100% found this document useful (1 vote)
364 views4 pagesCNC Router Calculations
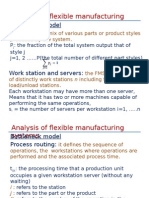
The document provides initial data and calculations to determine the acceleration rates and linear forces for a CNC router. It calculates values like acceleration time, axis masses, gear ratios, and assumes a cutting force. Using principles of work, energy, and linear motion equations, it then calculates the rapid movement forces and peak cutting forces for each axis. It determines the maximum linear force for each axis and uses formulas to calculate the peak motor torque requirements for the Z, Y, and X axes.
Uploaded by
morteza nourooziCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
364 views4 pagesCNC Router Calculations
The document provides initial data and calculations to determine the acceleration rates and linear forces for a CNC router. It calculates values like acceleration time, axis masses, gear ratios, and assumes a cutting force. Using principles of work, energy, and linear motion equations, it then calculates the rapid movement forces and peak cutting forces for each axis. It determines the maximum linear force for each axis and uses formulas to calculate the peak motor torque requirements for the Z, Y, and X axes.
Uploaded by
morteza nourooziCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd