Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bronchodilators (Respiratory Pharmacology)
Uploaded by
Rebecca Marshall0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views1 pageBronchodilators (Respiratory Pharmacology)
Uploaded by
Rebecca MarshallCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
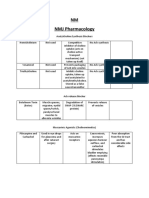
Bronchodilaters that are used in treatment of asthma
The drug mechanism of action Side effect Note
2- adrenoceptor agonist - Causes bronchial Temper palpitation Administration:
(e.g salbutamol, salmeterol smooth muscle hypokalemia - inhaled as powder
relaxation by - rarely given orally
increasing cAMP N.B. blocker can precipitate asthma
- inhibit mediator
release from mast
cell
- may cause
mucocilliary
clearance
Muscarinic antagonists Inhibition of the Few Administration:
release os - given by inhalation
acetylcholine at M1
M2 and M3
muscarinic receptors
Xanthine Relax bronchial NARROW therapeutic Administration:
( caffeine, theophylline) smooth muscle by range - oral
inhibiting - nausea/ anorexia - (Aminophylline) IV
phosphodiesterase - arrhythmias metabolised in liver
resulting in icreasing - nervousness NB drug intraction
cAMP
Anti inflammatory drugs used for treatment of asthma:
CORTICOSTEROID 1- Inhibit Inhaled: Adminstration:
transcription - dysphonia - Inhaled ..(e.g beclomethasone)
of COX 2 and important systemic - oral … (prednisolone)
inflammatory side effect: - IV (HYDROCORTISONE)
cytokines. - osteoprosis
2- reduced - adrenal
synthesis of suppression
prostaglandins - fluid retention
and
leukotrienes
Cromones 1- mast cell Cough and wheeze Administration :
(sodium cromoglycate and stabilisation post administration Inhaled
nedocromil ) 2- inhibition
of sensory C
fibre neurons
3- inhibition
of eosinophil
accumilation
in lungs
4- reduced
IgE
production
Lanti-eukotrienes Inhibition of 5 Gastrointestinal upset
lipoxygenase headache
Receptor
antagonist
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- RCSI Handbook of Clinical Medicine - V1, 2nd EdDocument574 pagesRCSI Handbook of Clinical Medicine - V1, 2nd EdRebecca Marshall86% (7)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- RCSI Handbook of Clinical Medicine - V2, 2nd EdDocument566 pagesRCSI Handbook of Clinical Medicine - V2, 2nd EdRebecca Marshall100% (4)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- City and Guilds Employability Portfolio Template 2015 2016Document54 pagesCity and Guilds Employability Portfolio Template 2015 2016Mansoor Bin Haji AliNo ratings yet
- Microbiology TablesDocument19 pagesMicrobiology TablesRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument8 pagesCardiovascular DiseasesRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- CVR PharmacologyDocument6 pagesCVR PharmacologyRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- NMJ PharmacologyDocument3 pagesNMJ PharmacologyRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- FUN1 Pharmacology TableDocument10 pagesFUN1 Pharmacology TableRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- Drugs Mechanism Side Effect DiureticDocument3 pagesDrugs Mechanism Side Effect DiureticRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- Boards and Beyond TableDocument11 pagesBoards and Beyond TableRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- Usmle Step 1 BreakdownDocument10 pagesUsmle Step 1 BreakdownRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- RCSI Clinical Examinations in Medicine 2018-19Document189 pagesRCSI Clinical Examinations in Medicine 2018-19Rebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- Thoughts After Amboss QbankDocument2 pagesThoughts After Amboss QbankRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- Neurotoxicity of E-CigarettesDocument15 pagesNeurotoxicity of E-CigarettesRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- CH-2034 Nalco Waters PermaCare Application Improved Productivity of A Reverse Osmosis SystemDocument2 pagesCH-2034 Nalco Waters PermaCare Application Improved Productivity of A Reverse Osmosis SystemLeonardo SimorangkirNo ratings yet
- Say No To PlasticDocument28 pagesSay No To Plasticpavithra nirmalaNo ratings yet
- Mediclear: Site Office - 90, Vasant Complex, Mayur Vihar, DelhiDocument3 pagesMediclear: Site Office - 90, Vasant Complex, Mayur Vihar, Delhiafsarkhan85No ratings yet
- Documents For Camp Attendance: I, Name....Document2 pagesDocuments For Camp Attendance: I, Name....Deva T N100% (1)
- Case 052: Biliary ColicDocument4 pagesCase 052: Biliary ColicZauzaNo ratings yet
- 7 Steps To Discovering Your Personal Values - Scott Jeffrey PDFDocument9 pages7 Steps To Discovering Your Personal Values - Scott Jeffrey PDFtraketeoNo ratings yet
- Biological BeginningsDocument24 pagesBiological BeginningsRabia DastiNo ratings yet
- Concepts To MasterDocument10 pagesConcepts To MasterJessa HiquianaNo ratings yet
- Copd VS AsthmaDocument2 pagesCopd VS AsthmaHarkirat AtwalNo ratings yet
- Department of Health v. C.V. Canchela & AssociatesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Health v. C.V. Canchela & AssociatesKelly RoxasNo ratings yet
- Phyto 2Document1 pagePhyto 2Farhan AshrafNo ratings yet
- Physical Education: Quarter 4 - Module 1 Week 1: FITT PrincipleDocument19 pagesPhysical Education: Quarter 4 - Module 1 Week 1: FITT PrincipleTrexia SingsonNo ratings yet
- HIV and YogaDocument3 pagesHIV and YogaAbhaya Raj UpadhayaNo ratings yet
- ListeningDocument7 pagesListeningPallavi JNo ratings yet
- Externalities & Public GoodsDocument13 pagesExternalities & Public GoodsAkshay ModakNo ratings yet
- Formula, Good or Not For The Babies ?: Written By: Rakhmah Sari Indah C. - XII P7 /28Document4 pagesFormula, Good or Not For The Babies ?: Written By: Rakhmah Sari Indah C. - XII P7 /28Inda KecilNo ratings yet
- Define Hospital ManagementDocument4 pagesDefine Hospital ManagementRenit AntoNo ratings yet
- 1P1 - Anna Kusumawati 323-329Document7 pages1P1 - Anna Kusumawati 323-329imam habibiNo ratings yet
- Arntz 1999 Childhood Imagery Rescripting Paper PDFDocument26 pagesArntz 1999 Childhood Imagery Rescripting Paper PDFelliotNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument4 pagesMicrobiologyHannah Grace CorveraNo ratings yet
- History of Perioperative Nursing 2023Document10 pagesHistory of Perioperative Nursing 2023Boniface MogakaNo ratings yet
- Pbs Register of SponsorsDocument1,727 pagesPbs Register of SponsorsZaili KastamNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of Quantitative StudiesDocument5 pagesLiterature Review of Quantitative Studiesd0vidihujam3100% (1)
- Angelina Hull Student - Heritagehs - Argumentative Essay - Student Name - Class Period - Spring 19 - H English 1Document5 pagesAngelina Hull Student - Heritagehs - Argumentative Essay - Student Name - Class Period - Spring 19 - H English 1api-461590822No ratings yet
- Anal Sex Secrets - A Guide To Great Anal Sex by Svetlana Ivanova - Read OnlineDocument4 pagesAnal Sex Secrets - A Guide To Great Anal Sex by Svetlana Ivanova - Read Onlinezamin4pak50% (2)
- MMQL Escala YoungDocument8 pagesMMQL Escala YoungDanny PazNo ratings yet
- Department of Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument13 pagesDepartment of Pharmaceutical ChemistrySuvarna KiniNo ratings yet
- Adaptacininstrumentos WASTDocument11 pagesAdaptacininstrumentos WASTAsley Cabrera LopezNo ratings yet
- ICU QuizDocument3 pagesICU QuizIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet