Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types BEARRING
Types BEARRING
Uploaded by
สมโภช แก้วเขียว0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesTypes BEARRING
Types BEARRING
Uploaded by
สมโภช แก้วเขียวYou are on page 1of 2
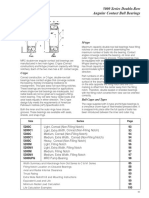
Types
Bearing types at a glance
Ball Bearings
Deep Groove Ball Bearings
‘Self Aligning Bal Bearings,
Bal Bearings
‘Angular-Cortact Ball Bearings
‘Thnwst Bal Bearings,
‘Tapered Roller Bearings
‘Gylineical Roller Bearings
[Neetle Roller Bearings
Ball Bearings utlize bals as the rolling elements. They are characterised by point contact between the balls and the raceways. As a rule,
ball bearings rotate very quickly but cannot support substantial loads.
ee
Deep-Groove Ball Bearings
The most commonly used bearings are Deep-Groove Ball Bearings. Thanks to the'r simple design,
they are easy to maintain and nol as sensitive fo operating conditions thus are used in a wide range of
different appiicaitons,
In addition to radial forces, they absorb axial forces in both directions. Th
them suitable for high speeds. >>
low torque also makes
Angular Contact Ball Bearings
‘Angular Contact Ball Bearings are characterised by a contact angle. This means that forces are
transferred from one raceway tothe other at a particular angle,
Angular-contact ball bearings ate therefore suitable for combined loads, where high axial
forces havo to be transforred in addition to radial forces, >>
Self-Aligning Ball Bearings
Self-Aligning Ball Bearings include a double row of balls guided by a cage and double row inner
Fing raceway but have the specal feature ofa continuous spherical outer ring raceway allowing the
Inner ring / ball complement to swivel within the outer ring. Ths is what enables a degree of solt-
alignment in the application
‘This type of beating is recommended when alignment ofthe shaft and the housing (misalignment) are
‘a problem and the shaft could deflect. Sel-aligning ball bearings are most sutable for absorbing radial
forces. >>
ill
Roller Bearings
Thrust Ball Bearings
Thrust Ball Bearings consis of two bearing discs with raceways forthe balls.
Thrust ball bearings were developed solely for absorbing axial forces in one direction, meaning they
can locate the shaft axially in one direction. >>
Roller Bearings are characterized by line contact. Line contact offers higher load rating than ball bearings of the same size; however the
speed ability is lower than a ball bearing due tothe increased friction of a contact ine,
Spherical Roller Bearings
‘Spherical Roller Bearings are very robust and work on the same principle as Sel-aligning bearings
with the exception that they use spherical rollers instead of ball rollers allowing higher loads to be
supported. This can compensate for misalignments between the shaft and the housing,
‘Spherical roller bearings are suitable for absorbing high radial loads and moderate axial loads, >>
Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Cylindrical Roller Bearings use line contact between the rolling elements and the raceways, which
‘optimizes the distribution of stress factors at the point of contact. This arrangement means tha
cylindrical roller bearings have a very high radial load rating,
Depending on the design, they may also be able to transmit imited amounts of axial loads. >>
Tapered Roller Bearings
Tapered Roller Bearings have tapered raceways in the inner and outer rings with conical
rollers arranged between them.
Due to the contact angle, tapered roler bearings can absorb high radial and axial forces in one
direction,
‘Tapered rollor bearings are often combinad in pairs to support axial forces in both directions. >>
Needle Roller Bearings
Needle Roller Bearings are a special type of cylindrical roller bearing which contain long, thin rolling
elements, known as needle rollers. The rallo of diameter to length is between 13 and 1:10.
[Needle roller bearings have a high load rating and are only suitable for radial forces,
It space is constricted, neeale bearings can be a good solution, >>
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Oil Cooler Rubber Oring & Kit: Nissan Rd8 Nissan Rd8Document3 pagesOil Cooler Rubber Oring & Kit: Nissan Rd8 Nissan Rd8สมโภช แก้วเขียวNo ratings yet
- Komatsu Gear Loader Hydraulic Pump 705-14-41040 705-12-44010 OptionalDocument2 pagesKomatsu Gear Loader Hydraulic Pump 705-14-41040 705-12-44010 Optionalสมโภช แก้วเขียวNo ratings yet
- Oil Cooler Rubber o Ring KitDocument3 pagesOil Cooler Rubber o Ring Kitสมโภช แก้วเขียวNo ratings yet
- Water Pump Seal - 718362Document2 pagesWater Pump Seal - 718362สมโภช แก้วเขียวNo ratings yet
- CumminsDocument3 pagesCumminsสมโภช แก้วเขียวNo ratings yet
- SKF 3305ATN9 - Bearing, SKF 3305ATN9 - Bearing DimensionsDocument2 pagesSKF 3305ATN9 - Bearing, SKF 3305ATN9 - Bearing Dimensionsสมโภช แก้วเขียวNo ratings yet
- M-Type: 5000 Series Double-Row Angular Contact Ball BearingsDocument18 pagesM-Type: 5000 Series Double-Row Angular Contact Ball Bearingsสมโภช แก้วเขียวNo ratings yet
- 6007 - SKFDocument5 pages6007 - SKFสมโภช แก้วเขียวNo ratings yet
- S4D105-1B S - N 18273-UP - ALTERNATOR (800W) Clark-TCM-75A-Parts-Manual PDFDocument2 pagesS4D105-1B S - N 18273-UP - ALTERNATOR (800W) Clark-TCM-75A-Parts-Manual PDFสมโภช แก้วเขียวNo ratings yet
- S.P.K. Tractor 006 - Engine WB93R-5, WB97R-5 Komatsu Backhoe-Loader Workshop ManualDocument24 pagesS.P.K. Tractor 006 - Engine WB93R-5, WB97R-5 Komatsu Backhoe-Loader Workshop Manualสมโภช แก้วเขียว100% (1)
- Komatsu Gear Loader Hydraulic Pump 705-14-41040 705-12-44010 OptionalDocument2 pagesKomatsu Gear Loader Hydraulic Pump 705-14-41040 705-12-44010 Optionalสมโภช แก้วเขียวNo ratings yet
- เอส พี เค แทรคเตอร์ แอนด์ เซอร์วิสDocument56 pagesเอส พี เค แทรคเตอร์ แอนด์ เซอร์วิสสมโภช แก้วเขียวNo ratings yet
- Daewoo: Full Set & Head Set & Cyl. HeadDocument2 pagesDaewoo: Full Set & Head Set & Cyl. Headสมโภช แก้วเขียวNo ratings yet
- TH63 TH64: Din Half Size Hour MeterDocument2 pagesTH63 TH64: Din Half Size Hour Meterสมโภช แก้วเขียวNo ratings yet