Professional Documents
Culture Documents
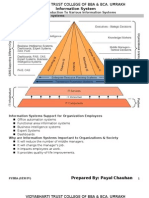
Management Information System
Uploaded by
dipanshooOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Management Information System
Uploaded by
dipanshooCopyright:
Available Formats
Management information system
A management information system (MIS) is a system that provides information needed to
manage organizations effectively. Management information systems are regarded to be a subset
of the overall internal controls procedures in a business, which cover the application of people,
documents, technologies, and procedures used by management accountants to solve business
problems such as costing a product, service or a business-wide strategy. Management
information systems are distinct from regular information systems in that they are used to
analyze other information systems applied in operational activities in the organization.
Academically, the term is commonly used to refer to the group of information management
methods tied to the automation or support of human decision making, e.g. Decision Support
Systems, Expert systems, and Executive information systems.
Transaction processing system
A transaction processing system is a type of information system. TPSs collect, store, modify, and
retrieve the transactions of an organization. A transaction is an event that generates or modifies
data that is eventually stored in an information system. To be considered a transaction processing
system the computer must pass the ACID test. The essence of a transaction program is that it
manages data that must be left in a consistent state. E.g. if an electronic payment is made, the
amount must be both withdrawn from one account and added to the other; it cannot complete
only one of those steps. Either both must occur, or neither. In case of a failure preventing
transaction completion, the partially executed transaction must be 'rolled back' by the TPS. While
this type of integrity must be provided also for batch transaction processing, it is particularly
important for online processing: if e.g. an airline seat reservation system is accessed by multiple
operators, after an empty seat inquiry, the seat reservation data must be locked until the
reservation is made, otherwise another user may get the impression a seat is still free while it is
actually being booked at the time. Without proper transaction monitoring, double bookings may
occur. Other transaction monitor functions include deadlock detection and resolution (deadlocks
may be inevitable in certain cases of cross-dependence on data), and transaction logging (in
'journals') for 'forward recovery' in case of massive failures.
Transaction Processing is not limited to application programs. The 'journaled file system'
provided with IBMs AIX Unix operating system employs similar techniques to maintain file
system integrity, including a journal.
You might also like
- Information System Transactions Data ACID Test: TypesDocument3 pagesInformation System Transactions Data ACID Test: TypesNilesh BidriNo ratings yet
- MIS Assignment: by Rubina Naaz Mba 4 SemDocument9 pagesMIS Assignment: by Rubina Naaz Mba 4 SemXoheb KhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Why Information Technology Is Needed?Document45 pagesAssignment: Why Information Technology Is Needed?harshadashitoleNo ratings yet
- DssDocument35 pagesDsshsrinivas_7No ratings yet
- Assignment - 1: Information Systems and Digital FirmsDocument12 pagesAssignment - 1: Information Systems and Digital FirmsKartik SinghNo ratings yet
- Transaction Programs (A Special Kind of Program) - The Essence of A Transaction ProgramDocument6 pagesTransaction Programs (A Special Kind of Program) - The Essence of A Transaction Programraazoo19No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2itbDocument23 pagesCHAPTER 2itbVarun VaruNo ratings yet
- TPS SystemDocument13 pagesTPS SystemTanvir Ahmed ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Information SystemsDocument6 pagesInformation Systemsa.dukhieNo ratings yet
- Mis & ErpDocument11 pagesMis & Erpkar3kNo ratings yet
- Information System: Navigation SearchDocument19 pagesInformation System: Navigation SearchChankel PasrichaNo ratings yet
- Notes-Types of Information SystemsDocument10 pagesNotes-Types of Information SystemsSaurav MaddyNo ratings yet
- Topic 7-8 Information Systems in An EnterpriseDocument19 pagesTopic 7-8 Information Systems in An EnterpriseBENSON NGARINo ratings yet
- AIS Chapter 1Document5 pagesAIS Chapter 1Reyna Marie Labadan-LasacarNo ratings yet
- Kathlyn A. Dela Cruz - BSAIS 1CDocument2 pagesKathlyn A. Dela Cruz - BSAIS 1CKathlyn Dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Types of Information SystemsDocument11 pagesTypes of Information SystemsvivekkumarsNo ratings yet
- Types of Information SystemDocument4 pagesTypes of Information SystemDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Management Information System (MIS)Document24 pagesManagement Information System (MIS)SaniSahNo ratings yet
- C Information Systemapplication Landscape: Aa SYSDocument6 pagesC Information Systemapplication Landscape: Aa SYSghuk_007No ratings yet
- IsmDocument22 pagesIsmdevenrawat.03No ratings yet
- Sheet For MID TermDocument34 pagesSheet For MID Termএ.বি.এস. আশিকNo ratings yet
- Panganiban, Micol D. Bsa - 3 Types of Information SystemsDocument4 pagesPanganiban, Micol D. Bsa - 3 Types of Information SystemsPmpl PmplNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument18 pagesManagement Information SystemHaqiqat AliNo ratings yet
- Unit 02Document21 pagesUnit 02harsh hariharnoNo ratings yet
- Transaction Processing SystemDocument12 pagesTransaction Processing Systemmelvinmegha0% (1)
- BUS 516 - Chapter 2 - Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument50 pagesBUS 516 - Chapter 2 - Global E-Business and CollaborationArju LubnaNo ratings yet
- JAMES A. HALL - Accounting Information System Chapter 1Document41 pagesJAMES A. HALL - Accounting Information System Chapter 1Joe VaTa75% (4)
- Unit 4 PDFDocument61 pagesUnit 4 PDFNivithaNo ratings yet
- Transaction Processing SystemsDocument6 pagesTransaction Processing SystemsJonathanNo ratings yet
- Subsystems of MisDocument2 pagesSubsystems of MisRam PriyaNo ratings yet
- Information SystemsDocument7 pagesInformation SystemsBalajiNo ratings yet
- Mis AssignmentDocument11 pagesMis AssignmentAbubakar UmarNo ratings yet
- Different Application of Information Systems: Packet Voip Broadband DSL IP AddressDocument5 pagesDifferent Application of Information Systems: Packet Voip Broadband DSL IP AddressAseel AseelNo ratings yet
- Test 2Document48 pagesTest 2Daniel DjpNo ratings yet
- Business Communication Assignment 02Document9 pagesBusiness Communication Assignment 02Aiou MSCNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document24 pagesChapter 2Rojesh BasnetNo ratings yet
- Accounting 1Document5 pagesAccounting 1Dương Nguyễn ThuỳNo ratings yet
- ISM Unit-4Document18 pagesISM Unit-4upkeeratspamNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - Dioquino, Myka Ella V.Document2 pagesAssignment 2 - Dioquino, Myka Ella V.Myka Ella DioquinoNo ratings yet
- Acc. Info. Sys By. James A. HallDocument3 pagesAcc. Info. Sys By. James A. HallKesiah FortunaNo ratings yet
- Section I Information Technology in ManagementDocument50 pagesSection I Information Technology in ManagementkrishrajputNo ratings yet
- Is ClassificationDocument9 pagesIs ClassificationJitendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Information System: Operational-Level Systems Support Operational Managers by Keeping TrackDocument17 pagesInformation System: Operational-Level Systems Support Operational Managers by Keeping TrackAvreile RabenaNo ratings yet
- Types of Management Information SystemsDocument15 pagesTypes of Management Information SystemsAeros Padua50% (2)
- Tactical and Operational Level of ManagementDocument5 pagesTactical and Operational Level of ManagementJowanna Burce100% (6)
- ALLLDocument21 pagesALLLJignesh VallappilekandyNo ratings yet
- Types of InformationDocument10 pagesTypes of InformationMary Grace Dimaculangan PobleteNo ratings yet
- Ch3.Intro To Various IsDocument18 pagesCh3.Intro To Various IsRajdeep M. MahidaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information System: HistoryDocument6 pagesAccounting Information System: HistorySamer IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Section I What Is "Information Systems"?Document19 pagesSection I What Is "Information Systems"?doscarfNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information System Chapter 1Document28 pagesAccounting Information System Chapter 1Cassie100% (1)
- James Hall IDocument8 pagesJames Hall ITafadzwa Leon SemuNo ratings yet
- Transaction Processing SystemDocument3 pagesTransaction Processing SystemAgrippa MungaziNo ratings yet
- Types of Information SystemDocument14 pagesTypes of Information SystemAleena IdreesNo ratings yet
- History : Accounting Decision MakersDocument8 pagesHistory : Accounting Decision MakersEmily BishopNo ratings yet
- Group Assigment - VADSDocument13 pagesGroup Assigment - VADSfizputeriNo ratings yet
- Zero To Mastery In Cybersecurity- Become Zero To Hero In Cybersecurity, This Cybersecurity Book Covers A-Z Cybersecurity Concepts, 2022 Latest EditionFrom EverandZero To Mastery In Cybersecurity- Become Zero To Hero In Cybersecurity, This Cybersecurity Book Covers A-Z Cybersecurity Concepts, 2022 Latest EditionNo ratings yet
- MISDocument193 pagesMISAmerulzai Syaza100% (1)
- It Notes CattolicaDocument44 pagesIt Notes CattolicaTeodora NedeljkovićNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Securing Information SystemDocument35 pagesChapter 8 Securing Information Systemjackie cramerNo ratings yet
- Studying at TU ClausthalDocument74 pagesStudying at TU ClausthalMahdi NuriantoNo ratings yet
- Justification For and Nature of ChangesDocument8 pagesJustification For and Nature of ChangesRida ZainebNo ratings yet
- AiS Module 1Document5 pagesAiS Module 1jhell dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Information Technology MISDocument21 pagesInformation Technology MISDeepak Daya Matta0% (1)
- Ais Development Strategies Suggested Answers To Discussion QuestionsDocument33 pagesAis Development Strategies Suggested Answers To Discussion QuestionsDon RajuNo ratings yet
- Ncircle WP NIST80053 1061 03Document9 pagesNcircle WP NIST80053 1061 03bonecrusherclanNo ratings yet
- Assefacv CbeDocument7 pagesAssefacv CbeTekelemariam FitwiNo ratings yet
- Abc Analysis of Eis & SMDocument12 pagesAbc Analysis of Eis & SMPrem ThakurNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Operational PlanDocument32 pagesMaintenance Operational PlanAry SetiyonoNo ratings yet
- Ict 11 PDFDocument166 pagesIct 11 PDFThurka Jayanth ThevakadatchamNo ratings yet
- MIS Assignment Question - RevisedDocument3 pagesMIS Assignment Question - RevisedSneha MuraliNo ratings yet
- HGES408 ModuleDocument138 pagesHGES408 ModuleBupe MaphosaNo ratings yet
- Health Management Information System: Lesson 6Document8 pagesHealth Management Information System: Lesson 6Jennifer Ledesma-PidoNo ratings yet
- Inter Paper9 PDFDocument770 pagesInter Paper9 PDFSagnik MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Tonya Barrier - IRM Press - 2002 - Human Computer Interaction Development and ManagementDocument336 pagesTonya Barrier - IRM Press - 2002 - Human Computer Interaction Development and ManagementlogtamNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 IscaDocument1 pageChapter-6 IscakishorejiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of ITDocument34 pagesFundamentals of ITYuyu GupthaNo ratings yet
- Online Chapter A - The Role of The Systems AnalystDocument12 pagesOnline Chapter A - The Role of The Systems AnalystNakye BibianaNo ratings yet
- Cia2002 Accounting Information Systems SEM 1 2017/2018 TUTORIAL 1 Thiba A/P Sathivel (Cia 160182)Document2 pagesCia2002 Accounting Information Systems SEM 1 2017/2018 TUTORIAL 1 Thiba A/P Sathivel (Cia 160182)Thiba SathivelNo ratings yet
- FAQ Basic Accounting ConceptsDocument183 pagesFAQ Basic Accounting ConceptsNowmaster100% (20)
- Mekelle University College of Business and Economics Department of ManagementDocument38 pagesMekelle University College of Business and Economics Department of Managementmeseret sisay100% (2)
- Detailed MBA CourseStructureDocument132 pagesDetailed MBA CourseStructureanchals_20No ratings yet
- Mis SCDLDocument180 pagesMis SCDLdubeyr_anand100% (1)
- Accounting Info and Financial PerformanceDocument61 pagesAccounting Info and Financial PerformancevitalisNo ratings yet
- International Conference On Automation, Control Engineering & Computer ScienceDocument107 pagesInternational Conference On Automation, Control Engineering & Computer ScienceIPCO AssistanteNo ratings yet
- What Ethical, Social, and Political Issues Are Raised: by Information Systems?Document19 pagesWhat Ethical, Social, and Political Issues Are Raised: by Information Systems?Muhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information SystemsDocument3 pagesAccounting Information SystemsMaria Eloisa BautistaNo ratings yet