Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sales of Goods Act 1930
Uploaded by
Biswanath MishraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sales of Goods Act 1930
Uploaded by
Biswanath MishraCopyright:
Available Formats
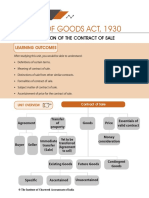
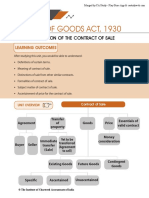
BUSINESS LAWS
CA Foundation - Paper 2A - Business Laws
In this capsule, we have summarized the important concepts of the Unit 1 and 2 of the Chapter 2: The Sale of Goods
Act, 1930. From Examination point of view, this chapter comprises of around 12 to 14 marks of the paper. In this
chapter, students are tested with conceptual understanding of the legal provisions, as well application of the important
concepts in the simple practical scenarios. This capsule will help the students to revise and retain essentials of some
of the important definitions and various requirements in the formation of the Contract of Sale.
The Sale of Goods Act, 1930
2. Goods [Section 2(7)] and related terms
Primer to the Sale of Goods Act, 1930
Other Also
Goods includes
than
• Sale of goods is one of the specific forms of contracts recognized
and regulated by law in India. M e a n s Actionable Stock &
• It is an Act to define and amend the laws relating to the sale of every kind claims Shares
goods. of movable
property
• It came into force on 1st July, 1930. Growing
• The provisions of the Act are applicable to the sale of ONLY crops
movable properties and the Act is not applicable to immovable “Goods” include both Money in
properties. tangible goods and circulation Grass, and
• It extends to the whole of India. intangible goods
T h i n g s
attached to
‘Actionable claims’ are claims, which or forming
can be enforced only by an action / suit. part of land
Formation of the Contract of Sale Ex: debt. A debt is not a movable which agreed
property or goods. to be severed
Framework
3. Classification of Goods
Contract of Sale
Broadly classified as Goods
Transfer of Essentials of Existing Future Contingent
Agreement Goods Price Valid contract Goods Goods Goods
property
Specific Ascertained Unascertained
Buyer Seller Existing Future Contingent
Goods Goods Goods
Specific classification of goods
Money
Immediate Yet to be consideration
transfer transferred
(sale) (Agreement Goods in existence
to sale) Specific Ascertained Unascertained at the time of the
contract of sale;
Existing Goods
(Section 6) or
Goods owned /
Important Terminologies possessed/ acquired by
the seller at the time of
1. Buyer and Seller Types of existing contract of sale
goods
A person who buys or agrees to buy goods [Section
2(1)].
Buyer • Goods identified & agreed upon at the time a
Specific contract of sale is made
Goods • Ex: Samsung Galaxy S7 Edge, IFB washing
• A person who sells or agrees to sell goods machine of 7 kg
[Section 2(13)].
Seller • Ex: On 1st June 2021, A agrees to sell 100 bales of • Goods which are identified in accordance with the
cotton to B for Rs. 1000. Here, A is a Seller and B agreement after the contract of sale is made.
Ascertained • Ex: “A” owns 10 Maruti Cars. “B” contracts with
is a Buyer. Goods “A” to buy one out of them. After the contract,
“A” keeps out one car to be given to “B”.
• Goods which are not specifically identified
or ascertained at the time of making of the
Unascertained
contract
goods • Ex: “A” owns 10 Maruti Cars. “B” contracts with
“A” to buy any one car out of them.
28 July 2021 The Chartered Accountant Student
BUSINESS LAWS
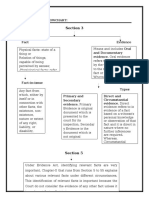
Future Goods Contingent Goods 7. Property [Section 2(11)]
[Section 2 (6)]. [Section 6(2)] Property means
• Goods to be • The acquisition of which
manufactured or • by the seller
produced or • depends upon an uncertain ownership in goods/ and not merely
acquired contingency (uncertain event) General Property a special property
• by the seller after making • Ex: P contracts to sell 500
the contract of sale pieces of particular item 8. Price [Section 2(10)]
• Ex: 1000 quintals of provided the ship which is
potatoes to be grown in Mr. bringing them reaches the
A's field. port safely. Money consideration for a sale of goods
4. Delivery – Meaning [Section 2(2)]
Essential
It is the value expressed in requirement to
of goods monetary terms make a contract
voluntary from one of sale of goods
transfer of person to Delivery
possession another
Sale and agreement to sell [Section 4]
1.Meaning of Contract of Sale of goods
5. Types of Delivery
It is a
(i) the seller transfers, or (ii) agrees to transfer
contract
- the property in goods to the buyer for a price
whereby
Constructive
delivery 2. Mode for contract of sale of goods
• Goods physically • delivery of a
delivered to the • without any thing in token A contract for the sale of goods may be either through
buyer. change in of a transfer of
• Ex: A shop- the custody something else Where the transfer
keeper sold one or actual • Ex: Key of a Where the of the property in
Apple Smart possession of warehouse property in the goods
watch to B. the thing. containing the goods
• Ex: A ware- goods is handed Agreement take place at
Sale to sell a future time
houseman over to buyer. is transferred
holding the from the subject to
goods of A seller to the fulfillment of
agrees to hold buyer some condition
them on behalf
of B, at A’s
request. Symbolic An agreement to sell becomes a sale-
Actual delivery
delivery when the time elapses or the conditions are
fulfilled subject to which the property in the
goods is to be transferred. [Section 4(4)]
3. Differences in Sale and Agreement to Sell
6. Document of title to goods [Section 2(4)]
Basis of difference Sale Agreement to sell
either by Transfer of Immediately Future Date or
endorsement or property fulfillment of condition
by delivery,
Nature of contract Executed Executory
the possessor of Remedies for Sue for price Sue for damages only
for authorizing the document to breach and not for price
or purporting to transfer or receive Liability of parties Liability of the buyer Liability of the seller
authorize, goods thereby
represented Burden of risk Buyer Seller
“Document Nature of rights Jus in rem Jus in personam
of title to Right of resale Seller cannot re-sell Seller may re-sell
goods Ex: Bill of lading, dock the goods
Proof of the
warrant, warehouse
possession or Insolvency of Official Assignee Official Assignee
keeper’s certificate,
control of goods seller • not be able to take • acquire control
or wharfinger’s certificate,
over the goods over the goods
railway receipt, warrant,
• will recover the • the price will not be
an order of delivery of
price from the recoverable.
goods
buyer.
Insolvency of Official Assignee Official Assignee
buyer • control over the • no control over the
goods. goods.
The Chartered Accountant Student July 2021 29
BUSINESS LAWS
4. Contract of sale – elements must co-exist
Procedure for conduct of Contract of Sale
[Section 5]
Nature of 1. Process
Two parties: Consideration: contract of sale:
Buyer & Seller Price in money May be absolute
or conditional a contract of sale is made by
Delivery of
Fulfil other an offer to by acceptance
goods: Transfer for a price
Subject matter: essential Buy/sell of such offer
of property i.e
Movable goods elements of a
ownership to
Valid contract
take place
2. Mode of delivery and Payment
Sale Distinguished from other Similar The contract may provide
Contracts
1. Sale and Hire Purchase
Basis of difference Sale Hire- Purchase for the immediate delivery of the goods or immediate
payment of the price or Both
Time of passing Immediately On payment of last
property instalment or
Position of the Buyer is like that of Position of the hirer
party owner is like that of bailee for the delivery or payment by instalments
till final payment
or
Termination of the buyer cannot The hirer may
contract terminate the terminate the
that the delivery or payment or both shall be
contract and bound contract by returning postponed.
to pay price the goods
Burden of Risk of risk of seller Owner takes no risk
insolvency of the and has right to take
buyer back the goods 3. Mode for entering into contract of Sale
Transfer of title The buyer can pass a Hirer cannot pass
good title to a bona any title even to a A contract of
fide purchaser bonafide purchaser sale may be
made in-
Resale The buyer can Hirer cannot, unless
all installments paid
2. Sale and Bailment words of partly in writing implied from
writing mouth and partly by the conduct of
Basis of difference Sale Bailment word of mouth the parties
Transfer of Transferred from Transfer of
property seller to buyer possession of goods
from bailor to bailee
Return of goods Not possible Bailee must return the
goods to the Bailor on Subject matter of Contract of Sale [Section
accomplishment of 6, 7, & 8]
the purpose
Consideration It is the Price in It may be gratuitous 1. Goods which form the subject matter of a contract of sale
terms of money or non-gratuitous.
Existing goods
existing goods that are acquired, owned or possessed by the seller
3. Sale and contract for work and labour
Future goods
Basis of difference Sale Contract for work
the acquisition of which by the seller depends upon a contingency
and labour
which may or may not happen
Nature of Contract It’s a contract in No goods are sold,
which some goods and there is only the Whereby a contract of sale the seller purports to effect a present
are sold or are to be doing or rendering of sale of future goods, the contract operates as an agreement to sell
sold for a price some work of labour. the goods
30 July 2021 The Chartered Accountant Student
BUSINESS LAWS
2. Nature of contract of sale with respect to perishing goods
Stipulation as to time of Payment and time
Perishing Goods Future Goods of delivery [Section 11]
Where there is a contract for the Stipulation as to the Stipulations as to time
If the future goods time of payment of delivery are usually
sale of specific goods,
are specific and the essence of the
• no knowledge to the seller contract
• at the time when the
• contract was made, goods the destruction are not deemed to be of Delivery of goods
perished or become so damaged of such goods the essence from the terms must be made
• Contract is void amount to of the contract of sale, without delay
supervening unless terms of contract
Where there is an agreement to sell impossibility state otherwise.
specific goods,
• without any fault on the part of
the seller or buyer
• before the risk passes to the buyer
contract Conditions and Warranties with reference
becomes void
• and subsequently the goods to the goods [Section 12]
perishes or become so damaged 1. Meaning -Condition and Warranty
• agreement can be avoided or
becomes void. Condition Warranty
is a stipulation is a stipulation
essential to the main purpose co-lateral to the main purpose
Ascertainment of price [Section 9] of the contract, of the contract,
the breach of which gives rise the breach of which gives rise
fixed by the contract, or
to a right to treat the contract to a claim for damages
as repudiated. but not to a right to reject the
goods and treat the contract
agreed to be fixed in a manner provided by the contract, or
as repudiated.
determined by the course of dealings between the parties. 2. Differences
Point of Condition Warranty
Where price is not determined, the buyer shall pay the seller a differences
reasonable price
Meaning A stipulation A stipulation
essential to the collateral to the
main purpose of the main purpose of the
Agreement to sell at valuation [Section 10] contract. contract.
Right in case of Repudiate or claim Claim only damages
Where there is an breach damages or both
agreement to sell goods on such third party
the terms that the price is cannot or does not Conversion of A breach of condition A breach of warranty
to be fixed by the valuation make such valuation, stipulations may be treated as a cannot be treated as
of third party; and breach of warranty. a breach of condition.
3. Waiver of conditions [Section 13]
if the goods or any
part thereof have
been delivered to, and the agreement is Voluntary Waiver Compulsory Waiver
appropriated by, the buyer, thereby avoided. Waives performance of contract Non-severability of contract
he shall pay a reasonable Elect to treat condition as Fulfilment of conditions excused
price therefore. warranty by law
Where such third party is the party not in fault
prevented from making may maintain a suit for Mode of Conditions and Warranties
the valuation by the fault damages against the
of the seller or buyer, party in default.
Ex: P is having two bikes. He agrees to sell both of the bikes to may be either
‘Conditions’ and express or
S at a price to be fixed by the Q. He gives delivery of one bike ‘Warranties’
immediately. Q refuses to fix the price. As such P ask S to return implied
the bike already delivered while S claims for the delivery of the
second bike too. In the given instance, buyer S shall pay reasonable
price to P for the bike already taken. As regards the Second bike,
the contract can be avoided.
The Chartered Accountant Student July 2021 31
BUSINESS LAWS
1. Express and Implied Conditions-Meaning 5. Sale by sample [Section 17]
• Agreed upon between the parties at the time of Sale by sample
Express contract and
conditions • are expressly provided in the contract.
bulk shall buyer shall have goods shall be free
• Which are presumed by law to be present in the contract. correspond with the a reasonable from any latent
sample in quality opportunity of defect i.e. a hidden
Implied • an implied condition may be negated or waived by an comparing the bulk defect.
conditions express agreement.
with the sample
Ex: A company sold certain shoes made of special sole by sample
2. Implied Conditions-Types for the French Army. The shoes were found to contain paper not
discoverable by ordinary inspection. Held, the buyer was entitled
to the refund of the price plus damages.
Implied Conditions
6. Sale by sample as well as by description [Section 15]
Condition as to title Condition as to description
Sale by sample bulk of the goods supplied shall correspond
as well as by both with the sample and the description
description
Sale by sample Sale by sample as well as In case the goods correspond with the sample
by description but do not tally with description or vice versa
or both, buyer can repudiate the contract.
Condition as to quality
or fitness
Condition as to Ex: A agreed with B to sell certain oil described as refined
merchantability sunflower oil, warranted only equal to sample. The goods tendered
Condition as to
wholesomeness were equal to sample but contained a mixture of hemp oil. B can
reject the goods.
3. Condition as to title [Section 14]
7. Condition as to quality or fitness [Section 16(1)]
Condition as to title-
In every contract of sale, the goods
the first implied condition supplied shall be
on the part of the seller is
reasonably fit for the
purpose for which the
buyer wants them, provided
in case of sale in case of an the stated Condition as to
agreement to sell quality or fitness
are fulfilled
• The buyer should have made known to the seller the
right to sell the particular purpose for which goods are required.
right to sell the goods at the time
goods • The buyer should rely on the skill and judgement of
when the property the seller.
is to pass.
• The goods must be of a description dealt in by the
seller, whether he be a manufacturer or not
Ex: A purchased a tractor from B who had no title to it. After 2
months, the true owner spotted the tractor and demanded it Ex: ‘A’ bought a set of false teeth from ‘B’, a dentist. But the set was
from A. Held that A was bound to hand over the tractor to its not fit for ‘A’s mouth. ‘A’ rejected the set of teeth and claimed the
true owner and that A could sue B, the seller without title, for the refund of price. It was held that ‘A’ was entitled to do so as the only
recovery of the purchase price. purpose for which he wanted the set of teeth was not fulfilled.
4. Sale by description [Section 15]
8. Condition as to Merchantability [Section 16(2)]
Contract of sale of goods the goods shall correspond Condition as to Merchantability
by description with the description
• Goods should be bought by description.
• The seller should be a dealer in goods of that description.
• Exception: If the buyer has examined the goods, there shall be
no implied condition as regards defects which such examination
there is an implied condition that ought to have revealed.
Ex: A ship was contracted to be sold as “copper-fastened vessel”
Ex: A bought a black velvet cloth from C and found it to be
but actually it was only partly copper-fastened. Held that goods
damaged by white ants. Held, the condition as to merchantability
did not correspond to description and hence could be returned or
was broken.
if buyer took the goods, he could claim damages for breach.
32 July 2021 The Chartered Accountant Student
BUSINESS LAWS
9. Condition as to wholesomeness 10. Implied Warranties-Types
• In the case of eatables and
provisions, Implied Warranties
• in addition to the implied
Condition as to condition as to merchantability,
wholesomeness • there is another implied
condition that the goods shall warranty as to warranty as to
be wholesome. undisturbed quality or fitness
possession by usage of trade
Ex: A supplied F with milk. The milk contained typhoid germs. F’s Warranty as to non- disclosure of dangerous
wife consumed the milk and was infected and died. Held, there was existence of encumbrances nature of goods
a breach of condition as to fitness and A was liable to pay damages.
11. Implied warranty
Warranty as to Warranty as to Warranty as to Disclosure
undisturbed non-existence of quality or fitness of dangerous
possession encumbrances by usage of trade nature of goods
buyer shall have the goods shall An implied the goods are
and enjoy quiet be free from warranty as to dangerous in
possession of the any charge or quality or fitness nature and
goods. encumbrance for a particular
purpose may
be annexed or the buyer is
attached by the ignorant of the
If the buyer having danger,
in favour of any usage of trade
got possession of
third party not
the goods, is later
declared or known
on disturbed in his the seller must
to the buyer
possession, Ex: Shares warn the buyer
purchased from of the probable
broker expected to danger.
he is entitled to be free from bad
before or at the
sue the seller for deliveries
time the contract If there is a breach
the breach of the
is entered into. of warranty, the
warranty.
seller may be
liable in damages.
Ex: A Purchased
Ex: : S sells a car
a second hand Ex : Lid of
which was given
typewriter which disinfectant
as security by Y
happened to be powder to be
against a loan
stolen opened with care.
2. Required conditions when doctrine is not attracted:
Caveat Emptor [Section 16]
1. Meaning of doctrine • Buyer had made known to the seller
the purpose of his purchase, and
It is the duty Conditions
• buyer relied on the seller’s skill and
of the buyer to be
judgement, and
to examine satisfied
• seller’s business to supply goods of
the goods that description
Let the thoroughly
buyer before he buys
beware General rule them in order to
Caveat 3. Exceptions to Doctrine of caveat Emptor:
satisfy himself
Emptor
that the goods
will be suitable Exceptions
for his purpose • Fitness as to quality or use
Ex: A purchases a horse from B. A needed for which he is • Goods purchased under patent or brand name
the horse for riding but he did not mention buying them. • Goods sold by description
this fact to B. The horse is not suitable for • Goods of Merchantable Quality
riding but is suitable only for being driven in • Sale by sample
the carriage. Caveat emptor rule applies here • Goods by sample as well as description
and so A can neither reject the horse nor can • Trade Usage
claim compensation from B. • Seller actively conceals a defect or is guilty of fraud
The Chartered Accountant Student July 2021 33
You might also like
- The Transfer of Property Act 1882Document48 pagesThe Transfer of Property Act 1882Iqra FarooqNo ratings yet
- APES 310 Audit ProgramDocument13 pagesAPES 310 Audit ProgramShamir Gupta100% (1)
- Extinguishment of Obligations (ObliCon)Document8 pagesExtinguishment of Obligations (ObliCon)badette_balao100% (25)
- ContractsDocument16 pagesContractsRiya Jain100% (1)
- Contract Act 1872Document26 pagesContract Act 1872akash100% (1)
- Conditional Transfer Section 25 of TransDocument16 pagesConditional Transfer Section 25 of TransPreetha PNo ratings yet
- Company Law 22 Page Rapid Revision NotesDocument22 pagesCompany Law 22 Page Rapid Revision NotesHarshNo ratings yet
- RULE Against PerpetuityDocument16 pagesRULE Against PerpetuityYhimanshNo ratings yet
- May June 2014 ZA Q2Document2 pagesMay June 2014 ZA Q2Ammar Amid Bukhari100% (1)
- Main Agt 2023Document11 pagesMain Agt 2023EllerNo ratings yet
- Formation of ContractDocument15 pagesFormation of ContractVi Pin SinghNo ratings yet
- The Sale of Goods Act, 1930 The Sale of Goods Act, 1930Document17 pagesThe Sale of Goods Act, 1930 The Sale of Goods Act, 1930Zainab UnnisaNo ratings yet
- Marathon Notes of SOGA, LLP (Inc. Mind Maps and Section Revision)Document442 pagesMarathon Notes of SOGA, LLP (Inc. Mind Maps and Section Revision)RGNNishant BhatiXIIENo ratings yet
- Sale of Goods Act NotesDocument45 pagesSale of Goods Act NotesAnkit JindalNo ratings yet
- Covenants Running With LandDocument27 pagesCovenants Running With LandDivyanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Property: Topic 1. Movable and Immovable PropertyDocument28 pagesTransfer of Property: Topic 1. Movable and Immovable PropertyManjare Hassin RaadNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Property ActDocument40 pagesTransfer of Property ActShivam TyagiNo ratings yet
- Specific Relief ActDocument26 pagesSpecific Relief ActSunil beniwal100% (3)
- Kaliaperumal Pillai Vs Visalakshmi AchiDocument7 pagesKaliaperumal Pillai Vs Visalakshmi AchiParvati Nair100% (1)
- Timber Tree As Movable or Immovable PropertyDocument6 pagesTimber Tree As Movable or Immovable PropertyAditya ShahNo ratings yet
- Mortgage 14 - Chapter 6Document37 pagesMortgage 14 - Chapter 6NishantvermaNo ratings yet
- BailmentDocument24 pagesBailmentakkig1100% (1)
- Transfer of Property Act - BelDocument36 pagesTransfer of Property Act - Belshaikhnazneen67% (3)
- I. Was It Implied in Fact?: 33 SaterialeDocument9 pagesI. Was It Implied in Fact?: 33 SaterialeJFNo ratings yet
- Will and CodicilDocument16 pagesWill and CodicilHarshit MalviyaNo ratings yet
- Indian Contract Act, 1872: (Act No 9 of 1872 Including XI Chapters 266 Sections)Document7 pagesIndian Contract Act, 1872: (Act No 9 of 1872 Including XI Chapters 266 Sections)heretostudyNo ratings yet
- VIDHYODAY - Law Revision ChartsDocument20 pagesVIDHYODAY - Law Revision Chartsshethdipati2100% (1)
- MPLRC NotesDocument73 pagesMPLRC NotesAdhar jain100% (1)
- Ibc 2019Document21 pagesIbc 2019Amar AlamNo ratings yet
- Avtar Singh Transfer of Property Act PDFDocument16 pagesAvtar Singh Transfer of Property Act PDFSharvari jadhav50% (2)
- Section 13 To 21Document39 pagesSection 13 To 21jinNo ratings yet
- TP 2Document36 pagesTP 2Dolly Singh OberoiNo ratings yet
- Property Law in Brief - G C Venkata SubbaraoDocument36 pagesProperty Law in Brief - G C Venkata SubbaraoEnkayNo ratings yet
- Free Ebook Before Memory Fades An AutobiographyDocument2 pagesFree Ebook Before Memory Fades An AutobiographyAmar0% (1)
- Define Property and Transfer of Property and Explain in Detail The Kinds of Property Under The Transfer of Property ActDocument3 pagesDefine Property and Transfer of Property and Explain in Detail The Kinds of Property Under The Transfer of Property Actjaivik_ce7584No ratings yet
- CONSTITUTIONDocument44 pagesCONSTITUTIONYashika WadhwaNo ratings yet
- Sem 10 Registration Act NotesDocument23 pagesSem 10 Registration Act Notesdebjit bhowmickNo ratings yet
- AlienationsDocument25 pagesAlienationsAnam KhanNo ratings yet
- Premlata Vs Ishhar DasDocument3 pagesPremlata Vs Ishhar DasSai Malavika TuluguNo ratings yet
- Indian Contract Act 2Document21 pagesIndian Contract Act 2Apurva StudiesNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Property in IndiaDocument76 pagesTransfer of Property in IndiaProf. Amit kashyap50% (2)
- Contract IDocument38 pagesContract Ideepti_kawatraNo ratings yet
- Law of BailmentDocument56 pagesLaw of BailmentAadhitya NarayananNo ratings yet
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016: Learning OutcomesDocument88 pagesInsolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016: Learning OutcomesMukesh DholakiaNo ratings yet
- Essential Elements of Drafting A Gift DeedDocument9 pagesEssential Elements of Drafting A Gift DeedAniruddha Kaul100% (1)
- The Indian Contract Act 1872Document48 pagesThe Indian Contract Act 1872Shradha PadhiNo ratings yet
- Parag RIGHTS AND LIABLITIES OF BENEFICIARIES UNDER TRUSTDocument18 pagesParag RIGHTS AND LIABLITIES OF BENEFICIARIES UNDER TRUSTVishal Saxena100% (1)
- The Essentials of Priviledged Will Under Indian Succession ActDocument8 pagesThe Essentials of Priviledged Will Under Indian Succession ActShivani TelangeNo ratings yet
- Modes of Transfer of Immovable Property - Sale and Gift By: Divyansh HanuDocument11 pagesModes of Transfer of Immovable Property - Sale and Gift By: Divyansh HanuLatest Laws Team100% (1)
- TOPA Questions and AnswerDocument14 pagesTOPA Questions and AnswerSamiksha PawarNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Property ActDocument8 pagesTransfer of Property ActAnkush JadaunNo ratings yet
- 2017-2018 Property Law-Ii Final Draft Topic - Comparative Study of Gift As Under The Transfer of Property Act, 1882Document14 pages2017-2018 Property Law-Ii Final Draft Topic - Comparative Study of Gift As Under The Transfer of Property Act, 1882Bharat JoshiNo ratings yet
- Case CommentDocument4 pagesCase CommentNirban ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Evidence Act - Flow ChartDocument4 pagesEvidence Act - Flow Charthasitha0% (1)
- Internal Moot Memo (Diya & Shaurya)Document24 pagesInternal Moot Memo (Diya & Shaurya)Diya MirajNo ratings yet
- TPA9Document58 pagesTPA9Dr. Dharmender Patial50% (2)
- Jurisprudence: You Ensure Your Hard Work, We Ensure Your SuccessDocument73 pagesJurisprudence: You Ensure Your Hard Work, We Ensure Your Successtushar sharma0% (1)
- Tpa AssignmentDocument12 pagesTpa AssignmentRiya SinghNo ratings yet
- Sale of Immovable Property AssignmentDocument12 pagesSale of Immovable Property AssignmentNusrat ShatyNo ratings yet
- The Indian Contract ActDocument26 pagesThe Indian Contract ActJinkalVyas100% (2)
- The Sale of Goods Act 1930Document12 pagesThe Sale of Goods Act 1930Shweta Bhadauria100% (1)
- The Sale of Goods ACT, 1930Document25 pagesThe Sale of Goods ACT, 1930Jatin GargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 The Sale of Goods Act 1930Document59 pagesChapter 2 The Sale of Goods Act 1930taufeequeNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 11 Sep 2021Document14 pagesAdobe Scan 11 Sep 2021Saswat PattnaikNo ratings yet
- Announcement 070621Document1 pageAnnouncement 070621Biswanath MishraNo ratings yet
- CA Final Nov 2020 Idt Solutions Paper Analysis Complete Solution CA Brindavan Giri (BG) SirDocument1 pageCA Final Nov 2020 Idt Solutions Paper Analysis Complete Solution CA Brindavan Giri (BG) SirBiswanath MishraNo ratings yet
- MTP - Intermediate - Syllabus 2016 - Jun 2020 - Set1: Paper 6-Laws and EthicsDocument4 pagesMTP - Intermediate - Syllabus 2016 - Jun 2020 - Set1: Paper 6-Laws and Ethicsvikash guptaNo ratings yet
- Viz. Passport, Driving Licence, PAN Card, UID Aadhaar Card, Voter I-Card, Etc. To Establish TheirDocument12 pagesViz. Passport, Driving Licence, PAN Card, UID Aadhaar Card, Voter I-Card, Etc. To Establish TheirBiswanath MishraNo ratings yet
- Appointment On Compassionate GroundsDocument1 pageAppointment On Compassionate GroundsTarget BankNo ratings yet
- 66107bos53355fold p8Document19 pages66107bos53355fold p8sam kapoorNo ratings yet
- Examination Department The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaDocument2 pagesExamination Department The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaBiswanath MishraNo ratings yet
- Statement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceDocument4 pagesStatement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceBiswanath MishraNo ratings yet
- Study Guidelines For Sec-B - Indirect Taxes For May, 2021 ExaminationDocument2 pagesStudy Guidelines For Sec-B - Indirect Taxes For May, 2021 ExaminationKarthikNo ratings yet
- Risk Management: Inal OurseDocument134 pagesRisk Management: Inal OurseBiswanath MishraNo ratings yet
- Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument49 pagesCorporate Social ResponsibilityBiswanath MishraNo ratings yet
- Scientific ManagementDocument15 pagesScientific ManagementBiswanath MishraNo ratings yet
- Yun Kwan Byung Vs PAGCOR GR No. 163553 December 11, 2009Document25 pagesYun Kwan Byung Vs PAGCOR GR No. 163553 December 11, 2009Elizabeth Jade D. CalaorNo ratings yet
- Limkaichong vs. Land Bank of The Philippines 799 SCRA 139, August 02, 2016Document4 pagesLimkaichong vs. Land Bank of The Philippines 799 SCRA 139, August 02, 2016Demi LewkNo ratings yet
- LML6001 Task 1, S2 2019Document2 pagesLML6001 Task 1, S2 2019rafia ahmedNo ratings yet
- Precedent 1 Memorandum of UnderstandingDocument4 pagesPrecedent 1 Memorandum of UnderstandingSbusiNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Commercial Covenant EnforcementDocument8 pagesAssignment of Commercial Covenant EnforcementChris AllevaNo ratings yet
- (A State University Established by Act No. 9 of 2012) Navalurkuttapattu, Srirangam Taluk, Tiruchirappalli - 620 009, Tamil NaduDocument17 pages(A State University Established by Act No. 9 of 2012) Navalurkuttapattu, Srirangam Taluk, Tiruchirappalli - 620 009, Tamil NaduSonali DalaiNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF Corporate Governance Cases and Materials Second Edition 2nd Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Corporate Governance Cases and Materials Second Edition 2nd Edition PDFwilliam.bodrick959100% (34)
- The Indian Ports Act 1908Document44 pagesThe Indian Ports Act 1908tallmansahuNo ratings yet
- Hyundai V15 Map Update Instructions S3 S4 S5Document8 pagesHyundai V15 Map Update Instructions S3 S4 S5Pedro Murúa MolinaNo ratings yet
- Delegated LegistationDocument27 pagesDelegated LegistationAmartya ChoubeyNo ratings yet
- VICSA Safety Comercial Ltda: SAI Global Hereby GrantsDocument9 pagesVICSA Safety Comercial Ltda: SAI Global Hereby GrantsFranklinNo ratings yet
- Supplement To SOLAS 12 2014 PDFDocument4 pagesSupplement To SOLAS 12 2014 PDFFreddy José CastroNo ratings yet
- For The Candidates Admitted From 2009-2010 To 2016-2017Document2 pagesFor The Candidates Admitted From 2009-2010 To 2016-2017shivaNo ratings yet
- Law and Legal Issue1.editedDocument4 pagesLaw and Legal Issue1.editedJoseph bill OnyangoNo ratings yet
- Blueprint by Judiciary Gold 02753baa8736bDocument20 pagesBlueprint by Judiciary Gold 02753baa8736bankitaNo ratings yet
- C. All Contracts Are Agreements But Not All Agreements Are ContractsDocument12 pagesC. All Contracts Are Agreements But Not All Agreements Are ContractsElla Marie LopezNo ratings yet
- Innocent Articles and Memorandum of Association.Document7 pagesInnocent Articles and Memorandum of Association.Bazanye BoscoNo ratings yet
- Application For Entering Into An Agreement With Department of Posts For Speed Post/ Express/ Business Parcel ServicesDocument9 pagesApplication For Entering Into An Agreement With Department of Posts For Speed Post/ Express/ Business Parcel ServicesChinnaappu100% (2)
- Stat Con Reviewer Chapter 7 9Document9 pagesStat Con Reviewer Chapter 7 9Tom BinfieldNo ratings yet
- Pabillo v. ComelecDocument66 pagesPabillo v. ComelecAlthea Angela GarciaNo ratings yet
- RFBT Preweek B94 - Questionnaire - AnswersDocument25 pagesRFBT Preweek B94 - Questionnaire - AnswersSilver LilyNo ratings yet
- Session 2 - Entities DIFCDocument17 pagesSession 2 - Entities DIFCZviagin & CoNo ratings yet
- Malaysian Legal SystemDocument2 pagesMalaysian Legal SystemAliciaNo ratings yet
- Appendix 26 - NewDocument2 pagesAppendix 26 - NewsenthilacaNo ratings yet
- WritsDocument42 pagesWritsSweety RoyNo ratings yet
- Private Setoff Bond TEMPLATEDocument7 pagesPrivate Setoff Bond TEMPLATEHï FrequencyNo ratings yet