Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Seatwork 1
Uploaded by
Ceej RevsCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Seatwork 1
Uploaded by
Ceej RevsCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Revilla, Christian James C.
Section: BSA-2B ACC 214 2:15-4:15 PM
Seatwork #1 – August 25, 2020
Economic Development
1. Define Traditional Economics
Traditional economics is concerned primarily with the efficient, least-cost
allocation of scarce productive resources and with the optimal growth of these
resources over time so as to produce an ever-expanding range of goods and
services. Traditional neoclassical economics deals with an advanced capitalist world
of perfect markets; consumer sovereignty; automatic price adjustments; decisions
made on the basis of marginal, private-profit, and utility calculations; and equilibrium
outcomes in all product and resource markets. It assumes economic “rationality” and
a purely materialistic, individualistic, self-interested orientation toward economic
decision making.
2. What is New Political Economy?
Political economy goes beyond traditional economics to study, among other
things, the social and institutional processes through which certain groups of
economic and political elites influence the allocation of scarce productive resources
now and in the future, either for their own benefit exclusively or for that of the larger
population as well. Political economy is therefore concerned with the relationship
between politics and economics, with a special emphasis on the role of power in
economic decision making.
3. Briefly describe the relationship of Traditional Economics and Political Economy
with Development Economics.
Traditional Economics talks about the proper allocation of scarce productive
resources while New Political Economy goes beyond traditional and considers
power in economic decision making. Development economics is a distinct yet very
important extension of both traditional economics and political economy because it is
concerned with efficient resource allocation and the steady growth of aggregate
output over time, development economics focuses primarily on the economic, social,
and institutional mechanisms needed to bring about rapid and large-scale
improvements in standards of living for the masses of poor people in developing
nations. Consequently, development economics must be concerned with the
formulation of appropriate public policies designed to effect major economic,
institutional, and social transformations of entire societies in a very short time.
4. Explain “Economies as Social Systems”.
Economics and economic systems are not just a simple concept. They must be
analyzed in a wider and broader prospective than traditional economics. They should be
analyzed as a “social system” in an international and global context. This means that
Economies as social system is the interdependence of economic and noneconomic
factors. When we say interdependence it is the interrelatedness of every factors in a
specific country, it may be economic related or not. This statement also emphasizes
that development economics is useful in understanding problems of economic and
social progress in poor nations but we should also be mindful of the crucial roles that
values, attitudes and institutions, both domestic and international, play in overall
development process.
5. Enumerate the three core values of development and briefly describe each.
Sustenance: Ability to Meet Basic Needs
Everyone have a certain basic needs namely, food, shelter, health and
protection. These life-sustaining needs are crucial in economic development. When
these needs aren’t met, an absolute underdevelopment exists. Economic development
is a necessary condition for the improvement of quality of life. Without economic
development, the realization of human potential would not be possible.
Self-Esteem: To Be a Person
Living in a modernized and globally competitive country with high economic
progress may give us the sense of identity and pride. It means that economic
development is an important way to gain esteem talking about the people living in a
technologically and economically advance society or country.
Freedom form Servitude: To Be Able to Choose
People in highly developed countries achieve a wide range of choices.
Development is related to freedom because when an economy is developing people will
be able to maximize their resources and maximize external constraints and to achieve a
goal. Highly developed economies enable people to gain greater control over nature
and their resources compared to those poor once.
You might also like
- Development Economics Full HandoutDocument69 pagesDevelopment Economics Full HandoutS Tariku GarseNo ratings yet
- ECO-321 Development Economics: Instructor Name: Syeda Nida RazaDocument12 pagesECO-321 Development Economics: Instructor Name: Syeda Nida RazaLaiba Malik100% (1)
- Development Economics 1 &2Document43 pagesDevelopment Economics 1 &2miadjafar463No ratings yet
- Economics Lessons for the Tea Party, Most Conservatives and Some EconomistsFrom EverandEconomics Lessons for the Tea Party, Most Conservatives and Some EconomistsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3...Document10 pagesChapter 3...hakseng lyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SummaryDocument7 pagesChapter 1 SummaryArbie MoralesNo ratings yet
- Development Economics I Chapter 1 HEdited .Document10 pagesDevelopment Economics I Chapter 1 HEdited .kasuNo ratings yet
- Eco Assignmnet 1Document9 pagesEco Assignmnet 1227112supriyaNo ratings yet
- Historical Perspectives of Economic DevelopmentDocument4 pagesHistorical Perspectives of Economic DevelopmentAlzen Marie DelvoNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Multidimensional Nature of Development EconomicsDocument2 pagesUnderstanding the Multidimensional Nature of Development EconomicsArriane Aquino ViveroNo ratings yet
- Assignment in Eco DevDocument7 pagesAssignment in Eco DevLorica EloisaNo ratings yet
- Notes in Dev PersDocument29 pagesNotes in Dev PersAbam AbamNo ratings yet
- Economic and Social HistoryDocument65 pagesEconomic and Social HistoryaQwhpe0fgwa0No ratings yet
- Unit 25 Political Economy of Indian Development: 25.0 ObjectivesDocument15 pagesUnit 25 Political Economy of Indian Development: 25.0 ObjectivesShambhavi RaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document23 pagesChapter 1iqra sarwarNo ratings yet
- Ed 1Document7 pagesEd 1JerraldCliff RamirezNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Introduction and Conceptual Analysis of Development Economics. Basic Concepts and Definition of Development EconomicsDocument23 pagesChapter One: Introduction and Conceptual Analysis of Development Economics. Basic Concepts and Definition of Development Economicsbirhane amareNo ratings yet
- Economics in Micro and Macro Consistency: Challenging Old Biases with New InsightsFrom EverandEconomics in Micro and Macro Consistency: Challenging Old Biases with New InsightsNo ratings yet
- Developmental Economics NoteDocument210 pagesDevelopmental Economics NoteEshetu Mathewos100% (1)
- Economic DevelopmentDocument7 pagesEconomic DevelopmentMin MyanmarNo ratings yet
- Economic Development Goals and MeasuresDocument26 pagesEconomic Development Goals and Measuresjohn carlos doringoNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument49 pagesChapter Onemeskerem yemereNo ratings yet
- Development Concepts, Theories and PerspectivesDocument33 pagesDevelopment Concepts, Theories and PerspectivesMaria Pia100% (1)
- Dev Lec 1 Chapter 1Document28 pagesDev Lec 1 Chapter 1وائل مصطفىNo ratings yet
- Indian Eco NotesDocument10 pagesIndian Eco NotespriyankaNo ratings yet
- Prelims ReviewerDocument10 pagesPrelims ReviewerShanna Cielo Jean BerondoNo ratings yet
- BASIC ECONOMICS CompilationDocument65 pagesBASIC ECONOMICS CompilationJabby SultanNo ratings yet
- Understanding EconomicsDocument5 pagesUnderstanding EconomicsAbegail BlancoNo ratings yet
- Economic Development NotesDocument25 pagesEconomic Development Notesapi-194241825No ratings yet
- Reflection Paper: Malabanan Avegail Bsa 1-CDocument8 pagesReflection Paper: Malabanan Avegail Bsa 1-Craymark felloneNo ratings yet
- Its All in the Price: A Business Solution to the EconomyFrom EverandIts All in the Price: A Business Solution to the EconomyNo ratings yet
- Concept of Development PDFDocument33 pagesConcept of Development PDFGerard Espinoza EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Define Traditional Economics.: Torado, M & Smith, S. (2015) - Economic Development 12 Edition, pg.9Document4 pagesDefine Traditional Economics.: Torado, M & Smith, S. (2015) - Economic Development 12 Edition, pg.9people ageNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Concept and Meaning of DevelopmentDocument27 pagesChapter 1 - Concept and Meaning of DevelopmentSyaie SyaiedaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Economic Development and Economic GrowthDocument22 pagesDifference Between Economic Development and Economic GrowthPaaforiNo ratings yet
- Development EconomicsDocument5 pagesDevelopment EconomicsReal Mae PeñaNo ratings yet
- reviewer-sa-econDocument10 pagesreviewer-sa-econAvos NnNo ratings yet
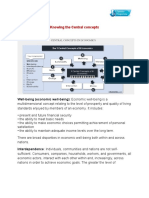
- Central ConceptsDocument3 pagesCentral ConceptsAqua PulitaNo ratings yet
- Globalization Offers Incredible OpportunitiesDocument2 pagesGlobalization Offers Incredible OpportunitiesSteffanie TalaueNo ratings yet
- Economic Development Theories and StrategiesDocument80 pagesEconomic Development Theories and Strategiestubenaweambrose100% (2)
- Dev Econ FinalDocument8 pagesDev Econ FinalPrincess Joy ManiboNo ratings yet
- San Jose Community College economic analysisDocument9 pagesSan Jose Community College economic analysisAbegail BlancoNo ratings yet
- DE I - PPT - Ch 1Document63 pagesDE I - PPT - Ch 1barkeNo ratings yet
- Development Economics ExplainedDocument88 pagesDevelopment Economics ExplainedSagar SunuwarNo ratings yet
- UNIT I - INTRODUCTION TO ECON (Part 2)Document7 pagesUNIT I - INTRODUCTION TO ECON (Part 2)Judy Mar Valdez, CPANo ratings yet
- Eco Dev ReportDocument4 pagesEco Dev ReportPostigo HajieNo ratings yet
- (Sales) Economics NotesDocument68 pages(Sales) Economics NotesFerdy (Ferdy)No ratings yet
- The Concept of Development DEFINITIONS, THEORIES AND Contemporary PerspectivesDocument35 pagesThe Concept of Development DEFINITIONS, THEORIES AND Contemporary PerspectivesAmidu Bidemi100% (1)
- Economic development goals for sustained growthDocument5 pagesEconomic development goals for sustained growthBernardokpeNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Development ReportDocument7 pagesApproaches To Development ReportHadji Mohammad Ajul MunicipalityNo ratings yet
- Dev Lec 1 Chapter 1Document28 pagesDev Lec 1 Chapter 1وائل مصطفى0% (1)
- Build The World EconomyDocument35 pagesBuild The World EconomyMusbri MohamedNo ratings yet
- Ecodev Module 2 Part 1Document12 pagesEcodev Module 2 Part 1Mae VillarNo ratings yet
- Concept and Dimension of DevelopmentDocument2 pagesConcept and Dimension of Developmentgheljosh100% (3)
- Reforming Asian Labor Systems: Economic Tensions and Worker DissentFrom EverandReforming Asian Labor Systems: Economic Tensions and Worker DissentNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document22 pagesLecture 1Muhammad Amir /FSSNo ratings yet
- Assignment Econ DevDocument2 pagesAssignment Econ DevKris Joseph LasayNo ratings yet
- Noli El WorksheetDocument3 pagesNoli El WorksheetCeej RevsNo ratings yet
- Infographics by Revilla, Sanchez, Jimenez, Hinlo, ArtajoDocument1 pageInfographics by Revilla, Sanchez, Jimenez, Hinlo, ArtajoCeej RevsNo ratings yet
- Sucesos WorksheetDocument3 pagesSucesos WorksheetCeej RevsNo ratings yet
- True of False 1. True 2. True 3. True 4. False 5. FalseDocument4 pagesTrue of False 1. True 2. True 3. True 4. False 5. FalseCeej RevsNo ratings yet
- True of False 1. True 2. True 3. True 4. False 5. FalseDocument4 pagesTrue of False 1. True 2. True 3. True 4. False 5. FalseCeej RevsNo ratings yet
- Movie Analysis (Revilla & Sanchez)Document2 pagesMovie Analysis (Revilla & Sanchez)Ceej RevsNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper - Revilla and SanchezDocument1 pageReaction Paper - Revilla and SanchezCeej RevsNo ratings yet
- Movie Review (REVILLA and SANCHEZ)Document4 pagesMovie Review (REVILLA and SANCHEZ)Ceej RevsNo ratings yet
- Movie Analysis (Revilla & Sanchez)Document2 pagesMovie Analysis (Revilla & Sanchez)Ceej RevsNo ratings yet
- MAPPING - GROUP 2 Revilla and SanchezDocument1 pageMAPPING - GROUP 2 Revilla and SanchezCeej RevsNo ratings yet
- Venetian Courtesans Annotated BibliographyDocument2 pagesVenetian Courtesans Annotated BibliographyNick WhitelawNo ratings yet
- PLJ Volume 29 Number 4 - 06 - Recent Decisions - Election LawDocument10 pagesPLJ Volume 29 Number 4 - 06 - Recent Decisions - Election LawTammy YahNo ratings yet
- REIC Form-I IIDocument3 pagesREIC Form-I IIIAS MeenaNo ratings yet
- Practice Cards - Josh LametDocument3 pagesPractice Cards - Josh LametJosh LameyNo ratings yet
- Malaysia and Construction Industry Present: ArticleDocument10 pagesMalaysia and Construction Industry Present: ArticleJoanneNo ratings yet
- Felix Klomega Vrs. Attorney General & 3 Ors.2Document18 pagesFelix Klomega Vrs. Attorney General & 3 Ors.2mba group2No ratings yet
- The Two Sides of SportsDocument8 pagesThe Two Sides of SportsDnl VelasquezNo ratings yet
- The Ethics of Care - An Obligation to Exercise Special CareDocument16 pagesThe Ethics of Care - An Obligation to Exercise Special CareamiteshnegiNo ratings yet
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Europe in The Modern World A New Narrative History Since 1500 PDF ScribdDocument42 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF Europe in The Modern World A New Narrative History Since 1500 PDF Scribdchester.whelan111100% (40)
- Origin of The Neighbourhood UnitDocument20 pagesOrigin of The Neighbourhood UnitHUI WANGNo ratings yet
- BFP Personnel Attend Fire Safety OrientationDocument5 pagesBFP Personnel Attend Fire Safety OrientationCandelaria FirefighterNo ratings yet
- How Barristers and Solicitors in England Could UnifyDocument21 pagesHow Barristers and Solicitors in England Could UnifyhelllooNo ratings yet
- 3rd 9 WEEKS BELLWORK AnsweredDocument4 pages3rd 9 WEEKS BELLWORK AnsweredobrezNo ratings yet
- Ching AgcaoiliDocument39 pagesChing AgcaoiliAlj SolemnNo ratings yet
- The 1988 Constitutional Crisis in MalaysiaDocument26 pagesThe 1988 Constitutional Crisis in MalaysiaJiaqi WongNo ratings yet
- Community Policing: Answer To SDG 16Document2 pagesCommunity Policing: Answer To SDG 16Bonz YbañezNo ratings yet
- Naskah Soal Sumatif Utama Bahasa Inggris 2023 KirimDocument14 pagesNaskah Soal Sumatif Utama Bahasa Inggris 2023 KirimSiti HoliaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Cyber AttacksDocument47 pagesPresentation On Cyber AttacksSyed Fahad KhanNo ratings yet
- Mirza Zulfiqur Rahman - MPhil SynopsisDocument19 pagesMirza Zulfiqur Rahman - MPhil SynopsisDeep Jyoti BarmanNo ratings yet
- Activity Design - KITA KAUBANDocument3 pagesActivity Design - KITA KAUBANJohn Keach CoyocaNo ratings yet
- An Irresistible Force Meets An Immovable Object:: The Minsk Group Negotiations On The Status of Nagorno KarabakhDocument25 pagesAn Irresistible Force Meets An Immovable Object:: The Minsk Group Negotiations On The Status of Nagorno KarabakhOctavian MaresNo ratings yet
- Form 1040Document2 pagesForm 1040karthu48No ratings yet
- Fomulario DS160Document4 pagesFomulario DS160José Ramón Marcelino RuizNo ratings yet
- Info Request FormDocument1 pageInfo Request FormAlexsei Aye-VapeNo ratings yet
- Shariati and Marx - A Critique of An Islamic Critique of Marxism - Asef BayatDocument24 pagesShariati and Marx - A Critique of An Islamic Critique of Marxism - Asef Bayatnegartaym100% (2)
- Pimentel v. Executive Secretary G.R. No. 158088Document13 pagesPimentel v. Executive Secretary G.R. No. 158088albemart100% (1)
- Student Council InfoDocument9 pagesStudent Council InfoShelby Nail100% (1)
- 12ATiffinPostcolonialLiteraturesandCounter Discourse (Weekes, Inniss,&Haynes)Document3 pages12ATiffinPostcolonialLiteraturesandCounter Discourse (Weekes, Inniss,&Haynes)paolaNo ratings yet
- Changing Attitudes Aging in AmericaDocument8 pagesChanging Attitudes Aging in AmericaMaruko KemNo ratings yet
- Digest - Arceta V Judge MangrobangDocument2 pagesDigest - Arceta V Judge MangrobangVic RabayaNo ratings yet