) and should be carefully assessed by the primary care 4. Read off the corresponding BMI centile from the slanting
hat or bonnet should be line back the number of weeks the infant was preterm. Mark
Measurement 18 team, including measuring length/height. lines.
removed. the spot with an arrow (see diagram): this is the child’s
Recording Date
gestationally corrected centile. Gestational correction should 5. Record the centile with the date and child’s age in the data
Weight Because it is difficult to measure length and height accurately in
continue until at least 1 year of age. box.
Head Circumference pre-school children, successive measurements commonly show
Length/Height
Centile terminology wide variation. If there are worries about growth, it is useful to Interpretation
Location If the point is within 1/4 of a space of measure on a few occasions over time; most healthy children will In a child over 2 years of age, the BMI centile is a better indicator
Health worker name the line they are on the centile: e.g. 91st. show a stable average position over time. of overweight or underweight than the weight centile; a child
Measurement 19 whose weight is average for their height will have a BMI
If not they should be described as Head circumference centiles usually track within a range of one between the 25th and 75th centiles, whatever their height
Recording Date When to weigh being between the two centiles:
Weight centile space. After the first few weeks a drop or rise through centile. BMI above the 91st centile suggests that the child is
Babies should be weighed in the first week as part of the e.g. 75th–91st.
two or more centile spaces is unusual (fewer than 1% of infants) overweight; a child above the 98th centile is very overweight
Head Circumference assessment of feeding and thereafter as needed. Recovery of
A centile space is the distance between and should be carefully assessed. (clinically obese). BMI below the 2nd centile is unusual and may
Length/Height birthweight indicates that feeding is effective and that the
two of the centile lines, or equivalent reflect undernutrition.
Location child is well. Once feeding is established, babies should
distance if midway between centiles. Why do the length/height centiles change at 2 years?
Health worker name usually be weighed at around 8, 12 and 16 weeks and 1 year References
at the time of routine immunisations. If there is concern, The growth standards show length data up to 2 years of age, 1. www.who.int/childgrowth/en
Measurement 20
weigh more often; however, weights measured too close and height from age 2 onwards. When a child is measured 2. Cole TJ, Freeman JV, Preece MA. British 1990 growth reference centiles for
Recording Date Plotting for preterm infants
standing up, the spine is squashed a little, so their height is weight, height, body mass index and head circumference fitted by maximum
Weight together are often misleading, so babies should be weighed (less than 37 weeks gestation): penalized likelihood. Stat Med 1998;17:407-29.
no more than once a month up to 6 months of age, once Gestational age Draw a line back the number of slightly less than their length; the centile lines shift down slightly
Head Circumference 3. www.sacn.gov.uk/reports_position_statements/index.html
every 2 months from 6 to 12 months of age, and once every (7 weeks preterm) weeks preterm and mark spot with at age 2 to allow for this. It is important that this difference does 4. Cole TJ. A chart to link child centiles of body mass index, weight and height.
Length/Height arrow.
3 months over the age of 1 year. However, most children do Actual age not worry parents; what matters is whether the child continues Eur J Clin Nutr 2002;56:1194-9.
Location
not need to be weighed this often. to follow the same centile after the transition.
Health worker name © DH Copyright 2009
You might also like
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 5: Language ArtsFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 5: Language ArtsNo ratings yet
- Boys 0-4 Years Growth ChartDocument2 pagesBoys 0-4 Years Growth ChartshahidkalimNo ratings yet
- Theme From The HBO Series GAME OF THRONES Violin 1: Arr. ItescoDocument1 pageTheme From The HBO Series GAME OF THRONES Violin 1: Arr. ItescoMicael Silva AraújoNo ratings yet
- Closer 2022-09-16 - ViolaDocument2 pagesCloser 2022-09-16 - Violanikita nikitaNo ratings yet
- Activity Center Front Elevation: Esj and Sons Construction and Construction Supply, IncDocument1 pageActivity Center Front Elevation: Esj and Sons Construction and Construction Supply, IncGerard Paul CusiNo ratings yet
- Hayabusa Colored Wiring DiagramDocument1 pageHayabusa Colored Wiring DiagramEder NH PereiraNo ratings yet
- Dec 2022Document1 pageDec 2022Create UsernaNo ratings yet
- Dec 2022Document1 pageDec 2022Create UsernaNo ratings yet
- Activity Center Rear Elevation: Esj and Sons Construction and Construction Supply, IncDocument1 pageActivity Center Rear Elevation: Esj and Sons Construction and Construction Supply, IncGerard Paul CusiNo ratings yet
- Harness Main Tripac Evolution: A REV List of MaterialDocument2 pagesHarness Main Tripac Evolution: A REV List of MaterialBroks ArriagaNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Cable /MM 6 CoreDocument1 pageFiber Optic Cable /MM 6 CoreMohamed RizkNo ratings yet
- Game of Thrones Theme ViolinDocument1 pageGame of Thrones Theme ViolinJulio Duarte BatistaNo ratings yet
- The Second Waltz Dimitri Shotakovich-Baritone (Treble Clef)Document2 pagesThe Second Waltz Dimitri Shotakovich-Baritone (Treble Clef)Lucas Passig HorstmannNo ratings yet
- Backbone Rack To Rack: Podium Hotel ApartmentDocument4 pagesBackbone Rack To Rack: Podium Hotel Apartmenti safrianNo ratings yet
- LoveOverGold PianoDocument2 pagesLoveOverGold PianoJY DupuyNo ratings yet
- Mida Akpe Na Mawu: Kenn KafuiDocument1 pageMida Akpe Na Mawu: Kenn KafuiKwasi Bempong50% (2)
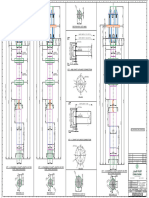
- Station - Qatar National Library Under Platform Level Ventilation Sad Layout SCALE: 1:100Document1 pageStation - Qatar National Library Under Platform Level Ventilation Sad Layout SCALE: 1:100ershadabsaifiNo ratings yet
- Nevando Está (2022) Violin IIDocument1 pageNevando Está (2022) Violin IIROVER DANIEL TAPIA VELASQUEZNo ratings yet
- DS450 2009 Wiring DiagramDocument1 pageDS450 2009 Wiring Diagrambobby brownNo ratings yet
- O LeãozinhoDocument1 pageO LeãozinhoARILTON JUNIORNo ratings yet
- Inicio de Tramo: RecreacionDocument1 pageInicio de Tramo: RecreacionJhelson JesusNo ratings yet
- Inicio de Tramo: RecreacionDocument1 pageInicio de Tramo: RecreacionJhelson JesusNo ratings yet
- Fuerzas Diagonales PDFDocument1 pageFuerzas Diagonales PDFEdwin EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Grande É o Senhor - Clarinete em BBDocument1 pageGrande É o Senhor - Clarinete em BBAlves Esdras EmanuelNo ratings yet
- Hauter Carpenter SFR Lot 2 Prelims 2-23-21Document5 pagesHauter Carpenter SFR Lot 2 Prelims 2-23-21Jan CarpenterNo ratings yet
- Updated (12!01!24) Timetable Even Semester 2023-24Document1 pageUpdated (12!01!24) Timetable Even Semester 2023-24Lokesh Kumar MeenaNo ratings yet
- Cultivo - Papa: Plano Clave de Las Áreas AfectadasDocument1 pageCultivo - Papa: Plano Clave de Las Áreas AfectadasJhelson JesusNo ratings yet
- Cultivo - Papa: Plano Clave de Las Áreas AfectadasDocument1 pageCultivo - Papa: Plano Clave de Las Áreas AfectadasJhelson JesusNo ratings yet
- REVITDocument13 pagesREVITOumayma TouatyNo ratings yet
- FRP-6 (SI NO.01) : PetroservDocument1 pageFRP-6 (SI NO.01) : PetroservDHANESH KcNo ratings yet
- Unit 6210Document1 pageUnit 6210Khairul IdhamNo ratings yet
- CS 4944 - JCT A B & C - CH5 SHAFT EX. DRAWING - R00 (Sheet 1of6)Document1 pageCS 4944 - JCT A B & C - CH5 SHAFT EX. DRAWING - R00 (Sheet 1of6)محمد طولانNo ratings yet
- Plano Clave de Las Áreas Afectadas: Esquema de LocalizaciónDocument1 pagePlano Clave de Las Áreas Afectadas: Esquema de LocalizaciónJhelson JesusNo ratings yet
- Plano Clave de Las Áreas Afectadas: Esquema de LocalizaciónDocument1 pagePlano Clave de Las Áreas Afectadas: Esquema de LocalizaciónJhelson JesusNo ratings yet
- Mayot Punya GambarrrrDocument1 pageMayot Punya GambarrrrMohamad IsaNo ratings yet
- MODELO Projeto DadosDocument1 pageMODELO Projeto DadosWilson PicininNo ratings yet
- Bom DetailsDocument1 pageBom DetailsAzad QureshiNo ratings yet
- Trumpet Staccato EtudeDocument1 pageTrumpet Staccato EtudeGeorge BabarakosNo ratings yet
- Aj 245 STDocument1 pageAj 245 STHernan B.No ratings yet
- Site Plan: Kec - Labakkang Des - Kassi LoeDocument1 pageSite Plan: Kec - Labakkang Des - Kassi LoeChaerul AnwarNo ratings yet
- Site Plan: Kec - Labakkang Des - Kassi LoeDocument1 pageSite Plan: Kec - Labakkang Des - Kassi LoeChaerul AnwarNo ratings yet
- SAN LORENZO Marcha - GuitarDocument2 pagesSAN LORENZO Marcha - GuitarAlfredo PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Third Floor DuctingDocument1 pageThird Floor DuctingENGINEERING- Carlson Innotech CorporationNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Ides of March TromboneDocument1 pageVehicle Ides of March TrombonePim van HartenNo ratings yet
- Em-2006-Mep-Eom-Mt-Sd-Plb-109-1 (Rev-1)Document1 pageEm-2006-Mep-Eom-Mt-Sd-Plb-109-1 (Rev-1)shreeNo ratings yet
- RCC Cladding Wall Detail-D CH-100+460-100+520: LWL Bed LevelDocument1 pageRCC Cladding Wall Detail-D CH-100+460-100+520: LWL Bed Levelrao shoaibNo ratings yet
- 14''/21'' Color TV Basic Schematic Diagram: CRT BoardDocument1 page14''/21'' Color TV Basic Schematic Diagram: CRT BoardSalim BlognetNo ratings yet
- Nassa Taipei Spinners Machine Layout Plan 31.08.21-ModelDocument1 pageNassa Taipei Spinners Machine Layout Plan 31.08.21-Modelfakir mohammadNo ratings yet
- Shalow Lady Gaga Guit 2Document4 pagesShalow Lady Gaga Guit 2ITALO MOLINARINo ratings yet
- Shema Yisrael (Violino)Document1 pageShema Yisrael (Violino)Breno Tomazinho JesusNo ratings yet
- Bleak Allure Josiah AustinDocument6 pagesBleak Allure Josiah AustinYana PolyanskayaNo ratings yet
- S-K5 Proposed LocationDocument1 pageS-K5 Proposed LocationRadius KhorNo ratings yet
- Bem Mais Que Tudo - Violoncello - MusDocument1 pageBem Mais Que Tudo - Violoncello - MusGiovani BalbiNo ratings yet
- Vendor:: Issued For Detailed Engineering Phase English Language Shall GovernDocument1 pageVendor:: Issued For Detailed Engineering Phase English Language Shall GovernGustavo ChoqueNo ratings yet
- Flauta I.encDocument1 pageFlauta I.encMaranatha CentroNo ratings yet
- Aj 245 LTDocument1 pageAj 245 LTHernan B.No ratings yet
- Castlevania II Simons Quest - Bloody TearsDocument2 pagesCastlevania II Simons Quest - Bloody TearsJuninho ViolaoNo ratings yet
- NPCE285Document1 pageNPCE285atefdinNo ratings yet
- Carta A Mi Madre (Lettre A Ma Mere) : Performer: Richard Clayderman by Paul de SenevilleDocument4 pagesCarta A Mi Madre (Lettre A Ma Mere) : Performer: Richard Clayderman by Paul de SenevilleMercedes VignaNo ratings yet
- Models of Maternal HealthDocument12 pagesModels of Maternal HealthLindsey Brock MoralesNo ratings yet
- Obs. InvestigationsDocument36 pagesObs. InvestigationsSameena Rose AjmeriNo ratings yet
- Preterm Postterm Prom1Document35 pagesPreterm Postterm Prom1api-3856051No ratings yet
- Pengaruh Prenatal Care Yoga Terhadap Pengurangan Keluhan Ketidaknyamanan Ibu Hamil Trimester Iii Di Puskesmas Putri Ayukota JambiDocument6 pagesPengaruh Prenatal Care Yoga Terhadap Pengurangan Keluhan Ketidaknyamanan Ibu Hamil Trimester Iii Di Puskesmas Putri Ayukota JambiWahyu ItuwsiTriNo ratings yet
- Impact of Preeclampsia On Birth Outcomes: Xu Xiong, MD, DRPHDocument15 pagesImpact of Preeclampsia On Birth Outcomes: Xu Xiong, MD, DRPHMichelle FortesNo ratings yet
- Resume Priyanka JoshiDocument7 pagesResume Priyanka JoshipriyankaNo ratings yet
- 2018-BJOG An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyDocument40 pages2018-BJOG An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyBagusHibridaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Sains Kebidanan: Hubungan Antara Status Gizi Ibu Hamil Dengan Berat Badan Bayi LahirDocument7 pagesJurnal Sains Kebidanan: Hubungan Antara Status Gizi Ibu Hamil Dengan Berat Badan Bayi LahirPriya Kepakisan KepakisanNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Historical Review and Contemporary Perspectives in MidwiferyDocument9 pagesSeminar On Historical Review and Contemporary Perspectives in MidwiferyHima AbhilashNo ratings yet
- Examination of Newborn A Practical Guide PDFDocument2 pagesExamination of Newborn A Practical Guide PDFNatalieNo ratings yet
- Prepregnancy Counseling NoprintDocument11 pagesPrepregnancy Counseling NoprintDo le QuangNo ratings yet
- Perimortem SCDocument4 pagesPerimortem SCyuni.kartika.ndoen92No ratings yet
- Shoulder DystociaDocument3 pagesShoulder Dystociakarl de guzmanNo ratings yet
- Changing Trends in Cesarean DeliveryDocument7 pagesChanging Trends in Cesarean DeliveryEditor_IAIMNo ratings yet
- Multiple Pregnancy NOR Poster PDFDocument1 pageMultiple Pregnancy NOR Poster PDFbigbossNo ratings yet
- Abnormal PregnancyDocument179 pagesAbnormal PregnancyMilkii Du NikusNo ratings yet
- Robson CriteriaDocument42 pagesRobson CriteriaNiteshNo ratings yet
- Artikel Jurnal ObgynDocument4 pagesArtikel Jurnal ObgynSherlyNo ratings yet
- Syekh Yusuf Hospital, Clinical Conference Friday, July 14th, 2023 (Period July 9th-July 12th, 2023) - 3Document10 pagesSyekh Yusuf Hospital, Clinical Conference Friday, July 14th, 2023 (Period July 9th-July 12th, 2023) - 3ahmed onterioNo ratings yet
- Kardiotokografija - Njeni Dosezi I Pretkazljivost: Cardiotocography - Its Achievements and PredictabilityDocument11 pagesKardiotokografija - Njeni Dosezi I Pretkazljivost: Cardiotocography - Its Achievements and Predictabilitylidija_milosevicNo ratings yet
- Maternal MortalityDocument27 pagesMaternal Mortalitydocsaurabh777No ratings yet
- Abnormal LaborDocument114 pagesAbnormal LaborMohammad AlrefaiNo ratings yet
- Cervical Stitch Give Birth Kelompok 2Document78 pagesCervical Stitch Give Birth Kelompok 2Larose Rossyta SariNo ratings yet
- The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine: To Cite This ArticleDocument10 pagesThe Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine: To Cite This ArticleFrancesca Doreen VegaNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Fetal DeathDocument2 pagesCertificate of Fetal Deathelle totNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa MarginalDocument50 pagesPlacenta Previa MarginalMedy WedhanggaNo ratings yet
- Factors Contributing To Perineal Tears Among Mothers During LabourDelivery in Kibuku Health Centre IV Kibuku DistrictDocument11 pagesFactors Contributing To Perineal Tears Among Mothers During LabourDelivery in Kibuku Health Centre IV Kibuku DistrictKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- Forceps Delivery and Vaccum ExtractionDocument84 pagesForceps Delivery and Vaccum ExtractionushaNo ratings yet
- International Obstetric and Gynecology Conference 2019 ScheduleDocument6 pagesInternational Obstetric and Gynecology Conference 2019 ScheduleAndianto IndrawanNo ratings yet
- Ajog MFMDocument29 pagesAjog MFMCristhian Ore HurtadoNo ratings yet