Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Labini Dienizs Day 4
Uploaded by
Dienizs Labini Tadena0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesThe nursing care plan addresses a patient at risk for infection due to inadequate primary defenses. Over 24 hours, the goal is for the patient to be able to identify interventions to prevent infection spread and demonstrate techniques to promote a safe environment. Over 12 hours, the goal is for the patient to maintain a patent airway, expectorate sputum without assistance, and participate in treatment regimens. The plan involves isolating the patient, monitoring for symptoms, and administering medications to clear airways and prevent infection.
Original Description:
Original Title
LABINI DIENIZS DAY 4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe nursing care plan addresses a patient at risk for infection due to inadequate primary defenses. Over 24 hours, the goal is for the patient to be able to identify interventions to prevent infection spread and demonstrate techniques to promote a safe environment. Over 12 hours, the goal is for the patient to maintain a patent airway, expectorate sputum without assistance, and participate in treatment regimens. The plan involves isolating the patient, monitoring for symptoms, and administering medications to clear airways and prevent infection.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesLabini Dienizs Day 4
Uploaded by
Dienizs Labini TadenaThe nursing care plan addresses a patient at risk for infection due to inadequate primary defenses. Over 24 hours, the goal is for the patient to be able to identify interventions to prevent infection spread and demonstrate techniques to promote a safe environment. Over 12 hours, the goal is for the patient to maintain a patent airway, expectorate sputum without assistance, and participate in treatment regimens. The plan involves isolating the patient, monitoring for symptoms, and administering medications to clear airways and prevent infection.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
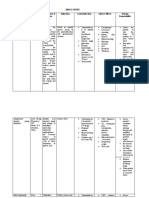
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective: Risk for After 24 hours, the patient will be Independent: Independent: After 24 hours, the patient will be
“Nadlaw ko infection r/t able to; able to;
toybagik nga inadequate 1. Maintain patient 3. Most hospitalized patient is
kimmutong nak ti primary Identify interventions and healthcare in a compromise immune Identify interventions
permi.” defenses. to prevent/reduce personnel state and at a higher risk of to prevent/reduce
risk of spread of isolations exposure to infectious risk of spread of
Objective: infection. precautions. disease. infection.
Weight 2. 4.
Identify other at Those exposed may require
loss of Demonstrate risks, such as a course of drug therapy to Demonstrate
about 10 techniques/initiate household prevent development of techniques/initiate
kg lifestyle changes to members and infection. lifestyle changes to
Fatigue promote safe friends. 5. May help patient promote safe
Productive environment. 3. Review necessity understand need for environment.
Cough of infection protecting others while
control acknowledging patient’s GOAL WAS PARTIALLY
measures. Put sense of isolation and MET.
in temporary social stigma associated
respiratory with communicable
isolation if diseases.
indicated. 6. Febrile reactions are
4. Monitor indicators of presence of
temperature as infection.
indicated. 7. Monitors adverse effects of
5. Liver function drug therapy
studies: including hepatitis.
AST/ALT. Dependent:
1. Initial therapy of
Dependent: uncomplicated pulmonary
disease usually includes
four drugs, e.g., four
1. Administer anti-
primary drugs or
infective agents.
combination of primary
2. Primary Drugs:
and secondary drugs.
Rifampicin,
Ethambutol,
Pyrazinamide,
Isoniazid,
Streptomycin
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
Objective Data: Ineffective After 12 hours, the patient will be Independent. Independent: After 12 hours, the patient will be
Productive airway able to; able to;
Cough clearance r/t Maintain patent airway. 1. Note the ability to 1. Expectoration may be Maintain patent airway.
infection as Expectorate sputum expectorate mucus difficult when secretions Expectorate sputum
evidenced by without assistance. and cough are thick, cloudy, without assistance.
productive Demonstrate behaviors effectively. sometimes bloody because Demonstrate behaviors
cough to improve or maintain Document the of infection. to improve or maintain
airway clearance. amount of sputum 2. Positioning may help lung airway clearance.
Participate in treatment and character. expansion and decreases Participate in treatment
regimen. 2. Place patient in a respiratory effort. regimen.
semi-fowlers 3. High fluid intake may help
position. Assist to thin secretions, making GOAL WAS MET.
client with them to expectorate.
coughing and
breathing exercise.
3. Maintain fluid
intake of at least Dependent:
2.5 liters unless
contraindicated. 1. Prevents drying
mucous membranes and helps
Dependent: thin secretions.
2. Bronchodilators
may help to improve oxygen
1. Humidify inspired
delivery and corticosteroids
oxygen.
may be useful in the presence
2. Administer
of extensive involvement with
medications:
profound hypoxemia.
Bronchodilators
and
Corticosteroids.
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Republic of The PhilippinesDocument12 pagesRepublic of The PhilippinesDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning: MedicationsDocument3 pagesDischarge Planning: MedicationsDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario Rotation 2Document3 pagesCase Scenario Rotation 2Dienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Poor Water Supply and SanitationDocument1 pagePoor Water Supply and SanitationDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- DS 4 To 6Document8 pagesDS 4 To 6Dienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Labini, Dienizs Act.1 CHNDocument4 pagesLabini, Dienizs Act.1 CHNDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Labini, Dienizs Bsn-3EDocument10 pagesDrug Study: Labini, Dienizs Bsn-3EDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Dienizs Labini - NCM 117 Skills Activity #1Document3 pagesDienizs Labini - NCM 117 Skills Activity #1Dienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Labini, Dienizs Bsn-3E: Incomplete Immunization Criteria Score Computation Answer JustificationDocument6 pagesLabini, Dienizs Bsn-3E: Incomplete Immunization Criteria Score Computation Answer JustificationDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Labini, Dienizs Bsn-3e Module 4 ActivtyDocument3 pagesLabini, Dienizs Bsn-3e Module 4 ActivtyDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Rhu Act. 2Document2 pagesRhu Act. 2Dienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanDienizs Labini Tadena100% (1)
- Kardex: GCS: 12-13/15 (M:5, V:4-5, E:3)Document11 pagesKardex: GCS: 12-13/15 (M:5, V:4-5, E:3)Dienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- MVH Ward Case ScenarioDocument3 pagesMVH Ward Case ScenarioDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario For ADHDDocument2 pagesCase Scenario For ADHDDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Do You Love MeDocument3 pagesDo You Love MeDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Dienizs Labini BSN-3E Brain Cancer Activities: B. Glioblastoma MultiformeDocument11 pagesDienizs Labini BSN-3E Brain Cancer Activities: B. Glioblastoma MultiformeDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Dienizs Labini BSN-3E Brain Cancer Activities: B. Glioblastoma MultiformeDocument11 pagesDienizs Labini BSN-3E Brain Cancer Activities: B. Glioblastoma MultiformeDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- D123 DRQDocument1 pageD123 DRQDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Face Sheet: Diabetes Millitus T2Document3 pagesClinical Face Sheet: Diabetes Millitus T2Dienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Artery Blockage May BeDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Artery Blockage May BeDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- University of Northern PhilippinesDocument15 pagesUniversity of Northern PhilippinesDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- U S. Medical Eligibility Criteria For Contraceptive Use, 2010Document77 pagesU S. Medical Eligibility Criteria For Contraceptive Use, 2010gerte_yuewNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Immunity: Yanne Pradwi EfendiDocument25 pagesAdaptive Immunity: Yanne Pradwi EfendiMelissa Indah SariNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On MalariaDocument10 pagesA Case Study On MalariaAnant KumarNo ratings yet
- MSDSDocument4 pagesMSDSkomite k3rsNo ratings yet
- Medtronic Earnings Presentation FY16Q4 FINALDocument21 pagesMedtronic Earnings Presentation FY16Q4 FINALmedtechyNo ratings yet
- Selective Awareness TherapyDocument10 pagesSelective Awareness TherapyHashem Al AttasNo ratings yet
- 1n2 OrganicSD-drshakyaDocument26 pages1n2 OrganicSD-drshakyaUMESH KANDELNo ratings yet
- Anaemia in Dogs and Cats (Part 2) : Continuing EducationDocument6 pagesAnaemia in Dogs and Cats (Part 2) : Continuing EducationAchmad NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Surveilans Terpadu Puskesmas: Umur (Tahun) 0-7hr 8-28hr 1 1-4 L P L P L P L PDocument3 pagesSurveilans Terpadu Puskesmas: Umur (Tahun) 0-7hr 8-28hr 1 1-4 L P L P L P L PkusNo ratings yet
- Surgery Songbook CompressedDocument69 pagesSurgery Songbook CompressedBrandon HayashiNo ratings yet
- Sush Unity Corrected EMERGENCY1700Document76 pagesSush Unity Corrected EMERGENCY1700Dr-Jahanzaib GondalNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan (3) Child Health NursingDocument5 pagesUnit Plan (3) Child Health Nursinggill priyaNo ratings yet
- Care of Older Adults (Prelims)Document12 pagesCare of Older Adults (Prelims)Ax’l SisterNo ratings yet
- Rules and Guidelines For Mortality and Morbidity CodingDocument5 pagesRules and Guidelines For Mortality and Morbidity Codingzulfikar100% (2)
- Health Talk TopicsDocument3 pagesHealth Talk Topicsvarshasharma0562% (13)
- Ludwig Heinrich Bojanus (1776-1827) On Gall's Craniognomic System, Zoology - UnlockedDocument20 pagesLudwig Heinrich Bojanus (1776-1827) On Gall's Craniognomic System, Zoology - UnlockedJaime JaimexNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio: Choose The Best Answer. What Do You Do?Document4 pagesEjercicio: Choose The Best Answer. What Do You Do?LenNo ratings yet
- Methodology and Project Design 4Document4 pagesMethodology and Project Design 4api-706947027No ratings yet
- Quantum Techniques Client ManualDocument42 pagesQuantum Techniques Client ManualVeres Beatrix100% (4)
- CHAMPP Part 1 20130104 NewDocument240 pagesCHAMPP Part 1 20130104 NewMarcu QuerubinNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Public Assessment Report For Pediatric StudiesDocument17 pagesMefenamic Acid Public Assessment Report For Pediatric StudiesNyoman SuryadinataNo ratings yet
- Bate's Guide To Physical examination+MCQsDocument4 pagesBate's Guide To Physical examination+MCQsRaden Adjeng PalupiNo ratings yet
- Kansas College Immunization WaiverDocument1 pageKansas College Immunization WaiverDonnaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaDocument30 pagesCongenital Adrenal HyperplasiaIrene Jordan100% (1)
- Midwifery KitDocument3 pagesMidwifery KitRitzel CreusNo ratings yet
- PathologyDocument31 pagesPathologyStudy Usmle100% (1)
- CDHDocument47 pagesCDHSameeta PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Pharyngitis: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Pharyngitis: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- A Clinical Success in The Management of Kotha (Digital Gangrene) by Leech Therapyandpanchtiktaghritaguggulu - A Single Case StudyDocument5 pagesA Clinical Success in The Management of Kotha (Digital Gangrene) by Leech Therapyandpanchtiktaghritaguggulu - A Single Case StudyIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Sleep Physiology and Disorders in Aging and DementiaDocument17 pagesSleep Physiology and Disorders in Aging and DementiaJúlio EmanoelNo ratings yet