0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views6 pagesChapter 7 Common Standard in Cloud Computing: Working Group
The document discusses several standards organizations and working groups related to cloud computing standards, including the Open Cloud Consortium and Distributed Management Task Force. It provides details on several working groups within the Open Cloud Consortium focused on areas like interoperability, security, and networking. It also discusses standards for virtualization developed by the Distributed Management Task Force, including the Open Virtualization Format. Finally, it covers some common application standards for web development, data transfer, and messaging.
Uploaded by
Muhammad Rɘʜʌŋ BakhshCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views6 pagesChapter 7 Common Standard in Cloud Computing: Working Group
The document discusses several standards organizations and working groups related to cloud computing standards, including the Open Cloud Consortium and Distributed Management Task Force. It provides details on several working groups within the Open Cloud Consortium focused on areas like interoperability, security, and networking. It also discusses standards for virtualization developed by the Distributed Management Task Force, including the Open Virtualization Format. Finally, it covers some common application standards for web development, data transfer, and messaging.
Uploaded by
Muhammad Rɘʜʌŋ BakhshCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
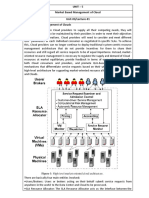
- Common Standard in Cloud Computing
- Open Virtualization Format
- Data Standards and Protocols
- Internet Messaging Protocols
- Communications and Security