Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Casein
Uploaded by
Vedant PradhanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Casein
Uploaded by
Vedant PradhanCopyright:
Available Formats
Casein
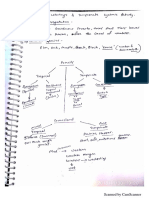
Goat milk or bovine is the major source of casein occurring in 24-29 g/l of the material. It
consists of 4 components- [1]
1. Alpha s1 casein (38%)
2. Beta casein (36%)
3. Alpha s2 casein (10%)
4. Kappa casein (13%)
Alpha s1 consists of a net charge of -21.9 at a pI of 4.94, consisting of 8 residues of
phosphorylated serine,25 glutamine residues and 17 proline residues but no cysteine
residue. It is sensitive to calcium ion, indicating that it gets precipitated in low ion
concentration.
Beta casein consisting of a polar N-terminal is of amphipathic protein type, having a large
hydrophobic part. As the temperature is dropped to 4 degree centigrade, its solubility
increases but it is also calcium sensitive like Alpha s1.
Alpha s2 casein having a net charge of -13.8 at a pI of 5.37, is also calcium ion sensitive
having two regions of high charge density, which makes it the most hydrophilic from the
other components.
Kappa casein is not calcium sensitive, located outside of casein micelle, often called hairy
layer due to this and is amphipathic in nature, having a polar side which interacts with the
polar solvents. [2,3]
Reference
1. Audic JL , Chaufer B , Daufin G (2003) Non-food applications of milk components and dairy co-
products: A review . Lair 83 : 417 – 438
2. Swaisgood HE (1993) Review and update of casein chemistry . J Dairy Sci 76 : 3054 –3061
3. Swaisgood HE (1996) Characteristics of milk . In: Fennema O (ed) Food chemistry . Marcel Dekker ,
New York, NY , p 1067
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Summary Sheet - Helpful For Retention For Corporate GovernanceDocument16 pagesSummary Sheet - Helpful For Retention For Corporate GovernanceVedant PradhanNo ratings yet
- Keywords: Edible Coatings and Films, Herbal Films, Shelf Life, Food Preservation, NovelDocument30 pagesKeywords: Edible Coatings and Films, Herbal Films, Shelf Life, Food Preservation, NovelVedant PradhanNo ratings yet
- Herbal Edible FilmsDocument8 pagesHerbal Edible FilmsVedant PradhanNo ratings yet
- Scanned by CamscannerDocument6 pagesScanned by CamscannerVedant PradhanNo ratings yet
- Scanned by CamscannerDocument4 pagesScanned by CamscannerVedant PradhanNo ratings yet
- Ethics PathakDocument67 pagesEthics PathakVedant PradhanNo ratings yet
- Eco. Jayant PDFDocument79 pagesEco. Jayant PDFVedant PradhanNo ratings yet
- BiomesDocument10 pagesBiomesVedant PradhanNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)