Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kidneys
Uploaded by
Memory MahwendaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kidneys
Uploaded by
Memory MahwendaCopyright:
Available Formats
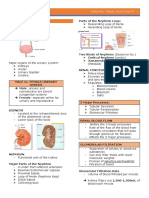
KIDNEYS
Nephron
Functional unit of the kidneys
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
- Depends on blood coming in
- Force of filtration depends on
1. Difference in diameter of afferent and efferent capillaries (afferent is thicker than
efferent) – increase in pressure as glomerulus capillaries become narrower
2. Knotting of glomerulus – increases pressure
- Molecules up to 70kDa can pass through endothelial cells of glomerulus (podocytes)
- Glomerulonephritis - inflammation of glomerulus
- Glomerulonephropathy – no inflammation
1. These two can widen the gap between endothelial cells – proteins, mainly albumin can
escape proteinuria
2. Triad of glomerulonephropathy
- Cholesterol increase in blood
- Proteinuria
- Hypoalbuminemia
3. Tests
- Protein in urine – proteinuria (albumin in particular) - exceeds threshold of
proximal tubule
- Urea in urine/urea in blood x creatinine in blood/creatinine in urine
- Fractional excretion rate (FER)
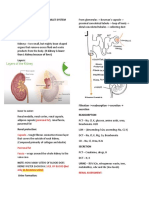
Azotemia
Used by clinical pathologists but the clinicians see a syndrome so use the term uraemia
Increased creatinine in blood
Look at the concentration of creatinine in kidneys and compare to ref values (unchanged is pre-
renal so dehydration)
Whole nephron theorem
Damaged area means whole nephron does work (i.e. bowmans capsule doesn’t work so nephron doesn’t)
- Remember no regeneration but the other nephrons compensate through hypertrophy – become
larger
Can start snowball effect
Phosphorus can accumulate in longer standing conditions which also means calcium and eventually EPO
Acidosis can persist from losing other elements
Acute renal failure
Chronic renal failure
Progressive
Dilute urine
Polydipsia
Increased creatinine
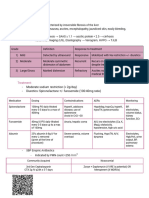
Primary renal function tests
Urea and creatinine in blood
Urine specific gravity (measure of diluteness of urine)
Ideally urine SG must be over SG 24 hours
Results not standardised in dogs and cats but can be used
PCV, phosphorus, fractional excretion of the variety of components
Pre renal – increase in everything
Post renal – increase urea and no marked creatinine increase, increased potassium
You might also like
- Genito UrinarysystemDocument7 pagesGenito Urinarysystemshenric16No ratings yet
- AsphyxiaDocument48 pagesAsphyxiapavi7muruganathanNo ratings yet
- Kidney Function and DiseasesDocument70 pagesKidney Function and DiseasesGovind SharmaNo ratings yet
- Renal Function Test Amcj 8Document42 pagesRenal Function Test Amcj 8Md. Saifur Rahman SunnyNo ratings yet
- Clinical Biochemistry Lab 3 PDFDocument7 pagesClinical Biochemistry Lab 3 PDFNael NomanNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Urinary System General IntroductionDocument63 pagesDisorders of The Urinary System General IntroductionsanjivdasNo ratings yet
- Organ Funt PDFDocument32 pagesOrgan Funt PDFs.k jamanNo ratings yet
- L2 - Disorders of The Kidney and Urinary TractDocument35 pagesL2 - Disorders of The Kidney and Urinary TractAhmad SobihNo ratings yet
- Kidney Function Tests 2Document30 pagesKidney Function Tests 2kamalNo ratings yet
- 2014 Curs Nefrologie-De Prezentat 4-Ian 2014Document291 pages2014 Curs Nefrologie-De Prezentat 4-Ian 2014Violeta Malina Bîrsan Hodivoianu100% (1)
- Nephrotic Syndrome: BY Dr. Clive Bowman: Dip. Rad Mbbs M.Med (Paediatrics)Document55 pagesNephrotic Syndrome: BY Dr. Clive Bowman: Dip. Rad Mbbs M.Med (Paediatrics)Pavi MuruganathanNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome: DR Putra Hendra SPPD UnibaDocument46 pagesNephrotic Syndrome: DR Putra Hendra SPPD UnibafifahNo ratings yet
- RFT - Theory Notes-: (Important For Practical Also)Document13 pagesRFT - Theory Notes-: (Important For Practical Also)ammuNo ratings yet
- AUBF Chapter 3-ReviewerDocument4 pagesAUBF Chapter 3-ReviewerSalvani, Shane JudeNo ratings yet
- CC2 PREMILS To FINALS MERGED PDFDocument65 pagesCC2 PREMILS To FINALS MERGED PDFAlecx LipatanNo ratings yet
- فسلجة ٣Document18 pagesفسلجة ٣ManWol JangNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome and Acute Nephritic Syndrome: CBD (4) Supervised by Presented byDocument58 pagesNephrotic Syndrome and Acute Nephritic Syndrome: CBD (4) Supervised by Presented byMaryam BajNo ratings yet
- RENALDocument10 pagesRENALTeriese BautistaNo ratings yet
- t2 Kidney DiseaseDocument52 pagest2 Kidney Diseasewany.fyza54No ratings yet
- Urinary System Diseases: PathophysiologyDocument31 pagesUrinary System Diseases: PathophysiologyMuhammad Wishal KhanNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology: DR Ihsan R Ebrahim/Physiology /college of PharmacyDocument10 pagesRenal Physiology: DR Ihsan R Ebrahim/Physiology /college of Pharmacyعلي صفاء عبد الزهرهNo ratings yet
- Clinicopath Correlation of Renal DiseasesDocument7 pagesClinicopath Correlation of Renal DiseasesDeshan AdikariNo ratings yet
- Pathophys UrinaryDocument31 pagesPathophys UrinaryDr Anais AsimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 ReviewDocument21 pagesChapter 16 Reviewjenn1722No ratings yet
- 6 BodyDocument110 pages6 Bodysinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Urinary System Diseases: PathophysiologyDocument31 pagesUrinary System Diseases: Pathophysiologyai nisa hasnasariNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis SBPDocument9 pagesCirrhosis SBPapi-690342013No ratings yet
- Lab 8 Anatomy Physiology of Urinary System - TaggedDocument27 pagesLab 8 Anatomy Physiology of Urinary System - TaggedSaraNo ratings yet
- 27glomerular and Tubular DysfunctionsDocument34 pages27glomerular and Tubular Dysfunctionsashok_solanki_23No ratings yet
- (Study Group) Diabetic Nephropathy, Hypertensive NephropathyDocument7 pages(Study Group) Diabetic Nephropathy, Hypertensive NephropathyZarif IzzuddinNo ratings yet
- Cardinal Manifestations of Renal Disease: ModeratorDocument82 pagesCardinal Manifestations of Renal Disease: ModeratorHaileprince MekonnenNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 - LIVER FUNCTION TESTSDocument93 pagesUnit 8 - LIVER FUNCTION TESTSRezan ThapaNo ratings yet
- Altered Elimination Multi System ProblemDocument9 pagesAltered Elimination Multi System ProblemCG Patron BamboNo ratings yet
- Stagii - Nefrologie Stagiu UnuDocument7 pagesStagii - Nefrologie Stagiu UnuIoana DiaconuNo ratings yet
- 6 - Clinical 2Document46 pages6 - Clinical 2levan guluaNo ratings yet
- Protein Uri ADocument2 pagesProtein Uri AAmelia PebriantiNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Genito-Urinary SystemDocument61 pagesCare of Clients With Genito-Urinary SystemAngelica Kaye BuanNo ratings yet
- Renal PhysiologyDocument129 pagesRenal PhysiologynehaNo ratings yet
- Clin PathInterns Review 2019Document33 pagesClin PathInterns Review 2019AmaetenNo ratings yet
- Urine Dipstick Testing + Common Renal Problem 2012Document52 pagesUrine Dipstick Testing + Common Renal Problem 2012Ainul ArinaNo ratings yet
- Renal SystemDocument29 pagesRenal Systemjsreyes.402No ratings yet
- Nephrology - Proteinuria - SOAP Note - Manish Suneja PDFDocument4 pagesNephrology - Proteinuria - SOAP Note - Manish Suneja PDFΝίκος ΣυρίγοςNo ratings yet
- Angeles University Foundation Angeles City Case AnalysisDocument41 pagesAngeles University Foundation Angeles City Case Analysischocoholic potchi100% (1)
- Lecture (5) Kidney Function Tests Part IDocument33 pagesLecture (5) Kidney Function Tests Part IAmine GobranNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis Group 1Document12 pagesCase Analysis Group 1mark_partolanNo ratings yet
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument17 pagesAcute GlomerulonephritisBayanSecond WardNo ratings yet
- CKD and Male ReproductionDocument55 pagesCKD and Male ReproductionMitchelle SaurambaNo ratings yet
- PhysiologyDocument85 pagesPhysiologyDyah WahliaNo ratings yet
- 10 Kidneys 2017 PDFDocument42 pages10 Kidneys 2017 PDFSajid AhmadNo ratings yet
- Approach: A. How The Kidney Handle The Proteins?Document9 pagesApproach: A. How The Kidney Handle The Proteins?Rashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Urine Formation-SGD 3Document9 pagesUrine Formation-SGD 3LA Yogore JermeoNo ratings yet
- Exam 6 NotesDocument17 pagesExam 6 NotesWhitney WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Our Lady of Fatima University - Valenzuela Campus College of NursingDocument29 pagesOur Lady of Fatima University - Valenzuela Campus College of NursingMary Shine GonidaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry Lec 5Document70 pagesClinical Chemistry Lec 5salamshakir56No ratings yet
- Routine Examination of Urine AND It'S InterpretationDocument64 pagesRoutine Examination of Urine AND It'S InterpretationmeherulafmcNo ratings yet
- Physiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)From EverandPhysiology for General Surgical Sciences Examination (GSSE)S. Ali MirjaliliNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Pyruvatkinase-Mangel für Patienten und Angehörige: Eine seltene genetische Erkrankung der roten Blutkörperchen Informationen + Mitreden-Können = Bestmöglicher VerlaufFrom EverandFast Facts: Pyruvatkinase-Mangel für Patienten und Angehörige: Eine seltene genetische Erkrankung der roten Blutkörperchen Informationen + Mitreden-Können = Bestmöglicher VerlaufNo ratings yet
- Ascites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAscites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Conn Syndrome, (Hyper-Aldosteronism) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandConn Syndrome, (Hyper-Aldosteronism) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Hematuria, (Blood in Urine) A Simple Guide to The Condition, Related Diseases And Use in Diagnosis of DiseasesFrom EverandHematuria, (Blood in Urine) A Simple Guide to The Condition, Related Diseases And Use in Diagnosis of DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Hepatic Encephalopathy: Causes, Tests, and Treatment OptionsFrom EverandHepatic Encephalopathy: Causes, Tests, and Treatment OptionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Nerve Physiology 1617 PracticalDocument26 pagesNerve Physiology 1617 PracticalMemory MahwendaNo ratings yet
- Nerve PhysiologyDocument75 pagesNerve PhysiologyMemory MahwendaNo ratings yet
- Result Reporting: Subjectively Graded As Few, Moderate, ManyDocument5 pagesResult Reporting: Subjectively Graded As Few, Moderate, ManyMemory MahwendaNo ratings yet
- Zinc Sulphate Turbidity (ZST) Test: Clinical Pathology Practicals Test For Adequate Ig IntakeDocument3 pagesZinc Sulphate Turbidity (ZST) Test: Clinical Pathology Practicals Test For Adequate Ig IntakeMemory MahwendaNo ratings yet
- Body FluidsDocument6 pagesBody FluidsMemory MahwendaNo ratings yet
- Urea/ Ammonia Tests: Primary Liver Function TestsDocument6 pagesUrea/ Ammonia Tests: Primary Liver Function TestsMemory MahwendaNo ratings yet
- Pancreas Function: Acute PancreatitisDocument2 pagesPancreas Function: Acute PancreatitisMemory MahwendaNo ratings yet
- Cytology: Differentiating Hypoplasia From Neoplasia Characteristic of NeoplasiaDocument1 pageCytology: Differentiating Hypoplasia From Neoplasia Characteristic of NeoplasiaMemory MahwendaNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument18 pagesHematologyMemory MahwendaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis of Urinary IncontinenceDocument18 pagesClinical Presentation and Diagnosis of Urinary IncontinenceMartín SánchezNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument59 pagesUrinary SystemSaajid AmraNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestations and Diagnostic Evaluation of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia - UpToDateDocument11 pagesClinical Manifestations and Diagnostic Evaluation of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia - UpToDateFeer VillarrealNo ratings yet
- Notes On UtiDocument15 pagesNotes On UtiSaleh Mohammad ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Family Planning - 3Document8 pagesFamily Planning - 3Khibul LimNo ratings yet
- Urology DNB Old QuestionsDocument8 pagesUrology DNB Old QuestionssjulurisNo ratings yet
- 5 Abnormalities of The PenisDocument11 pages5 Abnormalities of The PenisNICOLLE ENAMORADO ENCISONo ratings yet
- Case Study of UTI - Urinary Tract InfectionDocument9 pagesCase Study of UTI - Urinary Tract InfectionArvin Ian Penaflor75% (8)
- Acute PyelonephritisDocument16 pagesAcute PyelonephritisDilshan WickramanayakaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26Document7 pagesChapter 26jess waldenNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction WJECDocument12 pagesHuman Reproduction WJECTharanga HewabuhageNo ratings yet
- Examination Male Genitalia855090520Document4 pagesExamination Male Genitalia855090520HardiTariqHammaNo ratings yet
- Urinary System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesUrinary System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBDNo ratings yet
- The COMPLETE BOOK of PENIS - The Effective Guide To Penis From Size To Function and Everything in BetweenDocument70 pagesThe COMPLETE BOOK of PENIS - The Effective Guide To Penis From Size To Function and Everything in BetweenRyan GiocondoNo ratings yet
- Polycystic KidneyDocument10 pagesPolycystic Kidneymanish dafdaNo ratings yet
- Phim en IdDocument4 pagesPhim en IdAbel Nabila AstriNo ratings yet
- Female GenitaliaDocument96 pagesFemale GenitaliaJopaii TanakaNo ratings yet
- HymenectomyDocument5 pagesHymenectomyShamaine limNo ratings yet
- Project 1 PDFDocument2 pagesProject 1 PDFUshuaia Chely FilomenoNo ratings yet
- External Genital of Female and Internal Sex OrgnsDocument6 pagesExternal Genital of Female and Internal Sex OrgnsChristian BeninNo ratings yet
- Finals 4. Urinary System - Lecture Session 4Document49 pagesFinals 4. Urinary System - Lecture Session 4Agatha joy MadrazoNo ratings yet
- VBA-21-0960J-4-ARE Urinary PDFDocument4 pagesVBA-21-0960J-4-ARE Urinary PDFCombat CraigNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument3 pagesDaftar PustakamemeeeyyyNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Urinary SystemDocument4 pagesCase Study - Urinary SystemVanessa PalomaNo ratings yet
- CystolithiasisDocument7 pagesCystolithiasisRaul Nocete100% (1)
- Full Paper Trapped Penis Maria YustinaDocument6 pagesFull Paper Trapped Penis Maria YustinamariaNo ratings yet
- The Organs of The Male Reproductive System Are Specialized For The Following FunctionsDocument3 pagesThe Organs of The Male Reproductive System Are Specialized For The Following FunctionsGabrielaNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument31 pagesUrinary SystemFlyEngineer100% (2)
- SBI4U Unit 4 Homeostasis Excretory SystemDocument27 pagesSBI4U Unit 4 Homeostasis Excretory System전채연No ratings yet