Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ITIL 4 - IT Process Wiki
Uploaded by
Lea DevOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ITIL 4 - IT Process Wiki
Uploaded by
Lea DevCopyright:
Available Formats
Log in
Page Discussion Read View source View history Search IT Process Wiki
ITIL 4
Main Page
What is ITIL?
ITIL 4 ITIL 4 - the most recent release of ITIL® [1] - was launched in Feb 2019. It's the first major
ITIL Processes
update to the ITIL framework since 2007, designed in large part to keep up with recent
ITIL Implementation
trends in software development and IT operations.
ITIL Checklists
ITIL Glossary On this page we answer your questions about the changes introduced with the latest edition
ISO 20000 of ITIL (see fig. 1: ITIL 4 FAQs).
ITIL Process Templates
Project Management
IT Process Maps Objectives
it-processmaps.com
ITIL 4 provides a flexible foundation for organizations that need to integrate various
Legal notice
frameworks and approaches into their service management operating models.
Products ITIL 4 aims to help businesses navigate the new technological era of digital services.
ITIL Process Map
Contact
Contents [hide]
Useful Links ITIL® 4 - the latest version of ITIL (FAQs)
1 Objectives
ITIL Wiki - Deutsch
2 Why ITIL 4?
Wiki de ITIL - español
3 ITIL 4 components
YaSM Wiki
3.1 Four dimensions model
Special 3.2 Service value system
Special pages 4 ITIL 4 management practices
4.1 General management practices
4.2 Service management practices
4.3 Technical management practices
5 ITIL 4 and ITIL V3: What's the difference?
6 What about ITIL 4 processes?
7 ITIL 4 and ISO 20000, SIAM, VeriSM, ...
8 ITIL 4 certification scheme
8.1 What are the ITIL 4 certification levels?
8.2 Will my certifications stay valid?
8.3 How can I migrate to the new ITIL 4 certifications?
9 The timeline for ITIL 4
10 Notes
Why ITIL 4?
ITIL 4 brings the ITIL framework up to date, introducing a holistic approach to service management and focusing on 'end-to-end service management from
demand to value'.
The new edition of ITIL 4 is the first major update to ITIL since 2007 and is arguably a response to the emergence of newer service management frameworks
such as VeriSM™, SIAM® and FitSM. It expands the previous version of ITIL V3 ('ITIL 2011') and provides a flexible basis to support organizations on their
journey to the new world of digital transformation.
ITIL 4 describes an operating model for the delivery of tech-enabled products and services. The documentation has been completely revised and streamlined to
make it easier to read, and enhanced with many practical examples.
ITIL 4 also reflects recent trends in software development and IT operations, and includes advice on how to apply philosophies such as Agile, DevOps and Lean
in the domain of service management.
Last but not least, ITIL 4 makes a point of being "a framework for service management" (as opposed to "IT service management"), reflecting the growing trend of
applying service management best practices in the domain of enterprise and business services.
ITIL 4 components
ITIL 4 consists of two key components:
The four dimensions model
The service value system (SVS).
Four dimensions model
ITIL 4 defines four dimensions that should be considered to ensure a holistic approach to service management:
1. Organizations and people
2. Information and technology
3. Partners and suppliers
4. Value streams and processes.
These dimensions are applicable to the service value system in general and to specific services.
Service value system
The service value System (SVS) represents "how all the components and activities of an organization work together to facilitate value creation". The ITIL 4 SVS
includes several elements:
1. Guiding principles
2. Governance
3. Service value chain
4. Continual improvement
5. Practices.
ITIL 4 management practices
ITIL 4 includes 34 management practices as "sets of organizational resources designed for performing work or accomplishing an objective". For each practice,
ITIL 4 provides various types of guidance, such as key terms and concepts, success factors, key activities, information objects, etc.
The 34 ITIL 4 practices are grouped into three categories:
1. General management practices
2. Service management practices
3. Technical management practices
General management practices
The ITIL 4 general management practices include:
Strategy management
Portfolio management
Architecture management
Service financial management
Workforce and talent management
Continual improvement
Measurement and reporting
Risk management
Information security management
Knowledge management
Organizational change management
Project management
Relationship management
Supplier management
Service management practices
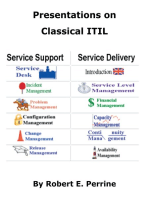
The service management practices in ITIL 4 include:
Business analysis
Service catalogue management
Service design
Service level management
Availability management
Capacity and performance management
Service continuity management
Monitoring and event management
Service desk
Incident management
Service request management
Problem management
Release management
Change enablement
Service validation and testing
Service configuration management
IT asset management
Technical management practices
The ITIL 4 technical management practices include:
Deployment management
Infrastructure and platform management
Software development and management
ITIL 4 and ITIL V3: What's the difference?
ITIL 4 is not about introducing new fundamental ideas of service management and should be seen as an expansion of the time-tested ITIL framework, not a
replacement. Essentially, ITIL 4 and ITIL V3 provide guidance based on the same underlying principles, but ITIL 4 takes a new approach to presenting this
guidance.
ITIL V3 contains detailed descriptions of 26 ITIL processes, arranged along the service lifecycle:
Service Strategy
Service Design
Service Transition
Service Operation
Continual Service Improvement
The service lifecycle has been dropped in ITIL 4 and the processes replaced with practices. But many of the ITIL 4 practices clearly correspond to the previous
ITIL V3 processes.
Other than that, ITIL 4 introduces additional guidance, to ensure practitioners better understand the core principles and concepts such as "value" and "outcomes".
ITIL 4 also provides advice for integrating ITIL with other frameworks and methodologies like DevOps, Lean and Agile.
Learn more about the differences between ITIL 4 and ITIL V3 (ITIL 2011) in our YaSM Service
Management Wiki.
⇒ Detailed mapping: ITIL V3 and ITIL 4
(in our YaSM® Service Management Wiki)
What about ITIL 4 processes?
While ITIL V3 defined a set of processes organized around the service lifecycle, ITIL 4 describes principles, concepts and practices. This includes key activities
and essential inputs and outputs for each practice, but not detailed process specifications. This departure from the previous process-oriented approach is a
fundamental change in ITIL 4 that enables service providers to adopt more flexible operating models.
ITIL 4 is thus not prescriptive regarding processes. But organizations still need to define their processes as a key element of their operating models (ITIL 4 says
that "organizations should define tailor-made processes", in line with their specific requirements).
Organizations looking for detailed process descriptions can still find them in the ITIL V3 publications (AXELOS state that ITIL 4 does not invalidate earlier vesions
of ITIL, and the processes as specified in ITIL V3 are therefore still valid guidance).
But the arrival of ITIL 4 and its preference for "simple and practical" ways of working also provides an opportunity for a fresh start with service management
processes.
If organizations are to keep things simple and become more agile, they will likely need processes
that are somewhat less complex than the 26 service management processes familiar from ITIL V3.
In the YaSM Service Management Wiki [2] we describe such a streamlined, clear-cut set of
service management processes that is a good match for the leaner, more flexible operating
models favored by today's service provider organizations.
⇒ 'ITIL V4 processes' based on YaSM
(in our YaSM® Service Management Wiki)
The benchmark for the YaSM processes is ISO 20000 (ISO 20000:2018) , the international standard for service management.
What is more, these service management processes are designed to be used with a variety of frameworks and methods, such as
ITIL® 4,
SIAM®,
VeriSM™,
COBIT®,
Agile
and Lean, etc.
ITIL 4 and ISO 20000, SIAM, VeriSM, ...
ITIL is some 30 years old and over the years has been adopted by a large number of organizations. It has been updated from time to time, but other, newer
service management frameworks and approaches have been quicker in recognizing emerging trends in service management and information technology. ITIL 4
has arguably taken a leaf or two out of these frameworks to keep up with the times. Here are a few examples:
ITIL 4 includes updated guidance on multi-sourcing and service integration. These are key topics in the SIAM® framework.
ITIL 4 embraces new ways of working, such as Agile, Lean and DevOps, as well as organizational change management. These management practices and
their relevance for service management are also described in the VeriSM™ approach.
The ITIL 4 service value chain is somewhat reminiscent of the VeriSM™ model, with key areas such as define, produce, provide and respond.
ITIL 4 introduces the concept of a service value system. This fits in with a key requirement in the latest 2018 edition of ISO 20000 for organizations to
"establish, implement, maintain and continually improve" a service management system.
ITIL 4 certification scheme
What are the ITIL 4 certification levels?
ITIL 4 introduces a completely new, "streamlined" certification scheme.
1. As in ITIL V3, Foundation is the entry level ITIL 4 certification, introducing the key elements, concepts and terminology used in ITIL.
2. After passing the Foundation exam, ITIL practitioners can choose between two ITIL 4 certification "streams", each consisting of several modules: ITIL 4
Managing Professional and ITIL 4 Strategic Leader.
The ITIL 4 Managing Professional (ITIL MP) stream "targets IT practitioners working within technology and digital teams across businesses". ITIL MP
consists of four modules:
1. ITIL 4 Specialist Create, Deliver and Support (CDS)
2. ITIL 4 Specialist Drive Stakeholder Value (DSV)
3. ITIL 4 Specialist High Velocity IT (HVIT)
4. ITIL 4 Strategist Direct Plan and Improve (DPI).
The ITIL 4 Strategic Leader (ITIL SL) stream focuses on business strategy and digitally enabled services. ITIL SL consists of two modules:
1. ITIL 4 Strategist Direct, Plan and Improve (DPI)
2. ITIL 4 Leader Digital and IT Strategy.
3. ITIL Master is the top-level qualification of the ITIL 4 certification scheme. There is no fixed training course or exam involved, but candidates need to
demonstrate "extensive practical hands-on experience with ITIL".
More information about the new ITIL 4 certification scheme is available on the AXELOS website: axelos.com/best-practice-solutions/itil .
Will my certifications stay valid?
ITIL V3 certifications will remain valid, but pressure to upgrade to the latest certifications is likely to grow. This is particularly true for ITSM consultants, whose
customers will often expect up-to-date qualifications.
For those who wish to migrate to the new ITIL 4 certification scheme, AXELOS have prepared a transition plan:
How can I migrate to the new ITIL 4 certifications?
Holders of ITIL V3 Foundation certificates:
There are significant changes in the ITIL 4 Foundation material.
AXELOS advise candidates who have taken the ITIL V3 Foundation exam to take ITIL 4 Foundation in order to be able to transition to the new scheme.
Holders of ITIL V3 Intermediate or Practitioner certifications:
The best migration path towards the ITIL 4 scheme will depend on the number of credits already earned.
Candidates may either choose to restart their certification itinerary with ITIL 4 Foundation, or to complete ITIL V3 Expert and then take the ITIL 4 Managing
Professional Transition module.
Holders of ITIL V3 Expert certifications:
Candidates who have achieved ITIL V3 Expert will be able to take the ITIL Managing Professional Transition module to achieve the ITIL Managing
Professional designation.
The timeline for ITIL 4
ITIL 4 was officially launched in February 2019 with the release of ITIL 4 Foundation. Accredited training organizations are now able to offer ITIL 4 Foundation
courses and exams.
Further publications and certifications, reflecting the advanced levels of the ITIL 4 certification scheme, are scheduled for release in 2019 and thereafter:
ITIL 4 Specialist Create, Deliver and Support (available since November 2019)
ITIL 4 Specialist Drive Stakeholder Value (launch expected in Q1/2020)
ITIL 4 Specialist High Velocity IT (launch expected in Q1/2020)
ITIL 4 Strategist Direct Plan and Improve (available since November 2019)
ITIL 4 Leader Digital and IT Strategy (launch expected in H1/2020).
Exams for the ITIL 4 Managing Professional Transition module have been available since October 2019.
Notes
[1] ITIL® is a registered trademark of AXELOS Limited.
[2] YaSM® is a registered trademark of IT Process Maps GbR.
By: Stefan Kempter , IT Process Maps.
Objectives › Why ITIL 4? › ITIL 4 and ITIL V3: Differences › What about ITIL 4 processes? › ITIL 4 certification scheme
Categories: ITIL 4 ITIL version
ITIL® Process Map & ITIL® Wiki | Join us!
YaSM® is a registered trade mark of IT Process Maps GbR.
ITIL®, IT Infrastructure Library® and the Swirl logo™ are registered trade marks of AXELOS Limited. -- COBIT® is a registered trademark of ISACA. ISO/IEC 20000® is a registered trademark of ISO.
CMMI® and Capability Maturity Model® are registered trademarks of Carnegie Mellon University. USMBOK™ is a registered trademark of Virtual Knowledge Solutions International Incorporated (VKSII).
SIAM™ is a registered trademark of EXIN. VeriSM™ is a registered trademark of IFDC. -- Microsoft®, Word™, Excel®, SharePoint® and Visio® are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corp. ARIS™ and
IDS Scheer are registered trademarks of Software AG. -- Sitemap
This page was last edited on 3 December 2019, at 18:40.
Content is available under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Germany License unless otherwise noted.
Privacy policy About IT Process Wiki Disclaimers Mobile view
You might also like
- Itil Capacity Management More Than Charts Over CoffeeDocument16 pagesItil Capacity Management More Than Charts Over CoffeeAhmed M. EzzatNo ratings yet
- An Overview of (IT) Service Management: Updated April 2020Document17 pagesAn Overview of (IT) Service Management: Updated April 2020Oscar MalaverNo ratings yet
- ITIL V3 vs ITIL 4 Key ChangesDocument26 pagesITIL V3 vs ITIL 4 Key Changespriyanjali sharmaNo ratings yet
- ITIL 4 Public FAQsDocument13 pagesITIL 4 Public FAQsLuiz Claudio SalesNo ratings yet
- What Is IT Service Management - ITIL - AXELOSDocument4 pagesWhat Is IT Service Management - ITIL - AXELOSaliNo ratings yet
- 123doku - Itil In4mation Whats New in It - 93857Document9 pages123doku - Itil In4mation Whats New in It - 93857iuhuhuNo ratings yet
- Itil 4 and IT4IT: Rob AkershoekDocument25 pagesItil 4 and IT4IT: Rob Akershoekfalcon.peregrine7775100% (1)
- Itil 4 Co-Create Value and Drive Business Success in The Digital EraDocument16 pagesItil 4 Co-Create Value and Drive Business Success in The Digital EraĐoàn Đức ĐềNo ratings yet
- ITILDocument7 pagesITILabcdNo ratings yet
- IT for Business (IT4B): From Genesis to Revolution, a business and IT approach to digital transformationFrom EverandIT for Business (IT4B): From Genesis to Revolution, a business and IT approach to digital transformationNo ratings yet
- Ten Steps to ITSM Success: A Practitioner’s Guide to Enterprise IT TransformationFrom EverandTen Steps to ITSM Success: A Practitioner’s Guide to Enterprise IT TransformationNo ratings yet
- Organizing Itsm: Transitioning the It Organization from Silos to Services with Practical Organizational ChangeFrom EverandOrganizing Itsm: Transitioning the It Organization from Silos to Services with Practical Organizational ChangeNo ratings yet
- ISO/IEC 20000: An Introduction to the global standard for service managementFrom EverandISO/IEC 20000: An Introduction to the global standard for service managementNo ratings yet
- Co-creating value in organisations with ITIL 4: A guide for consultants, executives and managersFrom EverandCo-creating value in organisations with ITIL 4: A guide for consultants, executives and managersNo ratings yet
- ITIL Lifecycle Essentials: Your essential guide for the ITIL Foundation exam and beyondFrom EverandITIL Lifecycle Essentials: Your essential guide for the ITIL Foundation exam and beyondNo ratings yet
- ITIL Foundation Essentials: The exam facts you needFrom EverandITIL Foundation Essentials: The exam facts you needRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (4)
- ITIL 4 : Drive Stakeholder Value: Reference and study guideFrom EverandITIL 4 : Drive Stakeholder Value: Reference and study guideNo ratings yet
- ITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideFrom EverandITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ITIL Self-Assessment for Small Digital AgenciesDocument6 pagesITIL Self-Assessment for Small Digital AgenciesVamsi aravetiNo ratings yet
- AXELOS SIAM WhitepaperDocument24 pagesAXELOS SIAM WhitepaperSurya Prakash Garg100% (1)
- ITIL Service Management FundamentalsDocument32 pagesITIL Service Management FundamentalsXtine Ramos100% (1)
- Itil 2011 Process ModelDocument1 pageItil 2011 Process ModelAlexandru Dan GheorghiuNo ratings yet
- ITIL ITSM SlidesDocument110 pagesITIL ITSM SlidesSP CFSINo ratings yet
- ITIL KPIs Service DesignDocument6 pagesITIL KPIs Service DesignAtaliba Lima100% (1)
- Vodafone Aligns Support Service Model To Itil 4Document7 pagesVodafone Aligns Support Service Model To Itil 4linamewsNo ratings yet
- Axelos - Itil The BasicsDocument6 pagesAxelos - Itil The Basicstest userNo ratings yet
- Using ITIL 4 and COBIT 2019 To Create Integrated Framework - Whpitilcb - WHP - Eng - 0621Document10 pagesUsing ITIL 4 and COBIT 2019 To Create Integrated Framework - Whpitilcb - WHP - Eng - 0621Diego MaradeiNo ratings yet
- Implementing Service Integration Across Multiple Providers Using COBIT 5Document9 pagesImplementing Service Integration Across Multiple Providers Using COBIT 5hdoornboNo ratings yet
- What Is ITIL® 4 High-Velocity IT?Document6 pagesWhat Is ITIL® 4 High-Velocity IT?Romysaa AwadNo ratings yet
- Itil Capacity Management - Larry Klosterboer - Prentice Hall - 2011Document14 pagesItil Capacity Management - Larry Klosterboer - Prentice Hall - 2011wilmertorresdNo ratings yet
- Taking IT4IT On The ITSM Journey: Anton Lykov and Roman JouravlevDocument13 pagesTaking IT4IT On The ITSM Journey: Anton Lykov and Roman JouravlevGerardobalbinoNo ratings yet
- Measures and Metrics (Study Guide)Document29 pagesMeasures and Metrics (Study Guide)Eduardo MucajiNo ratings yet
- Agile ITIL Integration White PaperDocument11 pagesAgile ITIL Integration White PaperIqbalurNo ratings yet
- ITIL IT Service Management 100 Most Asked Questions On IT Service Management and ITIL Foundation Certification Training and ExamsDocument216 pagesITIL IT Service Management 100 Most Asked Questions On IT Service Management and ITIL Foundation Certification Training and ExamsPranav VikasNo ratings yet
- 01 - ITIL V3 2011 Service Strategy SS PDFDocument500 pages01 - ITIL V3 2011 Service Strategy SS PDFOscar MalaverNo ratings yet
- ITSM Training Module FinalDocument45 pagesITSM Training Module FinalBushra AlbalushiaNo ratings yet
- Who Is The King of SIAM?: Simon Dorst, Michelle Major-Goldsmith, Steve RobinsonDocument19 pagesWho Is The King of SIAM?: Simon Dorst, Michelle Major-Goldsmith, Steve RobinsonEugene ArkadievNo ratings yet
- The University of Oxford and Itil Case StudyDocument5 pagesThe University of Oxford and Itil Case StudylinamewsNo ratings yet
- ITIL4FEN Practices v1.1Document42 pagesITIL4FEN Practices v1.1Wilfried Foalem100% (1)
- DR8.21 ITIL Presentation Service TrainingDocument41 pagesDR8.21 ITIL Presentation Service TrainingKshitiz SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Using ITSM to Optimize ResourcesDocument48 pagesUsing ITSM to Optimize ResourcesJulius Villacruz100% (1)
- Pragmatic Application of Service Management: The Five Anchor ApproachFrom EverandPragmatic Application of Service Management: The Five Anchor ApproachNo ratings yet
- ITIL 2011 Edition Quick Reference GuideDocument2 pagesITIL 2011 Edition Quick Reference GuideMadhur Sawant100% (2)
- Screenshots Itil Process Map VisioDocument16 pagesScreenshots Itil Process Map Visionico0j100% (1)
- ITIL 4 Managing Professional Drive Stakeholder Value Syllabus EnglishDocument9 pagesITIL 4 Managing Professional Drive Stakeholder Value Syllabus Englishrasa8084No ratings yet
- IT4IT Reference Card4Document1 pageIT4IT Reference Card4GuillermoVillalonNo ratings yet
- SERVICE DESK ESSENTIAL HANDBOOK A5 PDFDocument92 pagesSERVICE DESK ESSENTIAL HANDBOOK A5 PDFdmnk100% (1)
- BMC - Service Portfolio Management WhitepaperDocument10 pagesBMC - Service Portfolio Management WhitepaperRoss ManningNo ratings yet
- Togaf&itil PDFDocument12 pagesTogaf&itil PDFpolen chheangNo ratings yet
- Daftar RegulasiDocument2 pagesDaftar RegulasiLea DevNo ratings yet
- PTN BC 2022 02Document2 pagesPTN BC 2022 02Lea DevNo ratings yet
- Data Center Facility Standard Outline Formulated by Japan Data Center CouncilDocument8 pagesData Center Facility Standard Outline Formulated by Japan Data Center CouncilLea DevNo ratings yet
- Adhietya Putra Pranata CVDocument1 pageAdhietya Putra Pranata CVLea DevNo ratings yet
- Ab605001 112520Document14 pagesAb605001 112520Lea DevNo ratings yet
- User ManualDocument4 pagesUser ManualLea DevNo ratings yet
- SANOG33 Tutorials Data Centre Facility Design FuadDocument64 pagesSANOG33 Tutorials Data Centre Facility Design FuadTameta DadaNo ratings yet
- It4it 2.1Document178 pagesIt4it 2.1Lea DevNo ratings yet
- Regression Testing Interactive ProgramsDocument10 pagesRegression Testing Interactive ProgramsLea DevNo ratings yet
- ITIL Cobit MappingDocument16 pagesITIL Cobit Mappingapi-383689667% (3)
- Ym Conf Fun PDFDocument32 pagesYm Conf Fun PDFIman SabariNo ratings yet
- Certified HR Professional (CHRP) Program: Artdo InternationalDocument12 pagesCertified HR Professional (CHRP) Program: Artdo InternationalLea DevNo ratings yet
- What Are The Difference Between ITIL V4 and ITIL V3 - QuoraDocument1 pageWhat Are The Difference Between ITIL V4 and ITIL V3 - QuoraLea DevNo ratings yet
- ITIL v3 Vs v4Document27 pagesITIL v3 Vs v4nashwan mustafaNo ratings yet
- Capm 1Document164 pagesCapm 1Lea DevNo ratings yet
- Starting Guide For PHD May 2015Document22 pagesStarting Guide For PHD May 2015Careema ChoongNo ratings yet
- 549 Guidance For Creating Information Security Continuous Monitoring Pro..Document9 pages549 Guidance For Creating Information Security Continuous Monitoring Pro..Lea DevNo ratings yet
- IT Governance Charter PDFDocument26 pagesIT Governance Charter PDFLea DevNo ratings yet
- DeepFritz13Manual PDFDocument282 pagesDeepFritz13Manual PDFLea DevNo ratings yet
- AeU Application Form-1 PDFDocument5 pagesAeU Application Form-1 PDFLea DevNo ratings yet
- Plant Maintenance Terms For SAPDocument5 pagesPlant Maintenance Terms For SAPrhys_gauravNo ratings yet
- Sap PM 0410 PDFDocument45 pagesSap PM 0410 PDFNeng Amnad100% (1)
- Chapter 4 DC To AC Conversion (INVERTER)Document46 pagesChapter 4 DC To AC Conversion (INVERTER)xuanbac198467% (3)
- Mosfet Igbt BJT Difference and ApplicationDocument5 pagesMosfet Igbt BJT Difference and ApplicationSangammeshwra AbNo ratings yet
- Perencanaan Strategi Pemasaran Melalui Metode Swot Dan BCG Guna Menghadapi Persaingan Dan Menganalisis Peluang BisnisDocument12 pagesPerencanaan Strategi Pemasaran Melalui Metode Swot Dan BCG Guna Menghadapi Persaingan Dan Menganalisis Peluang Bisnisabur_vikingNo ratings yet
- Basic Magnetic07Document16 pagesBasic Magnetic07Lea DevNo ratings yet
- 013 1sadik SwotDocument12 pages013 1sadik SwotYuda AnggaraNo ratings yet
- WillaWare v Jesichris ManufacturingDocument2 pagesWillaWare v Jesichris ManufacturingloschudentNo ratings yet
- Certificado Reparación Carcasas Bombas y CompresoresDocument3 pagesCertificado Reparación Carcasas Bombas y CompresoresdanyNo ratings yet
- Accounts PaperDocument2 pagesAccounts PaperRohan Ghadge-46No ratings yet
- Marcopper Mining CorpDocument7 pagesMarcopper Mining CorpChristine Ivy Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Faculty Handbook MGT FinalDocument48 pagesFaculty Handbook MGT FinalTiwanka MadurangaNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document3 pagesHomework 2Tú QuyênNo ratings yet
- One of Your Responsibilities As Division Manager of An ImportantDocument1 pageOne of Your Responsibilities As Division Manager of An ImportantAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Problem 5: XY LTDDocument4 pagesProblem 5: XY LTDAF 1 Tejasri PamujulaNo ratings yet
- Res. MethodDocument100 pagesRes. Methodhimanshug_43No ratings yet
- Designing The Perfect Procurement Operating Model: OperationsDocument9 pagesDesigning The Perfect Procurement Operating Model: Operationspulsar77No ratings yet
- GUCCI - Case Only110910Document39 pagesGUCCI - Case Only110910sabastien_10dec5663No ratings yet
- Vinamilk Yogurt Report 2019: CTCP Sữa Việt Nam (Vinamilk)Document24 pagesVinamilk Yogurt Report 2019: CTCP Sữa Việt Nam (Vinamilk)Nguyễn Hoàng TrườngNo ratings yet
- Barangay transparency monitoring form titleDocument1 pageBarangay transparency monitoring form titleOmar Dizon100% (1)
- Unit 1 2018 Paper 2Document9 pagesUnit 1 2018 Paper 2Pettal BartlettNo ratings yet
- CH 32 A Macroeconomic Theory of The Open EconomyDocument45 pagesCH 32 A Macroeconomic Theory of The Open EconomyveroirenNo ratings yet
- New Invt MGT KesoramDocument69 pagesNew Invt MGT Kesoramtulasinad123No ratings yet
- Yatra Online Private LimitedDocument2 pagesYatra Online Private LimitedAkhilesh kumar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Pestle AustriaDocument1 pagePestle AustriaRananjay Singh100% (1)
- 05 Chapter2Document30 pages05 Chapter2Motiram paudelNo ratings yet
- Eks 9 en 2015 01 14Document157 pagesEks 9 en 2015 01 14aykutNo ratings yet
- Assessment On The Influence of Tax Education On Tax Compliance The Case Study of Tanzania Revenue Authority - Keko Bora Temeke BranchDocument33 pagesAssessment On The Influence of Tax Education On Tax Compliance The Case Study of Tanzania Revenue Authority - Keko Bora Temeke BranchSikudhani MmbagaNo ratings yet
- Kajaria Ceramics: Production and Consumption Trend of Ceramic Tiles in WorldDocument10 pagesKajaria Ceramics: Production and Consumption Trend of Ceramic Tiles in Worldapi-556903190No ratings yet
- Quotation - Householders - LAPSONDocument1 pageQuotation - Householders - LAPSONCredsureNo ratings yet
- Sustainbook PDFDocument225 pagesSustainbook PDFjNo ratings yet
- Fiata Back B-LDocument1 pageFiata Back B-LPhạm Bùi Bảo TuấnNo ratings yet
- Durado RRLDocument3 pagesDurado RRLJohneen DungqueNo ratings yet
- Session 12-Balance of PaymentsDocument19 pagesSession 12-Balance of PaymentsJai GaneshNo ratings yet
- Technical Appraisal: Unit 5Document16 pagesTechnical Appraisal: Unit 5DIPAKNo ratings yet
- 1271 XII Accountancy Study Material Supplementary Material HOTS and VBQ 2014 15 PDFDocument380 pages1271 XII Accountancy Study Material Supplementary Material HOTS and VBQ 2014 15 PDFBalaji TkpNo ratings yet
- Sas#20 Bam242Document9 pagesSas#20 Bam242Everly Mae ElondoNo ratings yet