Professional Documents
Culture Documents
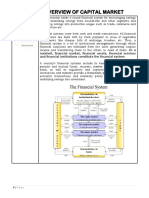
Indian Financial System An Introduction
Uploaded by
Ronan FerrerOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Indian Financial System An Introduction
Uploaded by
Ronan FerrerCopyright:
Available Formats
INDIAN FINANCIAL SYSTEM: AN INTRODUCTION Banking – creators and purveyors of credit
Non-banking – Only purveyors, ex. DFIs,
Introduction NBFCs,
Financial system intermediates between Term Finance
IDBI, ICICI, IFCI, SIDBI, IIBI
the flow of funds belonging to those who
Specialized
save a part of their income and those
EXIM, TFCI, ICICI Venture, IDFC, NABARD,
who invest in productive assets.
NHB
It mobilizes and usefully allocates scarce
Sectoral
resources of a country.
UTI, LIC, GIC
A financial system is a complex, well
Investment
integrated set of sub systems of financial
State-Level
institutions, markets, instruments & services State Financial Corporations, State
which facilitates the transfer and allocation of Industrial Development Corporations
funds efficiently & effectively.
FORMAL/ORGANIZED INFORMAL/ FINANCIAL MARKET
FINANCIAL SYSTEM UNORGANIZED
FINANCIAL SYSTEM Types
It is characterized by the presence It is an unorganized,
of an organized, institutional and non-institutional MONEY MARKET
regulated system which caters to and non-regulated
the financial needs of the modern system dealing with Treasury Bills
spheres of economy. traditional and rural Call Money Market
spheres of the Notice Money Market
economy
Commercial Papers
Regulators Components Individual money Certificate of Deposit
MoF 1. Financial lenders
Institutions Group of persons CAPITAL MARKET
SEBI 2. Financial Markets operating as
RBI 3. Financial funds Equity Market
Instruments Partnership firms Debt Market
IRDA 4. Financial Services
Segments
Pros and Cons of Informal Financial System Primary Market
Secondary Market
Advantages Disadvantages
Low transaction cost Wide range of
interest rates
Minimum default risk Higher rates of
interest
Transparency of Unregulated
procedures
FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
They are the intermediaries that mobilize savings and
facilitate the allocation of funds in efficient manner.
Classification of Financial Institutions
Banking & Non-banking
MONEY MARKET PRIMARY MARKET AND SECONDARY MARKET
It is market for short term debt instruments. The primary market creates long-term
A highly liquid market. instruments for borrowings.
Ex. Call money market, certificates of The secondary market provides liquidity
deposits, commercial paper and treasury and through the marketability of these
bills instruments
o It is also known as stock market
Functions:
LINK BETWEEN PRIMARY MARKET AND
Provide a balancing mechanism to even out
SECONDARY MARKET
the demand for and supply of short-term
funds A buoyant secondary market is indispensable
Provide a focal point for central bank for the presence of a vibrant primary capital
intervention for influencing liquidity market
The secondary market provides a basis for the
CAPITAL MARKET
determination of prices of new issues
It is a market for long-term securities like Depth of the secondary market depends on
equity or debt. the primary market
Bunching of new issues affects prices in the
Functions: secondary market.
Mobilize long term savings to finance long- FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
term investments
Enable quick valuation of financial A financial instrument is a claim against a
instruments - both equity and debt person or an institution for payment, at a
Disseminate information efficiently for future date, of a sum of money, and/or a
enabling participants to develop an informed periodic payment in the form of interest or
opinion about investment, disinvestment, dividend
reinvestment or holding a particular financial Many financial instruments are marketable as
asset. they are denominated in small amounts and
Provide liquidity with a mechanism enabling traded in organized markets.
the investors to sell financial assets. Distinct features of financial instruments:
o Marketable
o Tradable
o Tailor Made
LINK BETWEEN CAPITAL MARKET AND
MONEY MARKET
Often, financial institutions actively involved
in the capital market are also involved in the
money market
Funds raised in the money market are used to
provide liquidity for long-term investment and
redemption of funds raised in the capital
market
In the development proves of financial
markets, the development of the money
market typically precedes the development of
capital market
FINANCIAL SERVICES
MARKET BASED
Categories of financial services: o Financial markets play an important role
o Funds intermediation whole the banking industry is much less
o Payment mechanism concentrated
o Provision of liquidity o US, UK
o Risk management
o Financial engineering – ex. off-balance sheet
items, development of synthetic securities
BANK BASED
Need for financial services
o Borrowing and Funding Banks play a pivotal role in mobilizing savings,
o Lending and Investing allocation of capital, overseeing the investment
o Buying and selling securities decisions of corporate managers and providing
o Payment and settlements risk management facilities
It is tend to be stronger in countries where
governments have a direct hand in industrial
INTERACTION among FINANCIAL SYSTEM development.
COMPONENTS Advantages
Interdependent and interact continuously o Close relationship with parties
Interactive o Provides tailor-made contracts
Close link o No free-rider problem
Competing with each other
Disadvantages
FUNCTIONS OF FINANCIAL SYSTEM
o Retards innovation and growth
Mobilize and allocate savings o Impedes competition
Monitor corporate performance
Provide payment and settlement system
Optimum allocation of risk - bearing
MARKET BASED
and reduction
Disseminate price-related information The securities markets share centre stage with
Portfolio adjustment facility banks in mobilizing the society’s savings for firms,
exerting corporate control and easing risk
KEY ELEMENTS OF WELL FUNCTIONING
management
FINANCIAL SYSTEM
Advantages
Strong legal and regulatory environment
Stable money o Providers’ attractive terms to both investors
A central bank and borrowers
A sound banking system o Facilitates diversification
An information system o Allows risk sharing
A well-functioning security market o Allows financing of new technologies
FINANCIAL SYSTEM DESIGN Disadvantages
BANK BASED o Prone to instability
o A few large banks play a dominant role o Exposure to market risk
and the stock market is not important o Free-rider problem
o E.g. Germany, India
You might also like
- Unit 1: Overview of Capital MarketDocument23 pagesUnit 1: Overview of Capital MarketJanani Priya100% (2)
- Topic 1 - Financial SystemDocument29 pagesTopic 1 - Financial SystemMiera FrnhNo ratings yet
- 3 - Unit I - Introduction To Financial Systems and Financial MarketDocument41 pages3 - Unit I - Introduction To Financial Systems and Financial MarketAlexis Ann Angan AnganNo ratings yet
- Financial ServicesDocument77 pagesFinancial ServicesGiridhara Raju80% (5)
- Chapter 2 Canadian Securities Exam PreparationDocument14 pagesChapter 2 Canadian Securities Exam PreparationPRUTHVIRAJSINH ZALANo ratings yet
- 1.1 Finance and Financial SectorDocument36 pages1.1 Finance and Financial SectorPhanieNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Finance and Financial SectorDocument36 pages1.1 Finance and Financial SectorAki Crush koNo ratings yet
- FIMunit 2 Part 3Document7 pagesFIMunit 2 Part 3ShailjaNo ratings yet
- Sewc Law PDFDocument105 pagesSewc Law PDFRam IyerNo ratings yet
- 06 Viddhi FPM Assignment 03Document16 pages06 Viddhi FPM Assignment 03ViddhiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Questions (To Be Written With Answers in Blue Book....Document17 pagesWorksheet Questions (To Be Written With Answers in Blue Book....v namratNo ratings yet
- Câu hỏi review lý thuyết tiền tệDocument4 pagesCâu hỏi review lý thuyết tiền tệKim TiếnNo ratings yet
- Financial system overview and key componentsDocument20 pagesFinancial system overview and key componentsMad GirlNo ratings yet
- School of Law III Internals: Submitted To: Awadhesh Pathak Sir Submitted By: Isha Verma (2020/16)Document15 pagesSchool of Law III Internals: Submitted To: Awadhesh Pathak Sir Submitted By: Isha Verma (2020/16)Isha VermaNo ratings yet
- RP - CF1 - Financial Markets, Institutions and InstrumentsDocument24 pagesRP - CF1 - Financial Markets, Institutions and InstrumentsSamyu KNo ratings yet
- Money MarketDocument21 pagesMoney MarketAayush JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Role of Government in Indian Financial SystemDocument22 pagesRole of Government in Indian Financial Systemsdutta564100% (2)
- Overview of The Indian Financial SystemDocument22 pagesOverview of The Indian Financial SystemRahulNo ratings yet
- Capital Market Reforms and Development in IndiaDocument24 pagesCapital Market Reforms and Development in IndianitikanehiNo ratings yet
- Intro & FS OverviewDocument26 pagesIntro & FS OverviewEkaterina DeevaNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets ExplainedDocument29 pagesFinancial Markets Explainedlekha1997No ratings yet
- Ncert Financial MarketsDocument29 pagesNcert Financial Marketsjyoti singhNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial System SyllabusDocument32 pagesIndian Financial System SyllabusAkashNo ratings yet
- Industry ProfileDocument8 pagesIndustry ProfileKavitha JagadishNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial SystemDocument15 pagesIndian Financial SystemMukul VermaNo ratings yet
- Financial System Explained in 40 CharactersDocument16 pagesFinancial System Explained in 40 CharactersAkansha SinghNo ratings yet
- QuestionDocument3 pagesQuestionKanwal SaleemNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument3 pagesFinancial MarketsAbmel DreamerNo ratings yet
- Meaning of Indian Financial System - Meaning of Indian Financial SystemDocument2 pagesMeaning of Indian Financial System - Meaning of Indian Financial Systemwahab razaNo ratings yet
- CMSL REVISION NOTES DECEMBER 2020 AMENDED-Executive-RevisionDocument332 pagesCMSL REVISION NOTES DECEMBER 2020 AMENDED-Executive-RevisionT.V.B.M CHAITANYANo ratings yet
- Overview of Indian Financial MarketDocument22 pagesOverview of Indian Financial MarketPrinky SweetiepieNo ratings yet
- Derivatives As A Hedging Tool For Instrumental PlanDocument88 pagesDerivatives As A Hedging Tool For Instrumental Planjitendra jaushikNo ratings yet
- 01-1 Indian Financial SystemDocument160 pages01-1 Indian Financial Systemanmaya agarwalNo ratings yet
- Stock Market: Primary MarketDocument18 pagesStock Market: Primary MarketVarun VNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes of CMSL JUNE 2019 UPDATED-Executive-Revision PDFDocument283 pagesRevision Notes of CMSL JUNE 2019 UPDATED-Executive-Revision PDFShriya Gham0% (1)
- Financial MarketsDocument23 pagesFinancial MarketsCleo Coleen Lambo FortunadoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Financial MarketsDocument79 pagesUnit 1 - Financial Marketsvishwa princeNo ratings yet
- Capital Market - 26830Document89 pagesCapital Market - 26830NamrataShahaniNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 FINANACIAL MARKETS 30 MarksDocument58 pagesUnit 3 FINANACIAL MARKETS 30 Marksaishwarya raikarNo ratings yet
- Capital MarketDocument39 pagesCapital Marketpushkargarg14No ratings yet
- Finance Vs Financial SystemDocument61 pagesFinance Vs Financial Systempriyasumit100% (1)
- Great Learning - Session 1 - Overview of Indian Financial SytemDocument14 pagesGreat Learning - Session 1 - Overview of Indian Financial Sytemsudnandini86No ratings yet
- MONEY MARKET OVERVIEWDocument10 pagesMONEY MARKET OVERVIEWjhanvi tayalNo ratings yet
- Managerial Finance: An Overview of Financial Systems and MarketsDocument116 pagesManagerial Finance: An Overview of Financial Systems and MarketsJaja SutejaNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document29 pagesChap 1AIMA ACADEMYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Structure of Financial SystemDocument18 pagesChapter 1 - Structure of Financial SystemNur HazirahNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Indian Financial SystemDocument17 pagesAn Overview of Indian Financial SystemAbhinav ZijooNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Institutions ExplainedDocument78 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutions Explainedamol_more37100% (1)
- Banking Chapter 1Document7 pagesBanking Chapter 1Shasharu Fei-fei LimNo ratings yet
- To Indian Financial System: Courses Offered: Rbi Grade B Sebi Grade A Nabard Grade A and B Ugc Net Paper 1 and 2Document41 pagesTo Indian Financial System: Courses Offered: Rbi Grade B Sebi Grade A Nabard Grade A and B Ugc Net Paper 1 and 2ramNo ratings yet
- Financial Market Part 2 - Chakshoo Sir - 14-Sep-2023Document15 pagesFinancial Market Part 2 - Chakshoo Sir - 14-Sep-2023anupamsharma.srmsbsNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Financial System Structure and ComponentsDocument18 pagesIntroduction of Financial System Structure and ComponentsSyafiqahNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Institutions: ReadingsDocument10 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutions: ReadingsQuang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Capital Market & Institutional Finacing - Sajal JanaDocument23 pagesCapital Market & Institutional Finacing - Sajal JanasajalecoNo ratings yet
- Jntu University School of Management Studies.: 3 Sem, I-Mid ExamDocument22 pagesJntu University School of Management Studies.: 3 Sem, I-Mid ExamMadhuri AlNo ratings yet
- CAPITAL VS MONEY MARKETDocument4 pagesCAPITAL VS MONEY MARKETUsmanNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Overview of Financial MarketsDocument66 pagesChap 1 Overview of Financial MarketsSewale AbateNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial SystemDocument9 pagesIndian Financial Systemyashmehta91No ratings yet
- CH 5 The Capital MarketDocument23 pagesCH 5 The Capital MarketJyoti YadavNo ratings yet
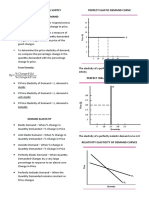
- ELASTICITY OF DEMAND & SUPPLY PERFECT CURVESDocument7 pagesELASTICITY OF DEMAND & SUPPLY PERFECT CURVESRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Contract of SaleDocument6 pagesEssentials of Contract of SaleRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- HUMAN POPULATION and THE ENVIRONMENTDocument4 pagesHUMAN POPULATION and THE ENVIRONMENTRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Indian Contract Act 1872 NewDocument17 pagesIndian Contract Act 1872 NewRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Environmental Studies Global Human Population GrowthDocument5 pagesEnvironmental Studies Global Human Population GrowthRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Effective CommunicationDocument7 pagesEffective CommunicationRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply Demand Cross DemandDocument5 pagesDemand and Supply Demand Cross DemandRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Distribution and Marketing Communications MixDocument11 pagesDistribution and Marketing Communications MixRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Corporate Law - Module 1 IntroductionDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Corporate Law - Module 1 IntroductionRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems ServicesDocument9 pagesEcosystems ServicesRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Consumer and Producer SurplusDocument3 pagesConsumer and Producer SurplusRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Contract of SaleDocument6 pagesEssentials of Contract of SaleRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Contract of Sale of GoodsDocument5 pagesContract of Sale of GoodsRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply Demand Cross DemandDocument5 pagesDemand and Supply Demand Cross DemandRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Contingent Assets and Contingent LiabilitiesDocument5 pagesContingent Assets and Contingent LiabilitiesRonan Ferrer100% (1)
- COMPETITION LAW and RIGHT TO INFORMATIONDocument6 pagesCOMPETITION LAW and RIGHT TO INFORMATIONRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Building Positive AttitudeDocument2 pagesBuilding Positive AttitudeRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Consumer Protection Act and Intelecctual Property LawDocument8 pagesConsumer Protection Act and Intelecctual Property LawRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Company Law: Kinds of CompaniesDocument14 pagesCompany Law: Kinds of CompaniesRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Central Bank Functions and TechniquesDocument3 pagesCentral Bank Functions and TechniquesRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- COMPETITION LAW and RIGHT TO INFORMATIONDocument6 pagesCOMPETITION LAW and RIGHT TO INFORMATIONRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Building Emotional CompetenceDocument2 pagesBuilding Emotional CompetenceRonan Ferrer100% (2)
- Capital vs Revenue ExpenditureDocument5 pagesCapital vs Revenue ExpenditureRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- BASIC CONCEPTS OF 5S KAZIEN and TQM APPROACHDocument2 pagesBASIC CONCEPTS OF 5S KAZIEN and TQM APPROACHRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Mutual Funds 2.1Document6 pagesMutual Funds 2.1Ronan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Analyzing internal & external marketing environmentsDocument7 pagesAnalyzing internal & external marketing environmentsRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- COMMUNICATION NETWORKS: UNDERSTANDING FORMAL AND INFORMAL SYSTEMSDocument3 pagesCOMMUNICATION NETWORKS: UNDERSTANDING FORMAL AND INFORMAL SYSTEMSRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- An Introduction of Cost and Revenue Classification of CostsDocument5 pagesAn Introduction of Cost and Revenue Classification of CostsRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Nature and Concepts of PlanningDocument8 pagesNature and Concepts of PlanningRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Neoclassical Growth TheoryDocument24 pagesNeoclassical Growth Theoryprince marcNo ratings yet
- Ekonomi Manajerial: Dalam Perekonomian GlobalDocument30 pagesEkonomi Manajerial: Dalam Perekonomian GlobalMaryam BurhanuddinNo ratings yet
- Impacts of Globalization on Indian AgricultureDocument2 pagesImpacts of Globalization on Indian AgricultureSandeep T M SandyNo ratings yet
- Trade Like A Pro With Japanese Candlesticks EbookDocument78 pagesTrade Like A Pro With Japanese Candlesticks EbookL M50% (2)
- Unit 7 Perfect CompetitionDocument12 pagesUnit 7 Perfect CompetitionRanjeet Kumar100% (1)
- BoomDocument74 pagesBoomtrek juneNo ratings yet
- Environmental Economics An Introduction 7th Edition Field Test BankDocument9 pagesEnvironmental Economics An Introduction 7th Edition Field Test Bankkennethmooreijdcmwbxtz100% (15)
- SPECIAL PAPER - EXPLORING THE BARRIERS TO ACCESSING FUNDING FOR MSMEs (Repaired)Document64 pagesSPECIAL PAPER - EXPLORING THE BARRIERS TO ACCESSING FUNDING FOR MSMEs (Repaired)Manfred AndohNo ratings yet
- Impact of Technology On JobsDocument12 pagesImpact of Technology On JobsJuyee JainNo ratings yet
- Mutul Fund of IciciDocument27 pagesMutul Fund of IciciShreya ShahNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 - Competition and Policies Toward Monopolies and Oligopolies Privatization and DeregulationDocument30 pagesCHAPTER 7 - Competition and Policies Toward Monopolies and Oligopolies Privatization and DeregulationCharlie Magne G. Santiaguel90% (10)
- Chapter 3 National Income. Where It Comes From and Where It GoesDocument11 pagesChapter 3 National Income. Where It Comes From and Where It GoesJoana Marie CalderonNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Indifference CurveDocument10 pagesModule 2 Indifference CurveAbhinab GogoiNo ratings yet
- Case Study Questions 1Document6 pagesCase Study Questions 1Nischal KanthNo ratings yet
- Impacts of COVID-19 Pandemic On International Trade in Goods of OECD CountriesDocument14 pagesImpacts of COVID-19 Pandemic On International Trade in Goods of OECD CountriesjomiljkovicNo ratings yet
- Inflation and Unemployment in Indonesia PDFDocument5 pagesInflation and Unemployment in Indonesia PDFSakilah ArbaniNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics GuideDocument36 pagesManagerial Economics GuideYogesh GirgirwarNo ratings yet
- 2012 H2 Revision For DdssDocument14 pages2012 H2 Revision For DdssdavidbohNo ratings yet
- Inflation DeflationDocument18 pagesInflation DeflationSteeeeeeeeph100% (2)
- Ansoff MatrixDocument1 pageAnsoff Matrixpunya.trivedi2003No ratings yet
- BM ReviewDocument10 pagesBM ReviewFish SuperNo ratings yet
- Daly - 1974-The Economics of The Steady StateDocument8 pagesDaly - 1974-The Economics of The Steady StateAliba OliverNo ratings yet
- CH6Document30 pagesCH6Fadi ChouNo ratings yet
- Recent Trends in Industrial Growth in IndiaDocument8 pagesRecent Trends in Industrial Growth in IndiaAppan Kandala Vasudevachary80% (5)
- (S) Topic 3 - Market Theory - Elasticities of Demand and SupplyDocument14 pages(S) Topic 3 - Market Theory - Elasticities of Demand and SupplyKelvin YapNo ratings yet
- Galanz Operation Strategy Case AnalysisDocument13 pagesGalanz Operation Strategy Case AnalysisSharad Pyakurel92% (13)
- Solutions Manual Mankiw Chap01Document4 pagesSolutions Manual Mankiw Chap01Tatjana Dahlhaus50% (2)
- FIN 352 Exam 2 Formula SheetDocument6 pagesFIN 352 Exam 2 Formula SheetHiếu Nguyễn Minh Hoàng0% (1)
- Realidad y Teoría EconómicaDocument31 pagesRealidad y Teoría EconómicaFatehdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Macro ExamDocument4 pagesMacro ExamAsmerom Mosineh75% (4)
- Burn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialFrom EverandBurn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialNo ratings yet
- Venture Deals, 4th Edition: Be Smarter than Your Lawyer and Venture CapitalistFrom EverandVenture Deals, 4th Edition: Be Smarter than Your Lawyer and Venture CapitalistRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (73)
- Joy of Agility: How to Solve Problems and Succeed SoonerFrom EverandJoy of Agility: How to Solve Problems and Succeed SoonerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Finance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)From EverandFinance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (32)
- These are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaFrom EverandThese are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- The Caesars Palace Coup: How a Billionaire Brawl Over the Famous Casino Exposed the Power and Greed of Wall StreetFrom EverandThe Caesars Palace Coup: How a Billionaire Brawl Over the Famous Casino Exposed the Power and Greed of Wall StreetRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Summary of The Black Swan: by Nassim Nicholas Taleb | Includes AnalysisFrom EverandSummary of The Black Swan: by Nassim Nicholas Taleb | Includes AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Mastering Private Equity: Transformation via Venture Capital, Minority Investments and BuyoutsFrom EverandMastering Private Equity: Transformation via Venture Capital, Minority Investments and BuyoutsNo ratings yet
- Financial Risk Management: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandFinancial Risk Management: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Financial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanFrom EverandFinancial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (79)
- 7 Financial Models for Analysts, Investors and Finance Professionals: Theory and practical tools to help investors analyse businesses using ExcelFrom Everand7 Financial Models for Analysts, Investors and Finance Professionals: Theory and practical tools to help investors analyse businesses using ExcelNo ratings yet
- The Six Secrets of Raising Capital: An Insider's Guide for EntrepreneursFrom EverandThe Six Secrets of Raising Capital: An Insider's Guide for EntrepreneursRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (34)
- Investment Valuation: Tools and Techniques for Determining the Value of any Asset, University EditionFrom EverandInvestment Valuation: Tools and Techniques for Determining the Value of any Asset, University EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Value: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceFrom EverandValue: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Product-Led Growth: How to Build a Product That Sells ItselfFrom EverandProduct-Led Growth: How to Build a Product That Sells ItselfRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How to Measure Anything: Finding the Value of Intangibles in BusinessFrom EverandHow to Measure Anything: Finding the Value of Intangibles in BusinessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- The Masters of Private Equity and Venture Capital: Management Lessons from the Pioneers of Private InvestingFrom EverandThe Masters of Private Equity and Venture Capital: Management Lessons from the Pioneers of Private InvestingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (17)
- Add Then Multiply: How small businesses can think like big businesses and achieve exponential growthFrom EverandAdd Then Multiply: How small businesses can think like big businesses and achieve exponential growthNo ratings yet
- Ready, Set, Growth hack:: A beginners guide to growth hacking successFrom EverandReady, Set, Growth hack:: A beginners guide to growth hacking successRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Financial Modeling and Valuation: A Practical Guide to Investment Banking and Private EquityFrom EverandFinancial Modeling and Valuation: A Practical Guide to Investment Banking and Private EquityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Startup CEO: A Field Guide to Scaling Up Your Business (Techstars)From EverandStartup CEO: A Field Guide to Scaling Up Your Business (Techstars)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Warren Buffett Book of Investing Wisdom: 350 Quotes from the World's Most Successful InvestorFrom EverandWarren Buffett Book of Investing Wisdom: 350 Quotes from the World's Most Successful InvestorNo ratings yet
- Note Brokering for Profit: Your Complete Work At Home Success ManualFrom EverandNote Brokering for Profit: Your Complete Work At Home Success ManualNo ratings yet