Professional Documents
Culture Documents
I and Avf: Impulses May Establish A Ventricular Rhythm, or Even Ventricular Tachycardia
Uploaded by
mickey0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageOriginal Title
rates3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageI and Avf: Impulses May Establish A Ventricular Rhythm, or Even Ventricular Tachycardia
Uploaded by
mickeyCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
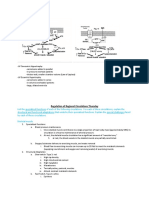
Axis: I and avF
o 1 and avF + = normal axis
o RAD: 1 (-) and avF (+)
RBBB
RVH
o LAD: 1 (-) and avF (+/-)
If avF (-) check if lead 2
If II is positive, normal axis.
If II is negative, left axis deviation is present
Intervals
o PR Intervals: 120-200 (< 1 big box)
PR prolongation (>200ms):
Fixed PR >200: 1st degree AV block
Progressively prolonged PR: 2nd degree Mobitz Type 1
Progressively prolonged PR until QRS is dropped = 2nd degree Mobitz Type 2
o Every 3rd or 4th P wave = 3:1 or 4:1
Shorter PR: re-entry tract (<120ms)
Atrial impulse gets to ventricle faster via accessory pathway
Delta waves = Wolf Parkinson White
o Slurred QRS upstroke
o QRS Interval: < 120 ms (< 3 small boxes)
Narrow
Wide: > 120ms = Bundle Branch Block
PVC, Ventricular rhythm, ventricular ectopy, vtach and pacemaker with
ventricular stimulation:
o Spontaneous action potentials discharged within the ventricles may
depolarize the ventricles. The cell/structure which discharges the action
potential is referred to as an ectopic focus. Such a focus may fire single or
multiple impulses (either consecutively or intermittently). A single
impulse gives rise to a premature ventricular beat, whereas multiple
impulses may establish a ventricular rhythm, or even ventricular
tachycardia.
External (artificial) pacemakers: inserted in the R ventricular apex
o Wide QRS + vertical tics near QRS
You might also like
- Lecture Objectives and Outlines-5Document9 pagesLecture Objectives and Outlines-5mickeyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Objectives and Outlines-7Document9 pagesLecture Objectives and Outlines-7mickeyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Objectives and Outlines-3Document9 pagesLecture Objectives and Outlines-3mickeyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Objectives and Outlines-4Document9 pagesLecture Objectives and Outlines-4mickeyNo ratings yet
- Cerner Basic Competencies 08-2019Document195 pagesCerner Basic Competencies 08-2019mickeyNo ratings yet
- 1 OutlineDocument5 pages1 OutlinemickeyNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal O The Esophagus O The Stomach O The Small Intestine O The Large Intestine The Liver The Gallbladder The Pancreas Diabetes The KidneyDocument53 pagesGastrointestinal O The Esophagus O The Stomach O The Small Intestine O The Large Intestine The Liver The Gallbladder The Pancreas Diabetes The KidneymickeyNo ratings yet
- Physical Exam Vital SignsDocument4 pagesPhysical Exam Vital SignsmickeyNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)