Professional Documents
Culture Documents
E-RAB Success Rate
Uploaded by
mausam_panchal2013Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
E-RAB Success Rate
Uploaded by
mausam_panchal2013Copyright:
Available Formats
LTE ERAB Success Rate
The second major KPI for LTE is the LTE ERAB Success Rate which is also part of the accessibility. After the UE has co
which has been explained in my previous article, LTE KPI Optimization: RRC Success Rate, it needs to get a Bearer as
services. The bearer can be default (usually Data QCI9) or dedicated (VoLTE QCI1). During initial access, the default b
constitutes the major portion of the total ERABs.
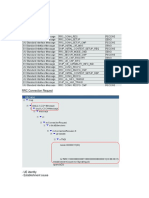
Firstly, lets understand the definition and points where the ERAB KPI is pegged. After the UE sends the RRC Setup Co
the eNB sends a S1 Initial UE Message to the MME indicating the purpose of the UE (Attach, TAU, CSFB, Service Req
Once the MME receives this message and it decides that a bearer is required, it will send an Initial Context Setup Re
message is considered as the ERAB Attempt as it contains the bearers to be added along with their QCI values. The e
and adds the DRB (Data Radio Bearer) based on the bearer profile in Initial Context Setup Request. But before the e
to activate the security for the connection. This is done by the Security Mode Command which carries the ciphering
algorithms. After this the eNB sends a RRC Connection Reconfiguration message to the UE which adds a DRB and it i
the DRB like bearer identity, PDCP & RLC configuration (AM/UM etc). SRB2 is also added at this point with this mess
messages and reconfigures the connection. Then the UE responds with Security Mode complete and RRC Connectio
messages. As the eNB receives these messages, it sends an Initial Context Setup Response to MME and this message
Success.
Common Failures In ERAB Setup Phase
Now let’s understand the common failures that usually cause a ERAB setup failure. Most of the times, the ERAB set
into two broad categories
Ø Radio Induced ERAB Setup Failures
Ø MME Induced ERAB Setup Failures
Let’s have an in-depth look at both of them and find ways to tackle them
You might also like
- Erab Set Up Fail: LTE KPI Optimization: RRC Success RateDocument4 pagesErab Set Up Fail: LTE KPI Optimization: RRC Success Ratemadanmohan22No ratings yet
- LTE KPI Optimization: RRC Success Rate: Common Failures in ERAB Setup PhaseDocument6 pagesLTE KPI Optimization: RRC Success Rate: Common Failures in ERAB Setup Phasededdi s samosirNo ratings yet
- RRC Re-EstablishmentDocument16 pagesRRC Re-EstablishmentRaheel ShahzadNo ratings yet
- LTE RRC Setup Success RateDocument5 pagesLTE RRC Setup Success RateGaneshkumar ArumugamNo ratings yet
- LTE KPI OptimizationDocument13 pagesLTE KPI Optimizationsonuvikas775No ratings yet
- Optimization For CSFB Call DelayDocument11 pagesOptimization For CSFB Call DelayAmit Butola100% (1)
- VoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkFrom EverandVoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkNo ratings yet
- Basic LTE Call Flow SequenceDocument3 pagesBasic LTE Call Flow SequenceTalent & Tech Global InfotechNo ratings yet
- LTE Network Architecture, Procedures and Technologies ExplainedDocument78 pagesLTE Network Architecture, Procedures and Technologies ExplainedPrabhat KumarNo ratings yet
- CDR Improvement by EDGE Handover OptimizationDocument4 pagesCDR Improvement by EDGE Handover Optimizationhunter nandoNo ratings yet
- Random access procedure in LTEDocument98 pagesRandom access procedure in LTEmohamed fadlNo ratings yet
- What is RTWP and how to reduce high RTWP valuesDocument5 pagesWhat is RTWP and how to reduce high RTWP valuesKunwar Atul SinghNo ratings yet
- Notice On Precaution For Possible VoLTE Performance Deterioration When Some VoLTE Parameters Are Not Set To Recommended ValuesDocument9 pagesNotice On Precaution For Possible VoLTE Performance Deterioration When Some VoLTE Parameters Are Not Set To Recommended Valuesmohamed fadlNo ratings yet
- MML commands to optimize 3G network parametersDocument72 pagesMML commands to optimize 3G network parametersAndri SetiawanNo ratings yet
- 06 - Ra4133 - rl20 - Lte Rab and Nas Counters - E01Document35 pages06 - Ra4133 - rl20 - Lte Rab and Nas Counters - E01Teguh YuliantoNo ratings yet
- CSSR Case StudyDocument11 pagesCSSR Case StudySahil KalaNo ratings yet
- RRC Connection ReestablishmentDocument2 pagesRRC Connection ReestablishmentsrimantaNo ratings yet
- RANAP CodesDocument42 pagesRANAP CodesParthasarathy ManiNo ratings yet
- Handover Parameters (Part 1 of 3) : Lauro 0Document14 pagesHandover Parameters (Part 1 of 3) : Lauro 0Prashant UjjawalNo ratings yet
- LTE Mobility Optimization-1Document13 pagesLTE Mobility Optimization-1kamal waniNo ratings yet
- KPI Name and Formula SummaryDocument6 pagesKPI Name and Formula Summarymanu waliaNo ratings yet
- RACH OptimizationDocument16 pagesRACH OptimizationSatish JadavNo ratings yet
- LTE Event A3Document2 pagesLTE Event A3eduardo_pl8256No ratings yet
- Radio Network Layer CauseDocument6 pagesRadio Network Layer CauseAnonymous kC8oFmSNo ratings yet
- Major Lte KpisDocument82 pagesMajor Lte KpisKarem AshrafNo ratings yet
- 10 Training Course - RAN17 1 Ultrafast CS Call Setup V1 03Document33 pages10 Training Course - RAN17 1 Ultrafast CS Call Setup V1 03shoaib.hadi7355No ratings yet
- Ran15.0 Umts-To-lte Fast ReturnDocument16 pagesRan15.0 Umts-To-lte Fast ReturnSahinba Sahin83% (6)
- ZTE LTE + Volte Radio Network Functionality (5 Days)Document5 pagesZTE LTE + Volte Radio Network Functionality (5 Days)vikasNo ratings yet
- Ping-Pong HO IssueDocument9 pagesPing-Pong HO IssueAhmed Torki0% (1)
- ZXSDR Enodeb Configuration: Zte UniversityDocument43 pagesZXSDR Enodeb Configuration: Zte UniversityHAWLITUNo ratings yet
- Huawei eRAN KPI Introduction - eRAN2.1-0801Document49 pagesHuawei eRAN KPI Introduction - eRAN2.1-0801Cristopher TimarioNo ratings yet
- LTE Handover Failure Examples and TroubleshootingDocument3 pagesLTE Handover Failure Examples and Troubleshootingafroxxx100% (1)
- RLFDocument25 pagesRLFFathy FaroukNo ratings yet
- SRVCC Preparation Success Rate Too LowDocument1 pageSRVCC Preparation Success Rate Too LowfideleNo ratings yet
- Huawei eRAN8.1 Intra-LTE Load B Alance Feature Discription: 2014 JuneDocument41 pagesHuawei eRAN8.1 Intra-LTE Load B Alance Feature Discription: 2014 Junebrahiti3No ratings yet
- Rach:: From Power-On To PRACHDocument10 pagesRach:: From Power-On To PRACHTalent & Tech Global InfotechNo ratings yet
- LTE Signaling - AttachDocument21 pagesLTE Signaling - AttachYoyok Dwi ParindraNo ratings yet
- Check and optimize LTE site issuesDocument1 pageCheck and optimize LTE site issuesNikhil Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- 5G NR-Load Sharing and Load Balancing Optimization: (As Per 3GPP TS37.816 v16.0.0)Document2 pages5G NR-Load Sharing and Load Balancing Optimization: (As Per 3GPP TS37.816 v16.0.0)mohamed fadlNo ratings yet
- SOW-Radio Network Optimization1Document7 pagesSOW-Radio Network Optimization1Muhammad TuriNo ratings yet
- UEH ExceptionsDocument17 pagesUEH ExceptionsIvan BagusNo ratings yet
- Optimize NetAct 5.2 with RRC countersDocument34 pagesOptimize NetAct 5.2 with RRC countersÖzgür ÖzcanNo ratings yet
- 10 Call Trace SessonDocument15 pages10 Call Trace SessonSantoshYadavNo ratings yet
- Manage SRVCC from LTE to UMTS with PS Handover and Fast Return to LTEDocument6 pagesManage SRVCC from LTE to UMTS with PS Handover and Fast Return to LTEbalamuruganNo ratings yet
- 08 e LTE Trigger-V1 1Document29 pages08 e LTE Trigger-V1 1MohammadNo ratings yet
- What Is The TRB and SRB Reset in WCDMADocument1 pageWhat Is The TRB and SRB Reset in WCDMAYuma M DasukiNo ratings yet
- Dashboard - Monitoring - VoLTE - KPI Formula - FinalDocument46 pagesDashboard - Monitoring - VoLTE - KPI Formula - FinalAnandNo ratings yet
- Lte Prach ChannelDocument7 pagesLte Prach ChannelmanishNo ratings yet
- IBS Modernization – RTWP Cause TracingDocument17 pagesIBS Modernization – RTWP Cause TracingSaeful AlmaslulNo ratings yet
- 008 WCDMA Primary Scrambling Code PlanningDocument14 pages008 WCDMA Primary Scrambling Code Planningank_alex209100% (1)
- 3g CDR CCH, CS, PS, r99, Hsdpa and Hsupa v1.0Document18 pages3g CDR CCH, CS, PS, r99, Hsdpa and Hsupa v1.0بطاهر محمدNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction (eRAN12.1 - 06)Document205 pagesEnergy Conservation and Emission Reduction (eRAN12.1 - 06)waelq2003No ratings yet
- Reselection Priority High 7: RSRP - 114 DBMDocument2 pagesReselection Priority High 7: RSRP - 114 DBMโดราเอม่อน คัก คักNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Coverage With Propagation Delay-PD and Timing Advance - TA - GSM-WCDMA-LTEDocument20 pagesAnalyzing Coverage With Propagation Delay-PD and Timing Advance - TA - GSM-WCDMA-LTEAzmat GaadNo ratings yet
- LTE Signaling: Troubleshooting and OptimizationFrom EverandLTE Signaling: Troubleshooting and OptimizationRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Observations - 121073 & 133472Document4 pagesObservations - 121073 & 133472mausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- Cell - Site - List - SLZ26 To 30 CompiledDocument16 pagesCell - Site - List - SLZ26 To 30 Compiledmausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- Rncid Best Cellid Ue Id RRC Establish Time Fault TypeDocument18 pagesRncid Best Cellid Ue Id RRC Establish Time Fault Typemausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- Lte Drive Test ParametersDocument3 pagesLte Drive Test ParametersHamrouni AdnenNo ratings yet
- Celllist For NLZ Baseline - LTE-AUG 30x31 2023Document326 pagesCelllist For NLZ Baseline - LTE-AUG 30x31 2023mausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- Rncid Best Cellid Ue Id RRC Establish Time Fault TypeDocument5 pagesRncid Best Cellid Ue Id RRC Establish Time Fault Typemausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- Rncid Best Cellid Ue Id RRC Establish Time Fault TypeDocument12 pagesRncid Best Cellid Ue Id RRC Establish Time Fault Typemausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- Rncid Best Cellid Ue Id RRC Establish Time Fault TypeDocument5 pagesRncid Best Cellid Ue Id RRC Establish Time Fault Typemausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- RAB Assignment Fault Records ReportDocument42 pagesRAB Assignment Fault Records Reportmausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- Vvolte BasicsA2425 PDFDocument12 pagesVvolte BasicsA2425 PDFabdul qadir NoorullahNo ratings yet
- Rncid Best Cellid Ue Id RRC Establish Time Fault TypeDocument5 pagesRncid Best Cellid Ue Id RRC Establish Time Fault Typemausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- Rncid Best Cellid Ue Id RRC Establish Time Fault TypeDocument24 pagesRncid Best Cellid Ue Id RRC Establish Time Fault Typemausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- LTE Parameters Commonly Used For Optimization RecommendationsDocument8 pagesLTE Parameters Commonly Used For Optimization RecommendationsBhaskar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Rncid Best Cellid Ue Id RRC Establish Time Fault TypeDocument5 pagesRncid Best Cellid Ue Id RRC Establish Time Fault Typemausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- Rncid Best Cellid Ue Id RRC Establish Time Fault TypeDocument5 pagesRncid Best Cellid Ue Id RRC Establish Time Fault Typemausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- 4.introduction To The VoLTE Solution ISSUE7.02Document87 pages4.introduction To The VoLTE Solution ISSUE7.02Bassem Abouamer100% (2)
- All Cells SPUDocument76 pagesAll Cells SPUmausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- RSSI on PUCCH and PUSCHDocument2 pagesRSSI on PUCCH and PUSCHDpkKSingh50% (2)
- KPI monitoring reportDocument4 pagesKPI monitoring reportmausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- Nokia Golden ParameterDocument36 pagesNokia Golden Parametermausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- Parameter Analysis Guideline VoLTE SRVCC v1 1Document67 pagesParameter Analysis Guideline VoLTE SRVCC v1 1mausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- DB, DBM, DBWDocument9 pagesDB, DBM, DBWtosurajjoshi2115No ratings yet
- LTE Important Parameters and Switches - DoDocument80 pagesLTE Important Parameters and Switches - Domausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- ACP Solution ChecklistDocument6 pagesACP Solution Checklistmausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- Handover Call FlowDocument1 pageHandover Call Flowmausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- Lte Attach PDFDocument6 pagesLte Attach PDFNitin KatariaNo ratings yet
- GC Physical Optimization ChangesDocument205 pagesGC Physical Optimization Changesmausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- Cluster Name Site Name: GC - Lords - View - 1 GC - Lords - View - 1Document2 pagesCluster Name Site Name: GC - Lords - View - 1 GC - Lords - View - 1mausam_panchal2013No ratings yet
- ACP Solution Training SlidesDocument21 pagesACP Solution Training Slidesmausam_panchal2013No ratings yet