0% found this document useful (0 votes)
345 views16 pagesContinuous Improvement Tools Guide
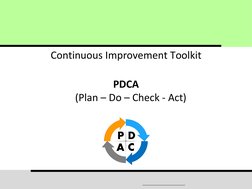
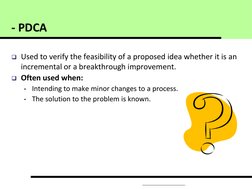
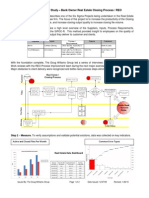
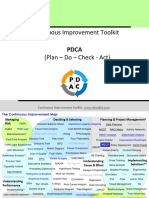
- PDCA is a four-step framework for continuous improvement and problem solving. The four steps are Plan, Do, Check, Act.
- It provides a structured approach to address quality problems through repeated cycles of planning, testing changes on a small scale, analyzing results, and implementing successful changes more broadly.
- Repeated application of the PDCA cycle helps drive continuous improvement through incremental changes and knowledge gained from each cycle.
Uploaded by
Vardhan ShahCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
345 views16 pagesContinuous Improvement Tools Guide
- PDCA is a four-step framework for continuous improvement and problem solving. The four steps are Plan, Do, Check, Act.
- It provides a structured approach to address quality problems through repeated cycles of planning, testing changes on a small scale, analyzing results, and implementing successful changes more broadly.
- Repeated application of the PDCA cycle helps drive continuous improvement through incremental changes and knowledge gained from each cycle.
Uploaded by
Vardhan ShahCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd