Professional Documents
Culture Documents
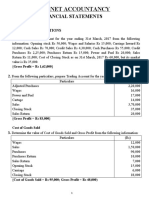
The Trial Balance
Uploaded by
Dhairya AilaniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Trial Balance
Uploaded by
Dhairya AilaniCopyright:
Available Formats
The Trial Balance
Definition: A trial balance is a list of
balances on the accounts in the ledger at a
certain date.
Note: It is not a part of the double entry system. It
Uses/ Purpose of a Trial Balance
1. It helps in locating arithmetical errors.
2. It is useful in preparing financial statements
(Income Statement & Statement of Financial Position)
3. It helps in the rectification of errors
4. To check the arithmetical accuracy
5. To know the ending balance of each account at a
glance
Limitations of a Trial Balance
1. It does not prove that all transactions have been recorded
2. Numerous errors may exist even though the trial balance columns agree
Format of Trial Balance
Name of the account Debit($) Credit($)
Capital √
Drawings √
Premises √
Discount Received √
Discount Allowed √
Salary √
Provision for Depreciation √
Bank Balance √
Bank Overdraft √
Inventory (only opening inventory NOT closing inventory) √
Cash √
Trade Payables √
Trade Receivables √
Total (Debit = Credit) √√√ √√√
The trial balance & errors
If the trial balance fails to balance, the reasons may be as follows:
1. an error of addition within the trial balance
2. An error of addition within one of the ledger accounts
3. Entering a different figure on the credit ti that entered on the debit when
making a double entry in the ledger
4. Making a single entry for a transaction rather than a double entry
5. Entering a transaction twice on the same side of the ledger
Types of Errors not revealed by a Trial Balance
Error of commission
This occurs when a transaction is enteres using the correct
amount and on the correct side,but in the wrong account
of the same class ( Personal, Real or Nominal).
Example: Cash received from Sara credited to Saira’s account
Correct Entry Debit Credit Wrong Entry Debit Credit
Cash √ Cash √
Sara √ Saira √
Types of Errors not revealed by a Trial Balance
Error of complete reversal
This occurs when the correct amount is entered in the
correct accounts, but the entry has been made on the
wrong side of each account.
Example: Cash drawings debited to the cash account
and credited to the drawings account.
Correct Entry Debit Credit Wrong Entry Debit Credit
Drawings √ Cash √
Cash √ Drawings √
Types of Errors not revealed by a Trial Balance
Error of omission
This occurs when a transaction has been completely
omitted from the accounting records. Neither a debit entry
nor a credit entry has been made.
Example: Payment of wages not entered in the books.
Correct Entry Debit Credit Wrong Entry Debit Credit
Wages √ NO ENTRY
Cash √ NO ENTRY
Types of Errors not revealed by a Trial Balance
Error of original entry
This occurs when an incorrect figure is used when a
transaction is first entered in the accounting records. The
double entry will therefore use the incorrect figure.
Example: Goods, $100, bought but recorded as $1000.
Correct Entry Debit Credit Wrong Entry Debit Credit
Purchase 100 Purchase 1000
Cash/Bank 100 Cash/Bank 1000
Types of Errors not revealed by a Trial Balance
Error of principle(rule)
This occurs when a transaction is entered using the correct
amount and on the correct side, but in the wrong class of
account.
Example: Motor expenses debited to the motor vehicles account.
Correct Entry Debit Credit Wrong Entry Debit Credit
Motor Expenses ( Nominal) √ Motor vehicles (Real) √
Cash/Bank √ Cash/Bank √
Types of Errors not revealed by a Trial Balance
Compensating Errors
These occur when two or more errors cancel each other
out.
Example: Purchases account under-added by $100 and
sales returns account over-added by $100.
Explanation: Purchases account which always has a debit balance is reduced
by $ 100- so the debit total in a trial balance is reduced by $100.
Sales returns account which always has a debit balance is increased by $100-so the
debit total in a trial balance increases by $100.
This was what was reduced in one account has been increased in another account.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- DeliveryDocument25 pagesDeliverymarcusjwheeler013No ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- EXAM Intermediate Accounting 2Document8 pagesEXAM Intermediate Accounting 2Grace100% (1)
- Assignment 2Document13 pagesAssignment 2Lyca Mae Cubangbang100% (2)
- M 2221 EvidenceDocument2 pagesM 2221 EvidenceDhairya AilaniNo ratings yet
- M2221STORAGEDocument2 pagesM2221STORAGEDhairya AilaniNo ratings yet
- M 2221 ExtraDocument1 pageM 2221 ExtraDhairya AilaniNo ratings yet
- M2221DELNOTEDocument1 pageM2221DELNOTEDhairya AilaniNo ratings yet
- M2221PRESDocument4 pagesM2221PRESDhairya AilaniNo ratings yet
- Double Entry Bookkeeping - Part ADocument1 pageDouble Entry Bookkeeping - Part ADhairya AilaniNo ratings yet
- 2.trial Balance-Hans Lee-9-6-2021Document5 pages2.trial Balance-Hans Lee-9-6-2021Dhairya AilaniNo ratings yet
- Double Entry Bookkeeping - Part ADocument1 pageDouble Entry Bookkeeping - Part ADhairya AilaniNo ratings yet
- 1.trial Balance and Ledger AccountsDocument3 pages1.trial Balance and Ledger AccountsDhairya AilaniNo ratings yet
- Podar International School: 1. Introduction To AccountingDocument3 pagesPodar International School: 1. Introduction To AccountingDhairya AilaniNo ratings yet
- Sonali Bank InternshipDocument55 pagesSonali Bank Internshipসৃজনশীলশুভ100% (1)
- Practical Questions (Sandeep Garg 2018-19)Document10 pagesPractical Questions (Sandeep Garg 2018-19)Kanishk SinglaNo ratings yet
- PPSC E-Pay User ManualDocument8 pagesPPSC E-Pay User ManualkaleemNo ratings yet
- Group Corporate Structure: Commercial Banking Investment BankingDocument1 pageGroup Corporate Structure: Commercial Banking Investment BankingizhsaidinNo ratings yet
- Financial AnalysisDocument4 pagesFinancial Analysischanellayang124No ratings yet
- Be Forward Co., LTD.: BK323869 CHASSIS NO.: JTJZA11A202409054Document1 pageBe Forward Co., LTD.: BK323869 CHASSIS NO.: JTJZA11A202409054Mohamed Umer100% (1)
- ExecutiveDocument1 pageExecutiveShams GalibNo ratings yet
- c02TheRecordingProcess in Class PDFDocument8 pagesc02TheRecordingProcess in Class PDFawin rahma zulviaNo ratings yet
- COA Unit 2 Issue of Shares - ProblemsDocument3 pagesCOA Unit 2 Issue of Shares - ProblemsGayatri Prasad BirabaraNo ratings yet
- PNB Personal Loan Scheme-Pnb Sahyog Covid 19Document17 pagesPNB Personal Loan Scheme-Pnb Sahyog Covid 19Nishesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Report Fin GroupDocument10 pagesReport Fin GroupFATIMAH ZAHRA BINTI ABDUL HADI KAMELNo ratings yet
- Chandak Insurance Services: Magic Mix Illustration For Mr. - (Age 25)Document5 pagesChandak Insurance Services: Magic Mix Illustration For Mr. - (Age 25)Mohit DhakaNo ratings yet
- Happy Tails Inc Has A September 1 Accounts Payable BalanceDocument1 pageHappy Tails Inc Has A September 1 Accounts Payable BalanceM Bilal SaleemNo ratings yet
- RELEBUS - Negotiable Instrument (Part 1)Document10 pagesRELEBUS - Negotiable Instrument (Part 1)Abby Gail TiongsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Cash and Cash Equivalents Expected Question(s) :: Cash On Hand Cash Fund Cash in BankDocument8 pagesChapter 1: Cash and Cash Equivalents Expected Question(s) :: Cash On Hand Cash Fund Cash in BankJulie Mae Caling MalitNo ratings yet
- AIG's Dangerous Collapse - by Daniel R. Amerman, FSU Editoria..Document10 pagesAIG's Dangerous Collapse - by Daniel R. Amerman, FSU Editoria..Todd BengertNo ratings yet
- Celesta Terms and ConditionsDocument6 pagesCelesta Terms and ConditionsLUCtech win10No ratings yet
- Fixed Income and Credit Risk: Prof. Michael RockingerDocument17 pagesFixed Income and Credit Risk: Prof. Michael RockingerJean BoncruNo ratings yet
- PDL BioPharma Selling Off Noden PDFDocument5 pagesPDL BioPharma Selling Off Noden PDFfilipandNo ratings yet
- 3371 9358 1 PBDocument8 pages3371 9358 1 PBMuhammad AkbarNo ratings yet
- NEFT/RTGS E-Receipt: Dayananda Sagar Academy of Tech and MGMT ICL9080754472685 ICIC0000103Document3 pagesNEFT/RTGS E-Receipt: Dayananda Sagar Academy of Tech and MGMT ICL9080754472685 ICIC0000103study materialNo ratings yet
- 4 Tangible Fixed Assets: DR CR 000 000Document7 pages4 Tangible Fixed Assets: DR CR 000 000Fazal Rehman MandokhailNo ratings yet
- MA Dissertation Final-1Document102 pagesMA Dissertation Final-1Ciara PatelNo ratings yet
- Application Form For UPDocument1 pageApplication Form For UPankitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 - Intercorporate Acquisitions and Investments in Other EntitiesDocument21 pagesChapter 01 - Intercorporate Acquisitions and Investments in Other Entitiesdella salsabilaNo ratings yet
- Remittance Directory: Metrobank Foreign Branches & SubsidiariesDocument11 pagesRemittance Directory: Metrobank Foreign Branches & SubsidiariesJay PelitroNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Financial Performance of Nationalized Commercial Banks (NCBS) in BangladeshDocument78 pagesAn Analysis of Financial Performance of Nationalized Commercial Banks (NCBS) in BangladeshPhilip KotlerNo ratings yet